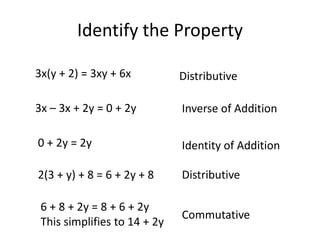
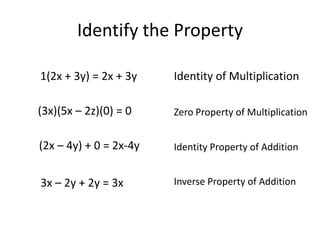
This document defines and provides examples of several important algebraic properties:
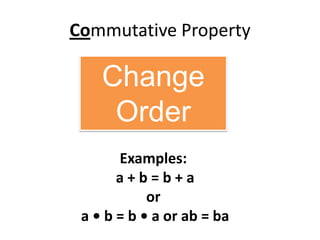
- The commutative and associative properties of addition and multiplication, which allow changing the order or grouping of terms.
- The identity properties of addition and multiplication, where adding/multiplying a number by the identity element (0 for addition, 1 for multiplication) does not change the number.
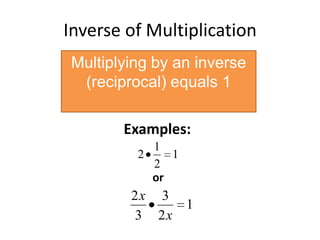
- The inverse properties of addition and multiplication, where adding/multiplying the inverse or opposite of a number results in the identity element.
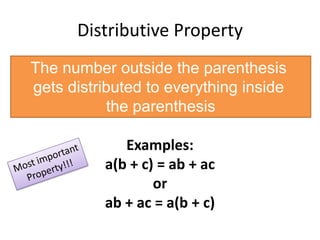
- The distributive property, where a number outside parentheses distributes to each term inside.
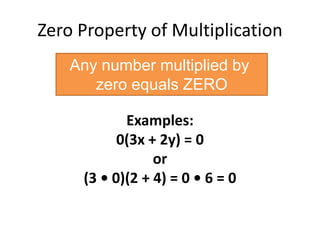
- The zero property of multiplication, where any number multiplied by zero equals zero.