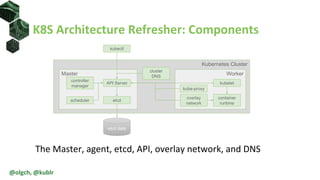
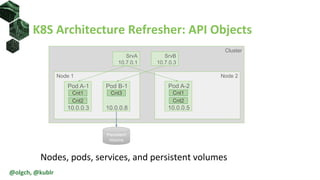
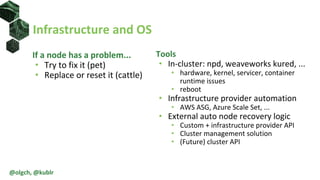
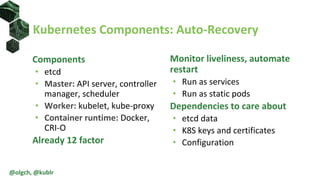
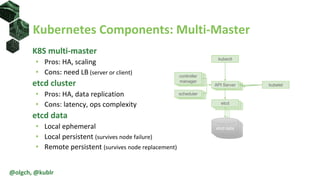
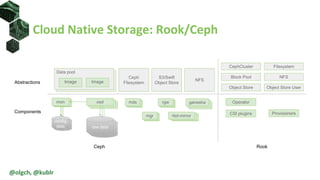
The document discusses the impact of self-healing nodes and infrastructure management on system reliability within Kubernetes environments. It covers various architectural components, monitoring tools, and reliability strategies essential for maintaining robust operations. Key takeaways include the importance of understanding Kubernetes layers and the responsibilities of cluster operators in managing recovery and performance.