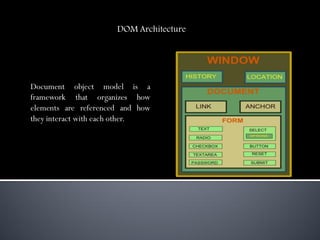
The DOM (Document Object Model) allows programs and scripts to dynamically access and update the content, structure and style of documents. It gives generic access to elements, styles and attributes in a document. The DOM organizes how elements are referenced and interact with each other. Examples show how scripts reference elements, apply styles, and change styles. Different document objects like the document, anchor, button, form, image and event objects are used to access and manipulate HTML and XML documents. The DOM provides a standard programming interface for working with documents across environments and applications.









![Form object -Example
<html><body bgcolor="#87cb56">
<form id="frm1" action="form_action.asp">
Last name: <input type="text" name="lname" value="Adi" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form>
<p>Return the value of each element in the form:</p>
<script type="text/javascript">
var x=document.getElementById("frm1");
for (var i=0;i<x.length;i++)
{
document.write(x.elements[i].value);
document.write("<br />");
} </script></body></html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dom-110825010636-phpapp02/85/Dom-11-320.jpg)








