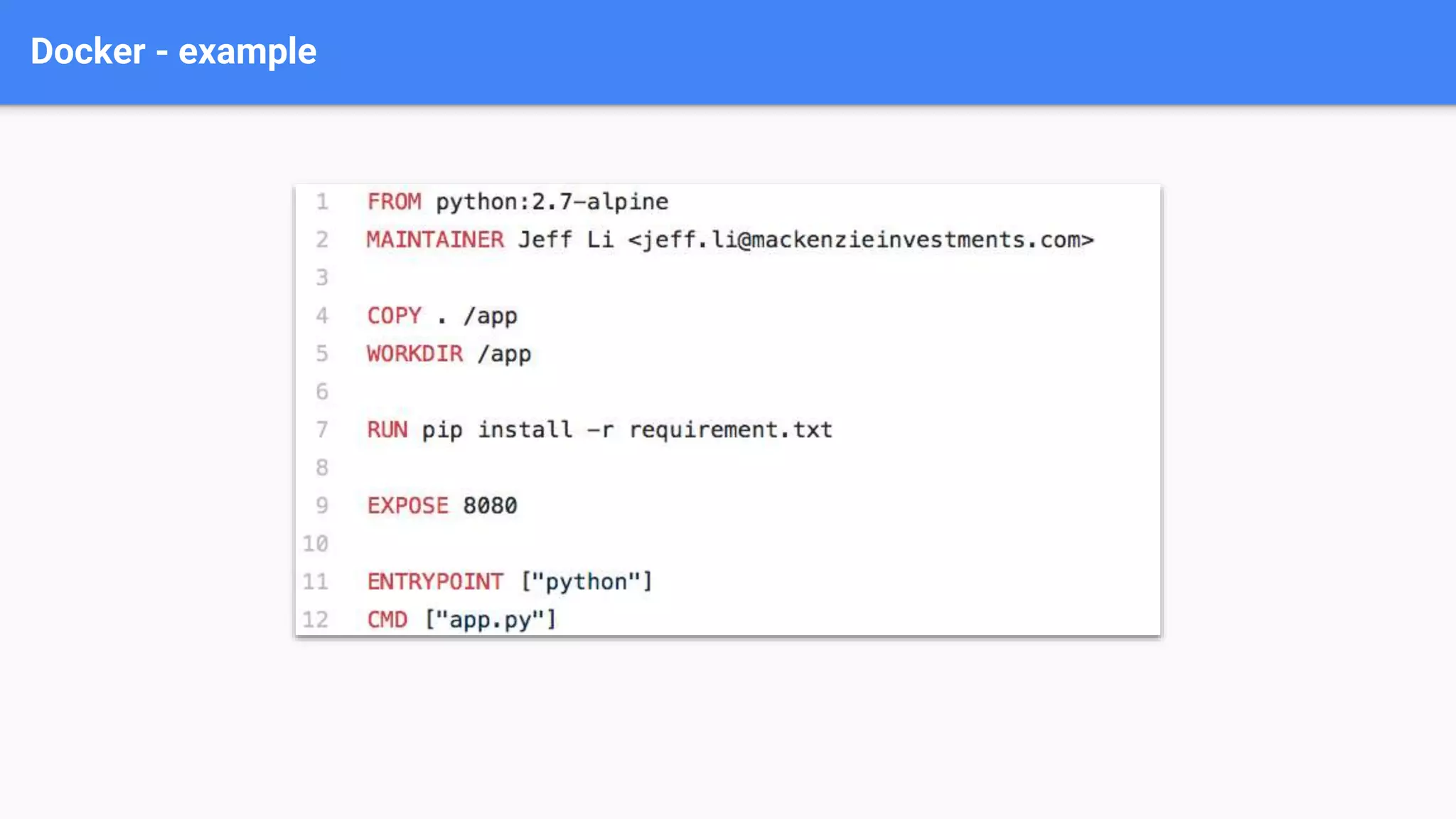
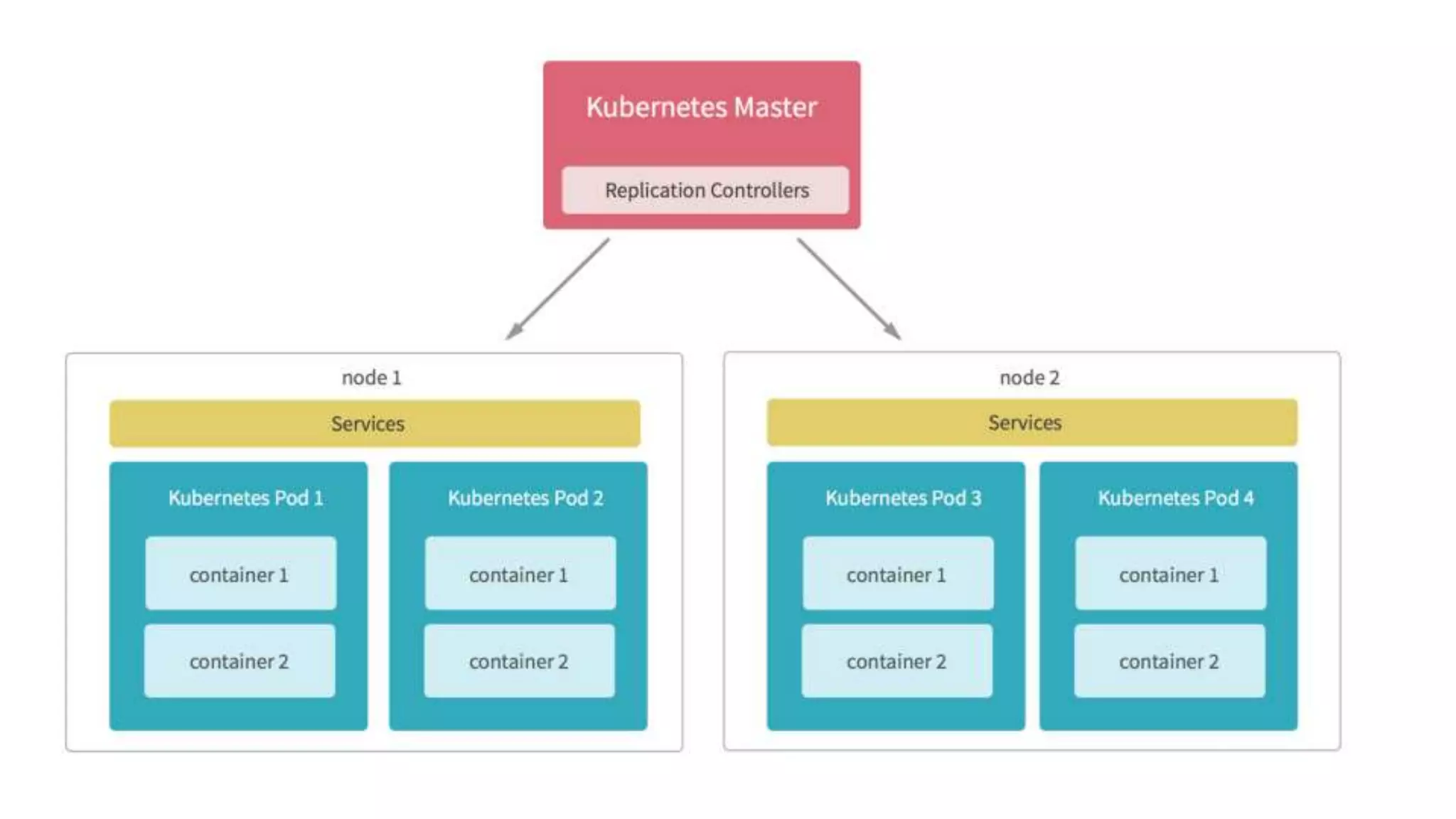
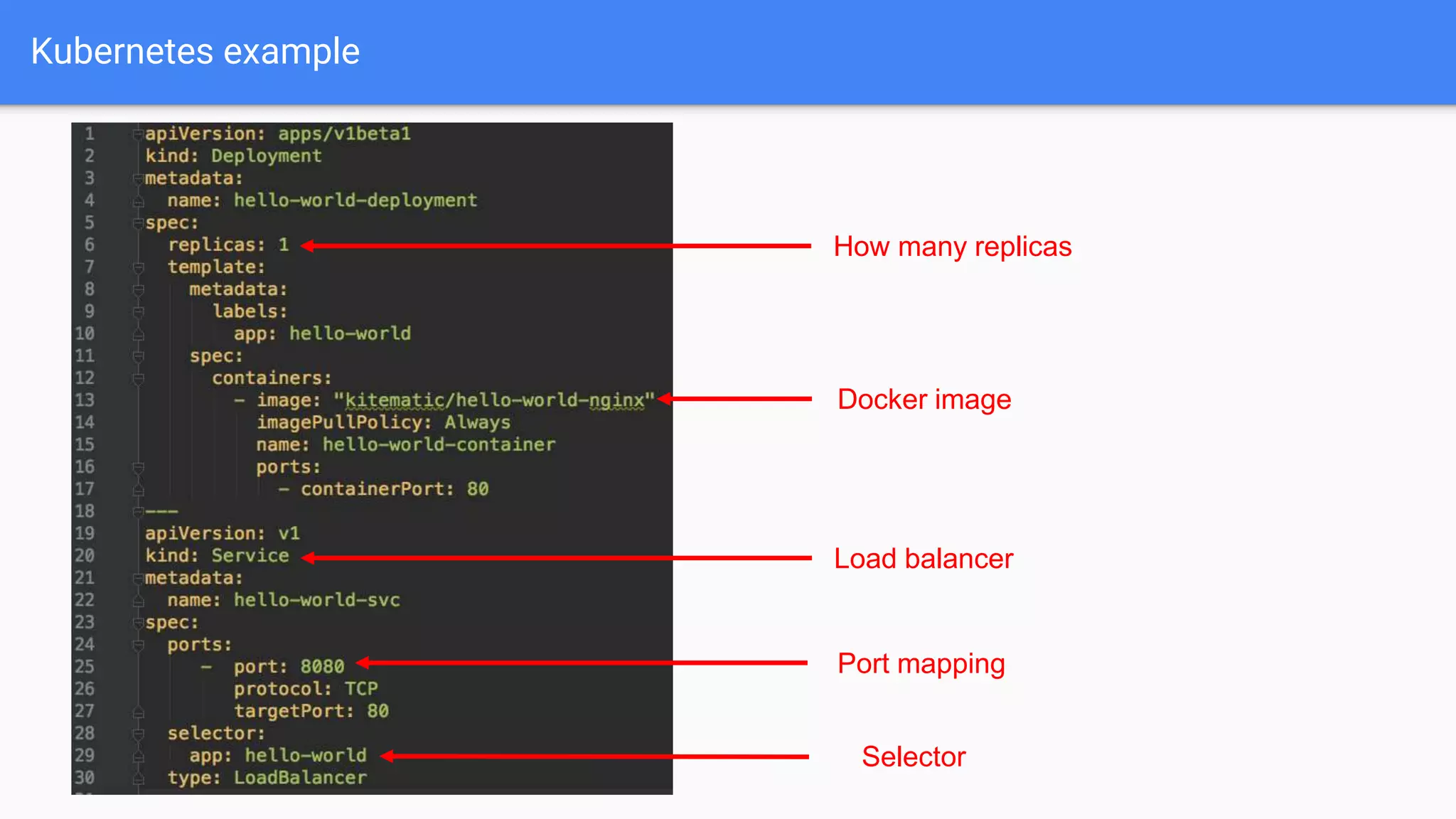
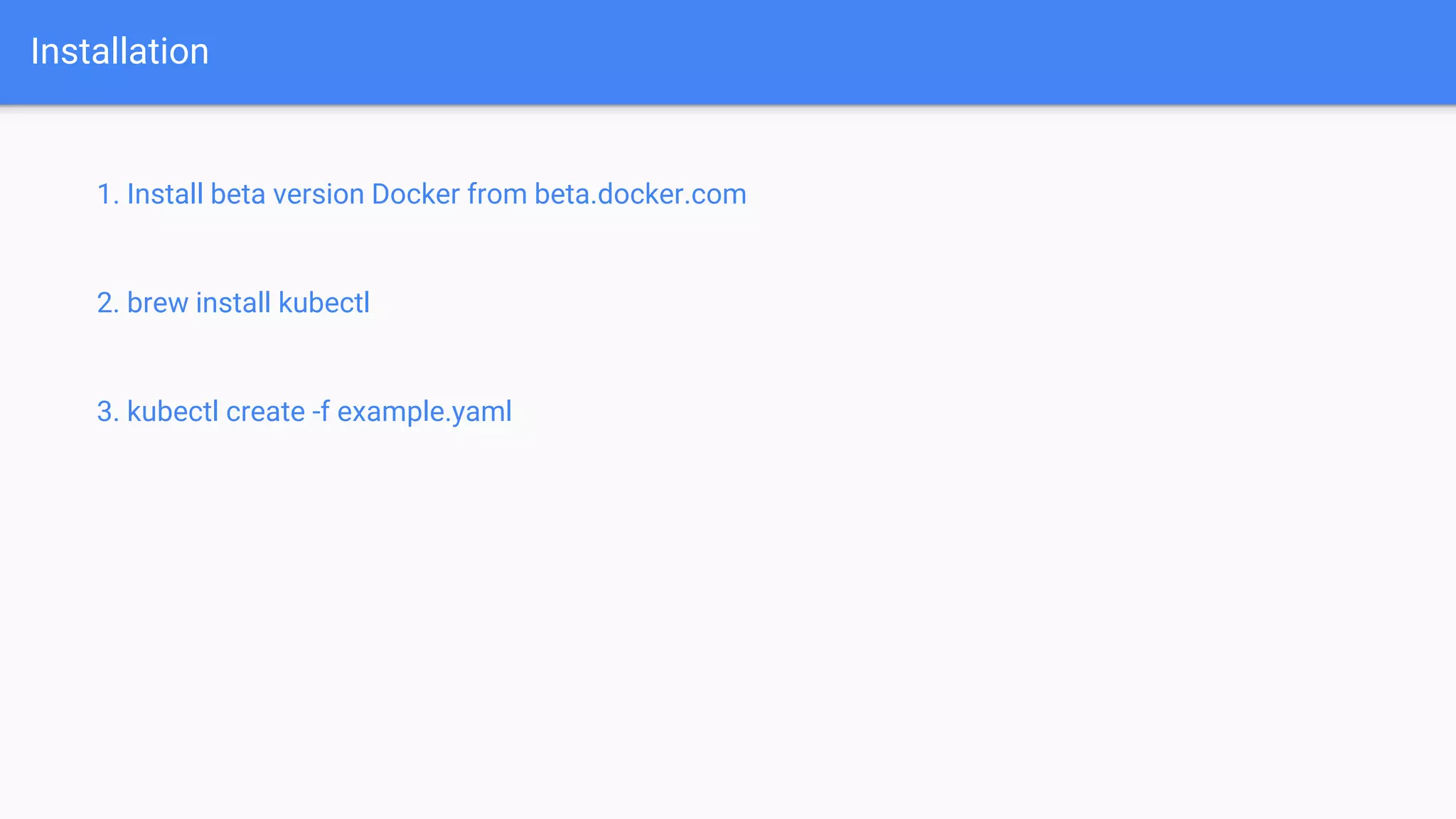
This document provides an introduction to orchestrating software deployments with Kubernetes. It discusses common challenges like deploying code to the cloud, horizontal scaling, rollouts and rollbacks that Kubernetes addresses. The basics of Kubernetes components like pods, deployments and ingress are explained. It also gives an example of creating a Kubernetes deployment and lists some important Kubernetes commands.