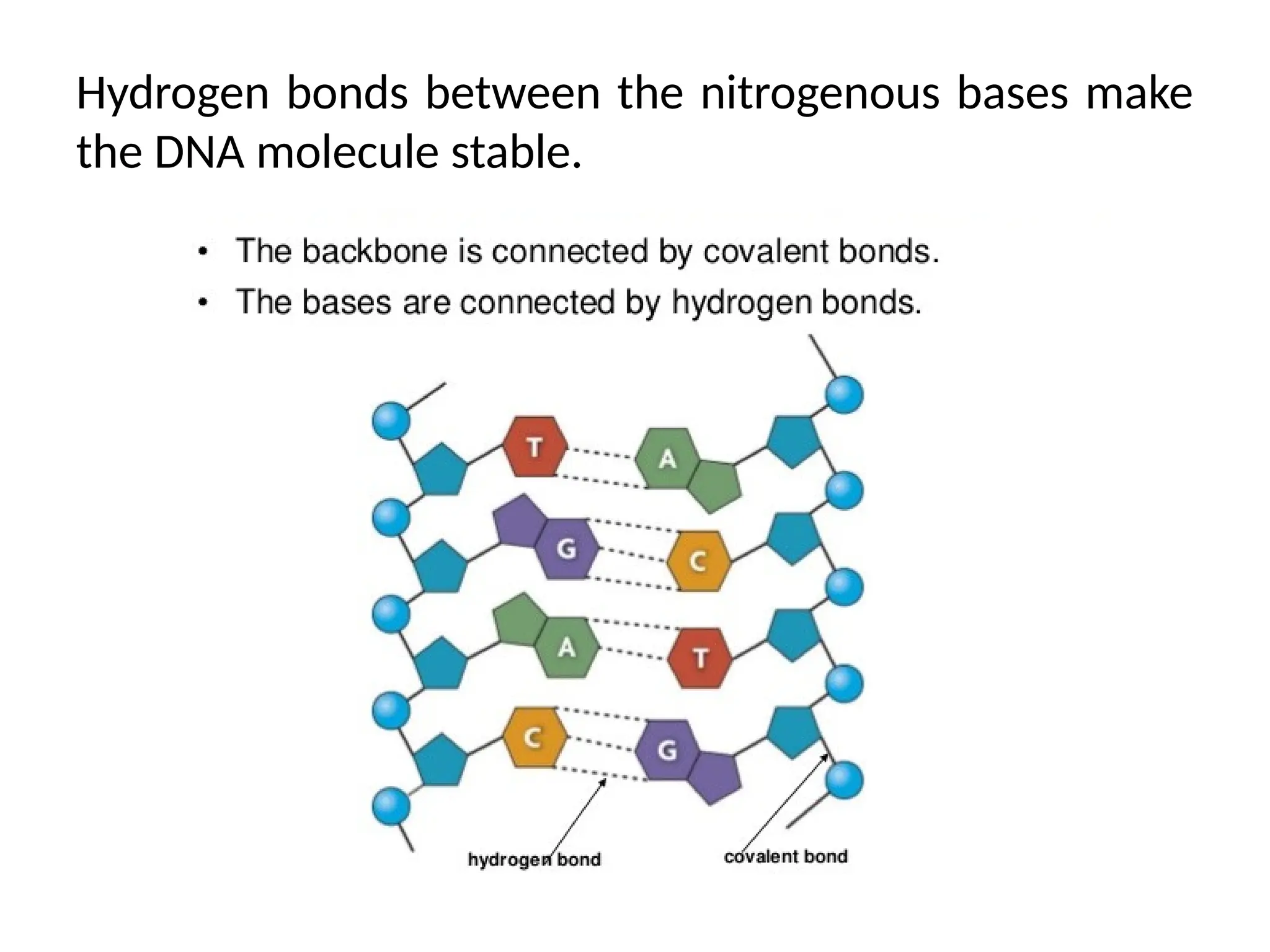
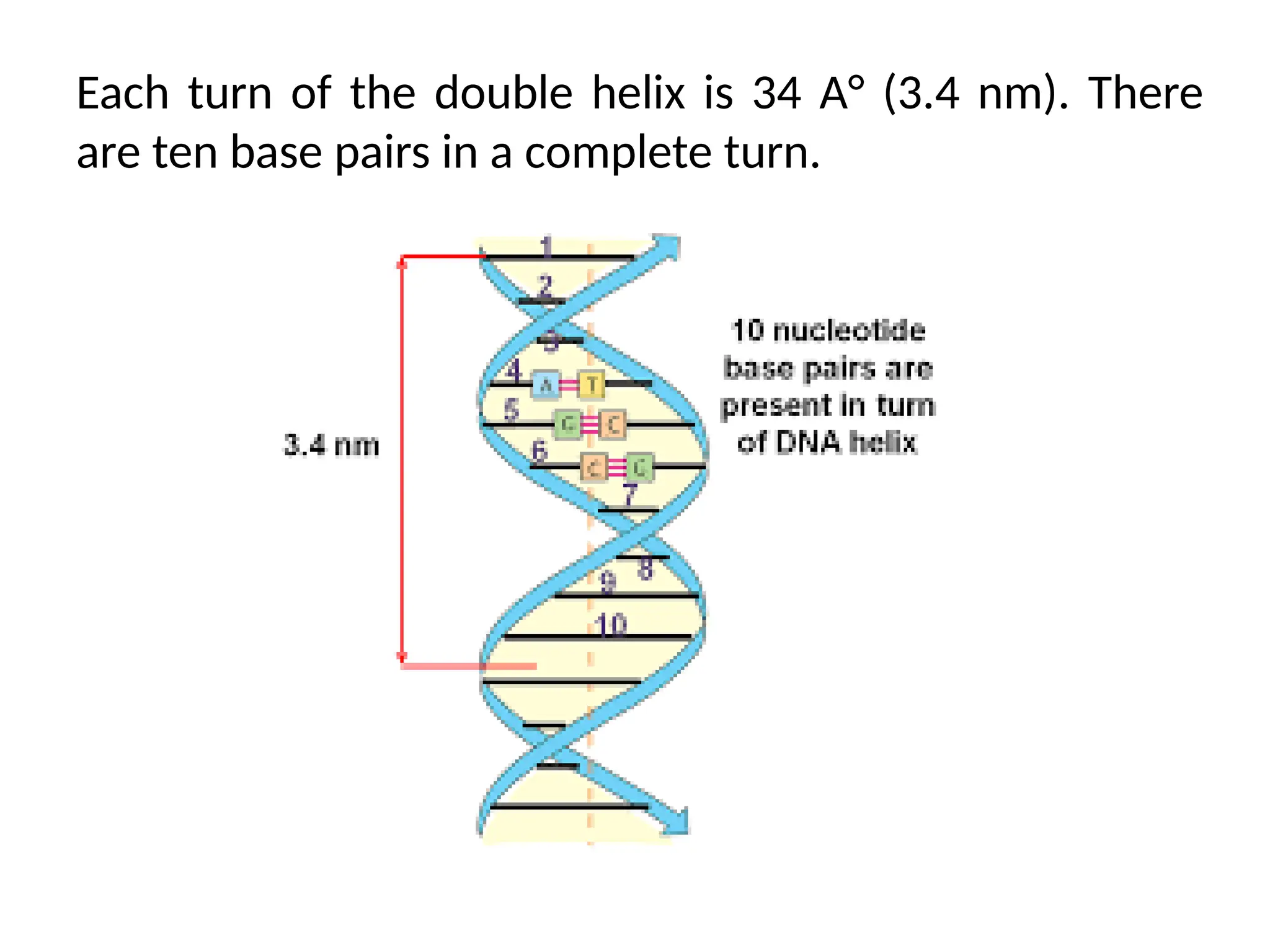
DNA is composed of deoxyribose sugar, nitrogenous bases (purines: adenine and guanine, and pyrimidines: cytosine and thymine), and a phosphate group. Watson and Crick described the double helix structure, where two anti-parallel polynucleotide strands form a stable structure through complementary base pairing (adenine with thymine and cytosine with guanine). Each turn of the helix spans 34 Å (3.4 nm) with ten base pairs per turn, linked by phosphodiester bonds.