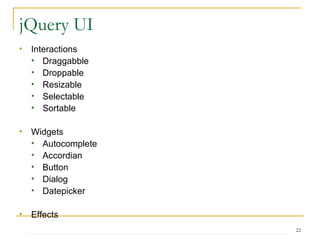
This document provides an overview of AJAX, JSON, jQuery, and livequery. It discusses how these technologies enable asynchronous communication with servers and manipulation of web pages. It also provides examples of using jQuery to select elements, modify attributes and styles, handle events, and perform animations. The document concludes with assignments for demonstrating skills with jQuery selectors, effects, and calendar functionality.






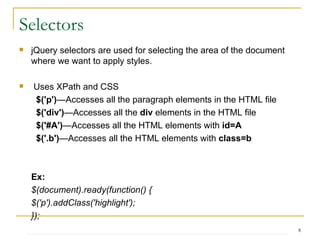

![Selectors Get a specific element where ID like “m_tabel”: $(“table[id*=m_table]”) Attribute filters: = equal to != not equal to *= contains given substring ^= starts with string |= starts with given string or starts with string and ‘-‘ $= ends with Multiple selector: $(“input[id*=DescriptionBlock][type=text]”)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jquerypublic-12780492572706-phpapp01/85/J-Query-Public-10-320.jpg)



![Attributes Toggle Class: $(“div”).toggleClass(“red”); Get\Set HTML: $(“div”).html(); var html_value = “<div id=’m_dv’>New Div</>”; $(“div”).html(html_value); Get\Set value: $(“input[id*=txtName]”).val(); $(“ input[id*=txtName]”).val(“Example”);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jquerypublic-12780492572706-phpapp01/85/J-Query-Public-14-320.jpg)

![Traversing Find elements under a parent element: $(“#m_divSection”).find([selector]) Get children: $(“#m_divSection”).children([selector]) Get first or first matching parent: $(“#m_txtName”).parent([selector]) Get parents by selector: $(“#m_txtName”).parents([selector]) Get next node: $(“#m_txtName”).next([selector])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jquerypublic-12780492572706-phpapp01/85/J-Query-Public-16-320.jpg)
![Traversing Get all next node: $(“#m_txtName”).nextAll([selector]) Get previous node: $(“#m_txtName”).prev([selector]) Get all previous node: $(“#m_txtName”).prevAll([selector]) Get siblings: $(“#m_txtName”).sibling([selector])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jquerypublic-12780492572706-phpapp01/85/J-Query-Public-17-320.jpg)



![AJAX jQuery.ajax() $.ajax({ url: 'ajax/test.html', success: function(data) { $('.result').html(data); alert('Load was performed.'); } }); Callback functions: beforeSend , error , dataFilter , success and complete .ajaxComplete() .ajaxError() .ajaxSuccess() jQuery.getJSON() jQuery.getJSON( url, [ data ], [ callback(data, textStatus) ] )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jquerypublic-12780492572706-phpapp01/85/J-Query-Public-21-320.jpg)