Embed presentation
Download to read offline


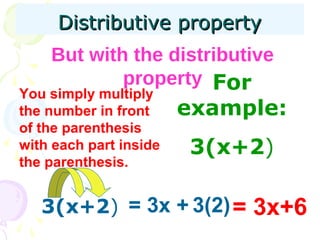




The document discusses the distributive property in algebra. The distributive property allows terms inside parentheses to be distributed so that expressions can be simplified out of order from the standard order of operations. It involves multiplying the number outside of the parentheses by each term inside the parentheses. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to use the distributive property to simplify expressions.






