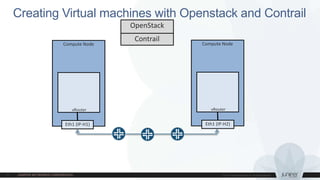
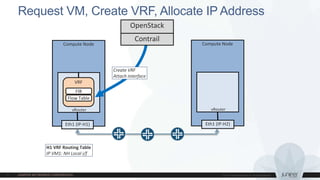
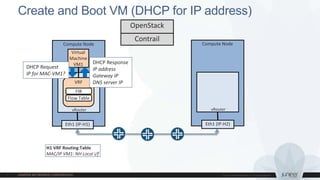
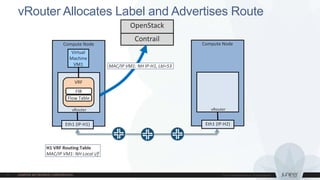
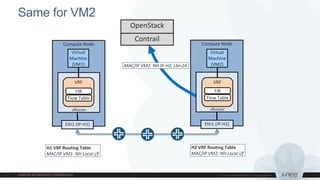
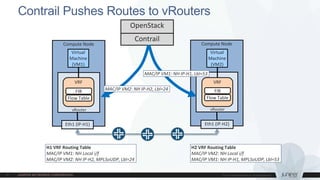
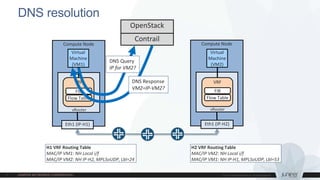
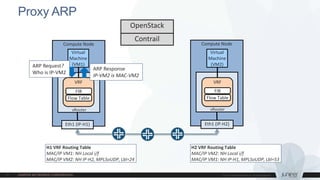
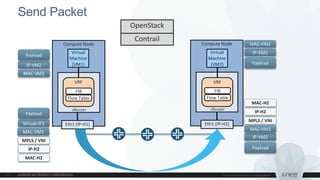
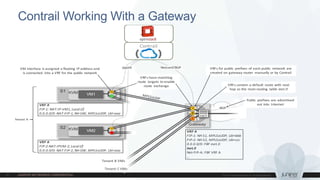
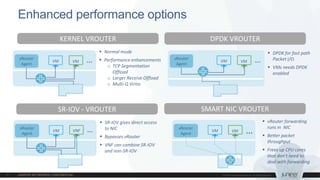
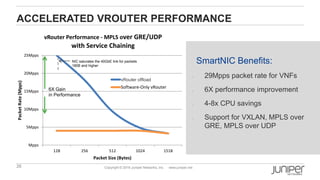
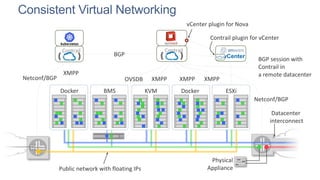
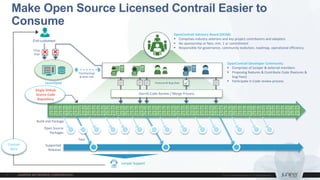
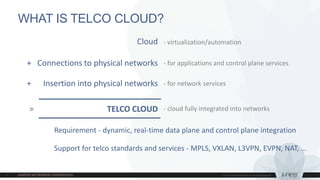
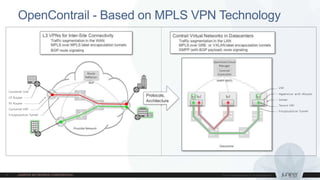
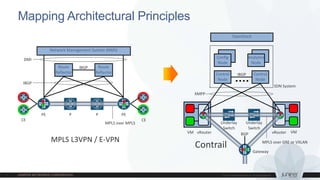
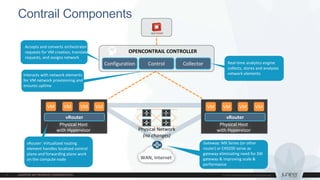
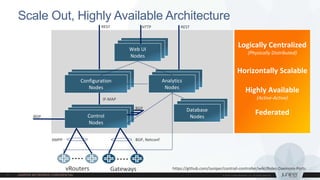
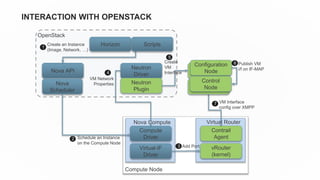
This document discusses use cases and requirements for different cloud customer segments using Contrail. It describes Contrail's ability to enable IT as a service, enterprise migration to the cloud with legacy interconnects, public cloud services, and IoT/M2M use cases. It provides an overview of how Contrail works including its components, scale out architecture, and interaction with OpenStack. It also summarizes Contrail's features such as routing, security, analytics, and gateway services.



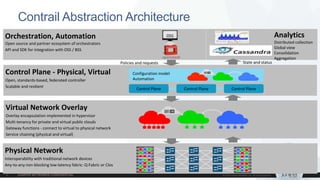

![Compute node (vRouter)
Forwarding
Blue VRF
Flow Table
Tap Interface (vif)
FIB
VM 1
(Tenant A)
Green VRF
Flow Table
FIB
Red VRF
Flow Table
FIB
VM 2
(Tenant B)
VM 1
(Tenant B)
…eth 1 eth N
vRouter Agent
vRouter replaces the Linux Bridge or OVS
module in Hypervisor Kernel
vRouter performs bridging (E-VPN) and
routing (L3VPN)
vRouter performs networking services like
Security Policies, NAT, Multicast, Mirroring,
and Load Balancing
No need for Service Nodes or L2/L3 Gateways
for Routing, Broadcast/Multicast, NAT
Routes are automatically leaked into the VRF
based on Policies
Support for Multiple Interfaces on the Virtual
Machines
Support for Multiple Interfaces from Compute
Node to the Switching Fabric
config Policy
Table
VRFs
Overlay Tunnels:
MPLSoUDP/GRE,VXLAN
pkt
0
[kernel]
[user space]
CONTRAIL CONTROLLER](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opencontrail-openstackmeetup-170602175325/85/OpenStack-MeetUp-OpenContrail-Presentation-13-320.jpg)