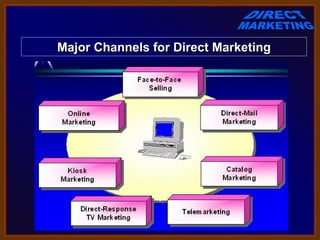
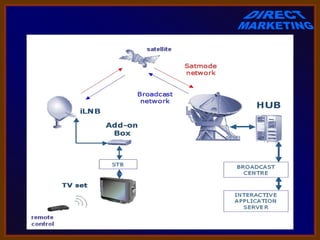
The document discusses various aspects of direct marketing including definitions, growth factors, benefits, major channels, and key concepts like database marketing. Direct marketing involves non-store retailing where customers purchase through phone or mail after exposure to products through an impersonal medium. It has grown due to changing lifestyles, technology growth, and other economic factors. Benefits include convenience for customers and data-driven targeting for companies. Major channels include direct mail, catalogs, telemarketing, and digital/online channels. Database marketing uses customer data to generate personalized communications.