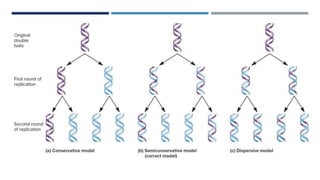
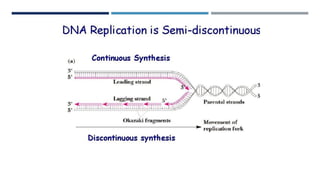
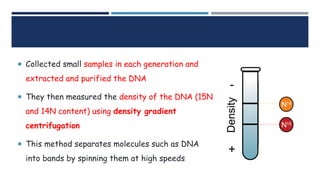
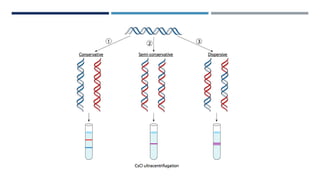
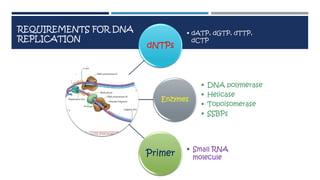
DNA replication is the process by which a parent DNA molecule makes two identical daughter DNA molecules. It is semi-conservative, meaning the parent DNA strands separate and each serves as a template for a new complementary daughter strand. Meselson and Stahl's experiment provided evidence for this semi-conservative model of replication. They grew E. coli in medium containing a heavy isotope of nitrogen, then switched to light nitrogen medium. After multiple generations, they found DNA bands corresponding to hybrid heavy-light DNA strands, supporting the semi-conservative model. DNA replication requires dNTPs, DNA polymerase and other enzymes, primers, and separation of the parental strands by helicase.