This document provides an overview of DNS fundamentals including what DNS is, its components and characteristics, how DNS queries work, and how DNS has evolved. Specifically:
- DNS is the phonebook of the internet that translates domain names to IP addresses in a globally distributed and hierarchical system that is critical internet infrastructure.
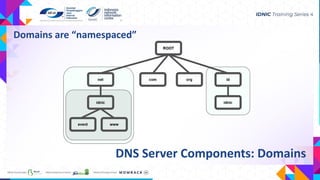
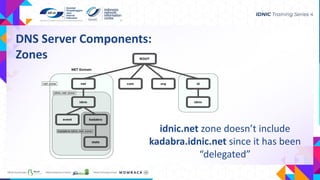
- It has components like root servers, domains and namespaces that organize addressing, nameservers that respond to queries, and resolvers on devices that initiate requests.
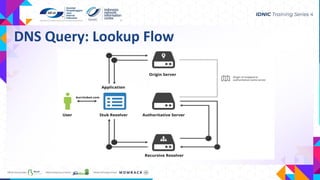
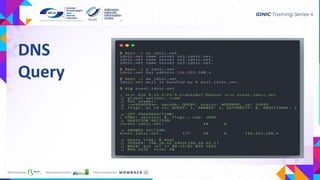
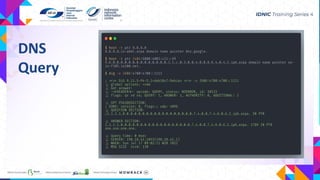
- DNS is distributed, loosely coherent, scalable and reliable by design. It uses ports 53 UDP and TCP to lookup records like A, AAAA, MX, NS, PTR and TXT.
- Evolutions










![❖ The top of the DNS hierarchy
❖ The root servers contain global list of top level domains
(TLD)
➢ Generic top level domains (gTLD): .com, .net, .org
➢ Country top level domains (cTLD): .us, .id, .au
❖ There are 13 root name servers operated around the world
[a-m].root-servers.net
❖ Actually there are more than 13 physical root nameservers
➢ Each has an instance deployed via anycast
➢ As of 2021, there are more than 1300 instances
DNS Server Components: Root Servers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnspresentationpandi-2022-240127042407-fadb63fc/85/DNS-Fundamentals-Presentation_PANDI-2022-pdf-12-320.jpg)