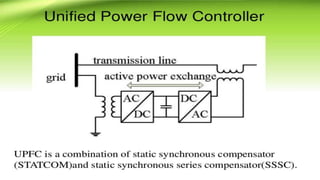
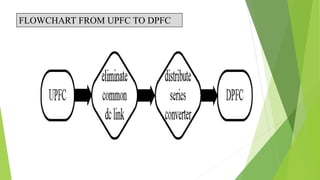
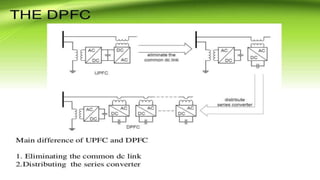
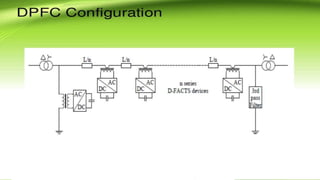
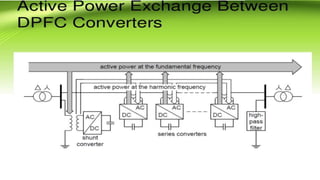
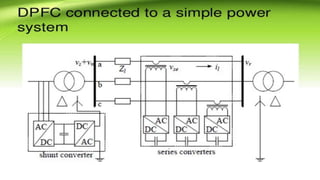
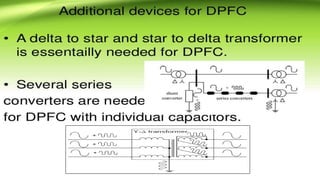
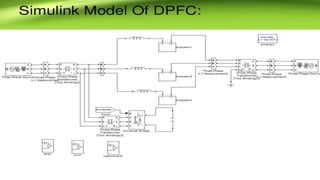
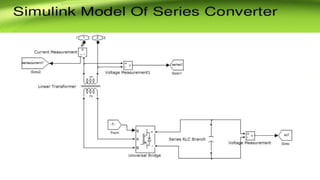
This document describes a project to implement a distributed power flow controller (DPFC) for controlling power flow. The DPFC is derived from the unified power flow controller (UPFC) but eliminates the common DC link. Instead, active power is exchanged between the shunt and series converters through the transmission lines at the third harmonic frequency. The DPFC employs multiple single-phase distributed converters instead of a single three-phase series converter for increased reliability. As the converters are single-phase, there is no high voltage isolation required between phases, lowering the cost compared to the UPFC. The objectives are to compensate reactive power and overcome disadvantages of the UPFC.