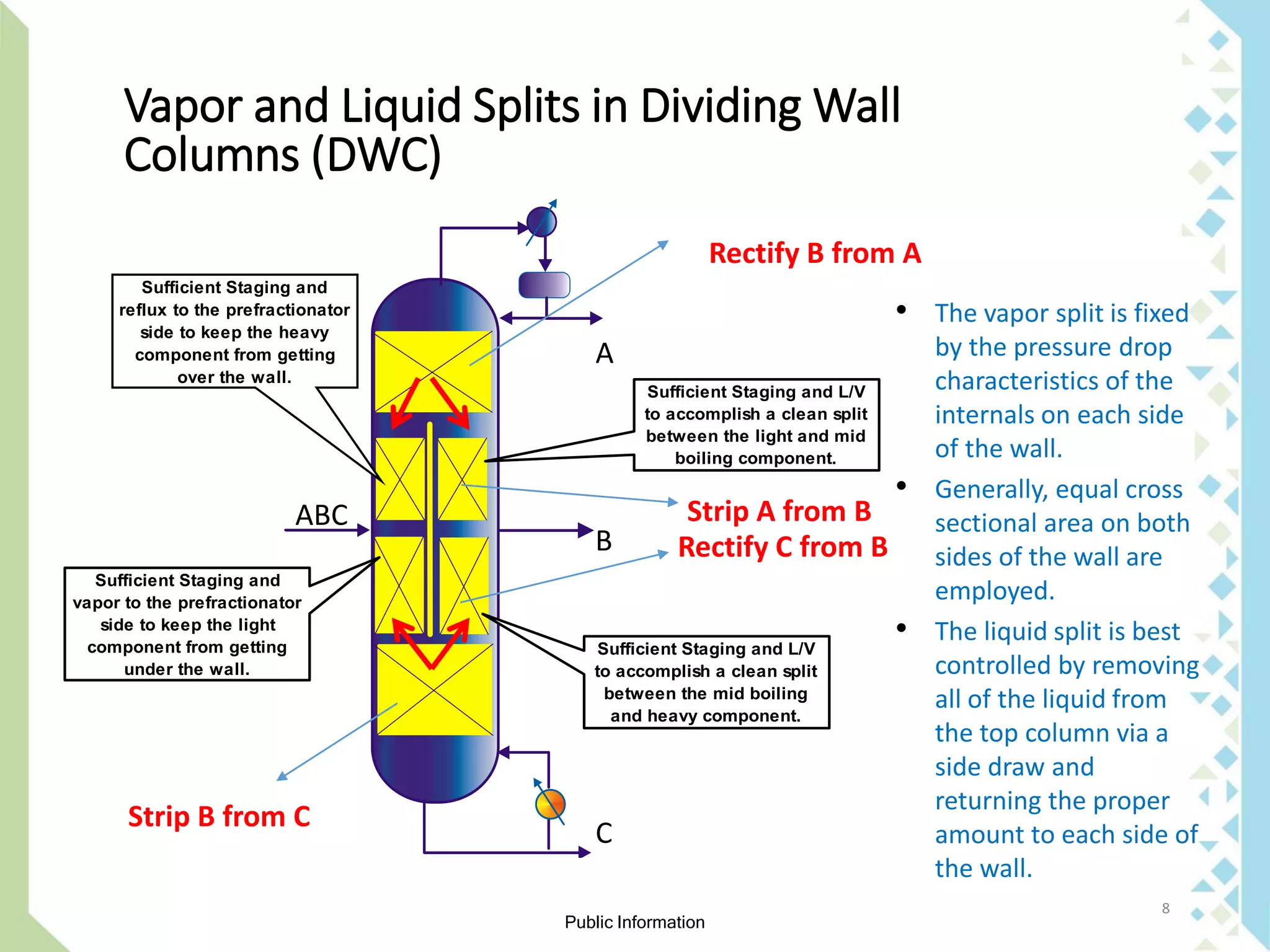
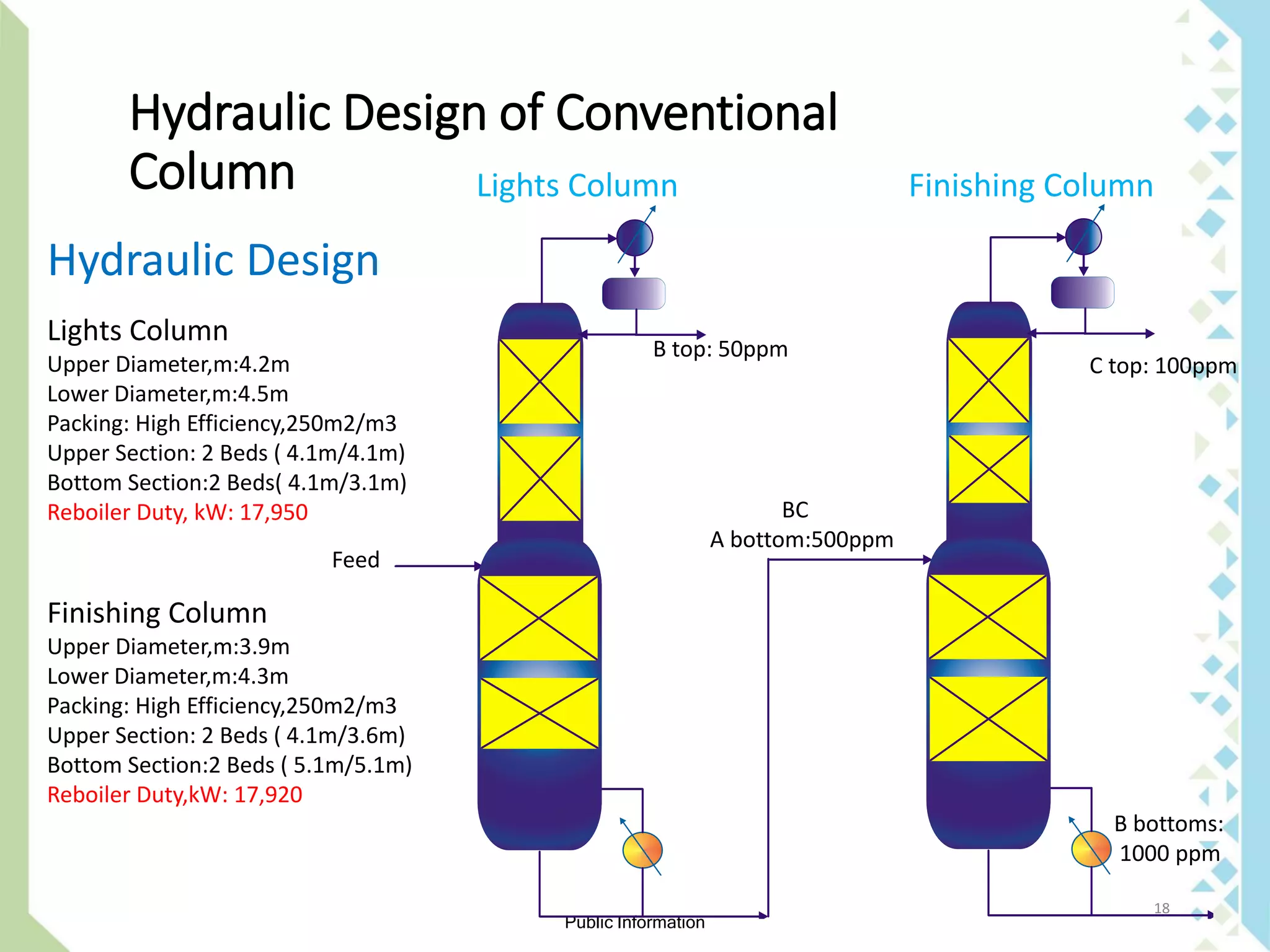
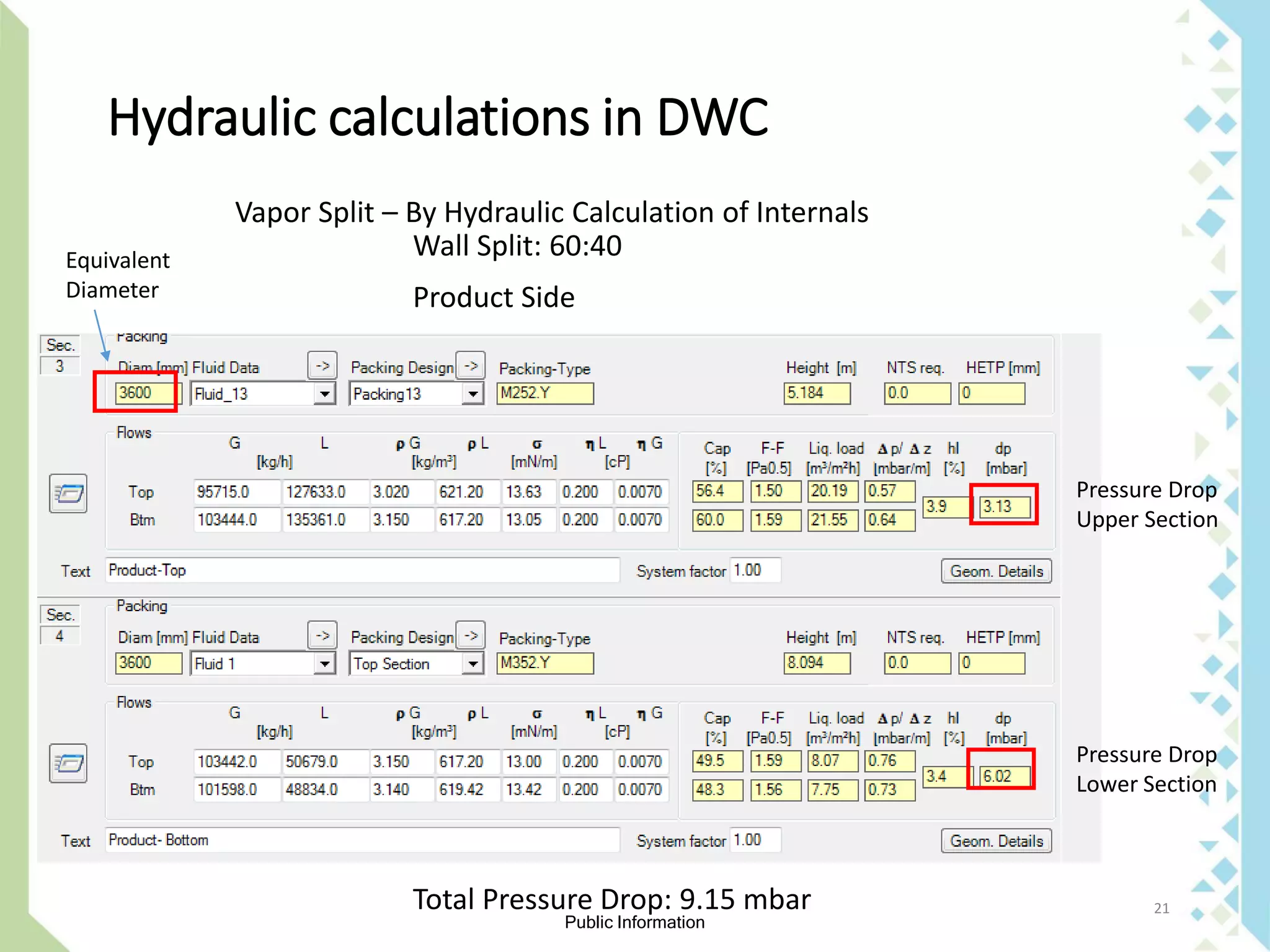
The document explains the concept and benefits of a dividing wall column (DWC) for separating ternary mixtures, allowing for more efficient separation of components compared to conventional columns. It discusses the operational conditions, limitations, and modeling approaches for DWCs, as well as specific designs and internal arrangements. Additionally, it highlights the cost savings in investment and utility consumption achieved through the use of DWCs.