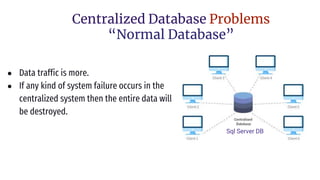
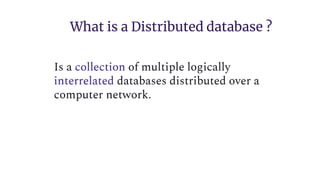
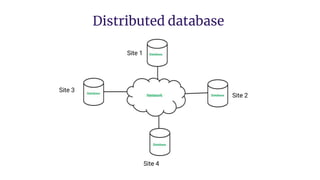
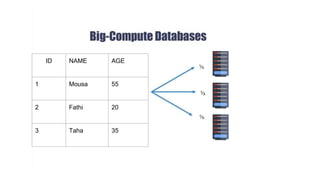
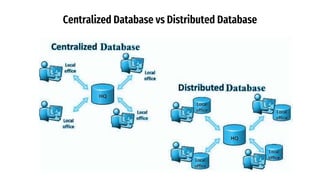
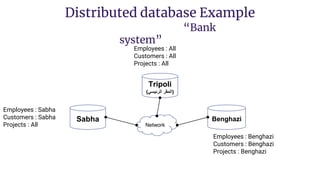
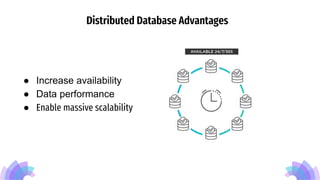
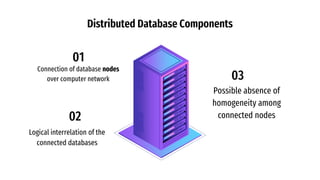
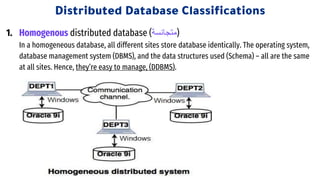
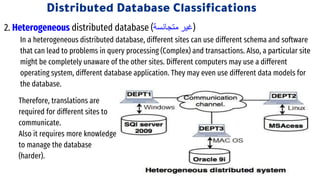
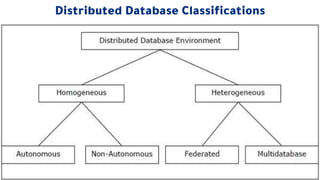
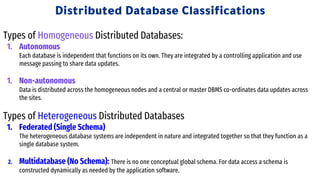
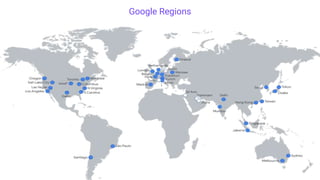
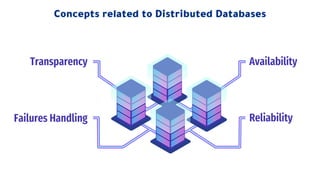
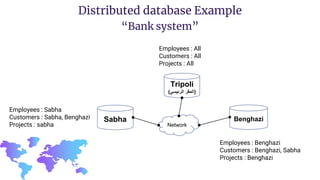
Distributed databases allow data to be stored across multiple interconnected sites. They provide advantages like increased availability, improved performance, and massive scalability. Distributed databases can be either homogeneous, where all sites use identical database systems, or heterogeneous, where sites may use different systems requiring translations. Data can be distributed through replication, where copies are stored at each site, or fragmentation, where relations are divided into parts stored at different sites. Major companies like Amazon, Google, Netflix and Uber use distributed databases to handle large volumes of diverse data across global networks.