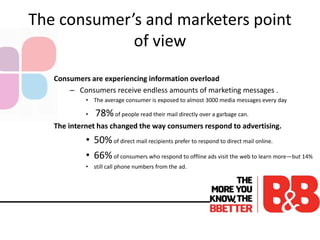
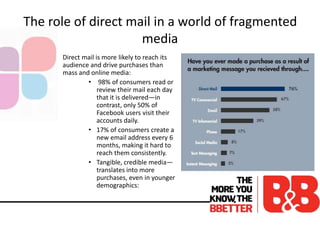
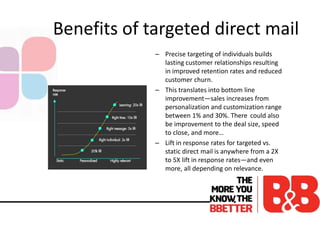
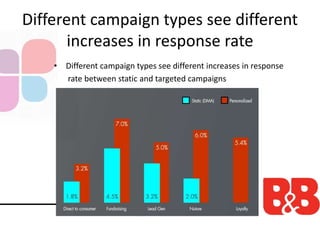
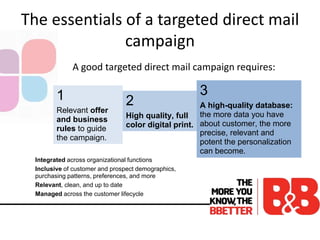
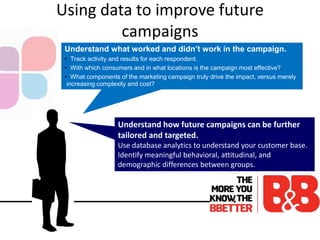
The document discusses the importance of direct marketing, emphasizing how targeted direct mail can effectively engage consumers and improve return on investment (ROI) while navigating the challenges of information overload and changing consumer behavior. It highlights the benefits of tailored communications, the significance of multichannel marketing strategies, and the role of marketing storefronts in customizing direct mail campaigns. Additionally, it outlines essential metrics for measuring campaign success and best practices for optimizing marketing efforts.