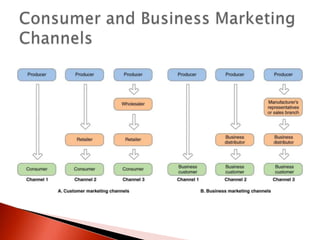
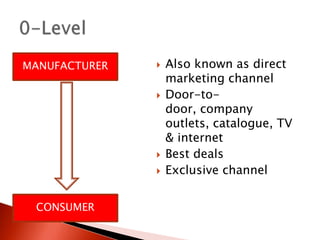
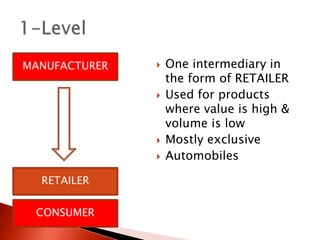
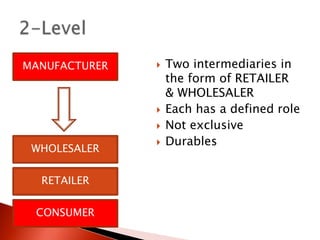
The document discusses distribution channels and physical distribution. It describes distribution as making products available for consumers through direct or indirect means. Effective distribution relies on inventory, warehousing, communications, packaging, and transport. Distribution channels can be short, involving just manufacturer and consumer, or longer with intermediaries like wholesalers and retailers. Physical distribution involves planning and controlling the flow of goods from origin to consumption to meet customer needs.