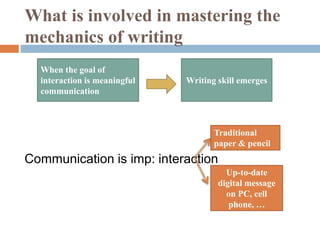
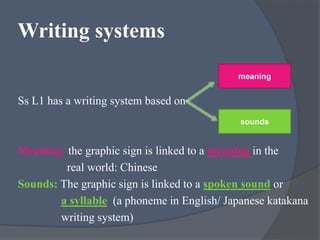
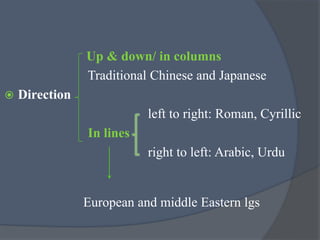
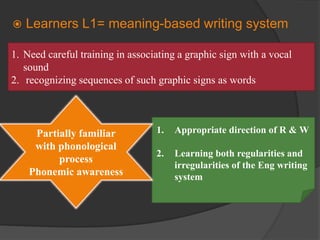
The document discusses practical tasks for mastering the mechanics of writing in English, including focusing on sound-spelling correspondences, letter recognition, and meaningful writing exercises that move from individual words and sentences to longer texts. It also addresses differences in writing systems and provides examples of early writing tasks for learners depending on whether their first language uses an alphabetic, syllabic, or logographic writing system.