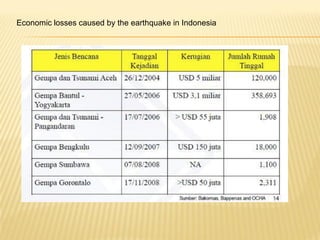
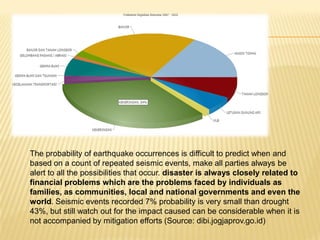
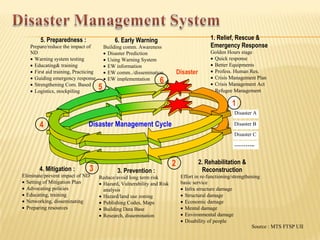
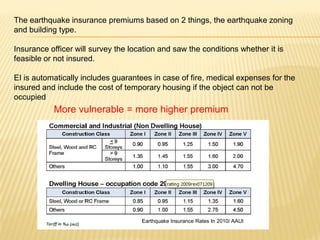
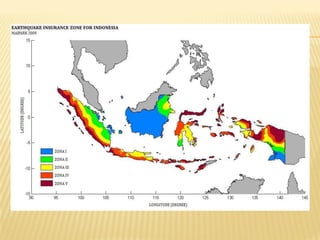
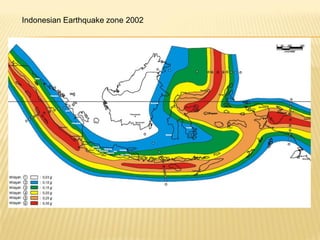
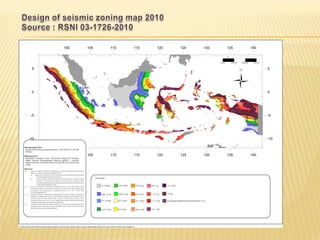
This document discusses earthquake risk in Indonesia and the role of insurance in disaster risk reduction. Indonesia is highly prone to earthquakes due to its location between major tectonic plates. Several major quakes in recent years have caused significant loss of life and property damage. Earthquake insurance provides a means to transfer risk and share the financial burden of potential losses. While insurance can help mitigate risks, it is important it does not reduce incentives for risk reduction and resilience measures.