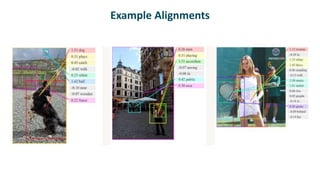
The document summarizes several papers on image captioning using neural networks. It describes Karpathy and Fei-Fei (2015), which obtains image and sentence embeddings, trains them to align image patches with words, and uses an RNN to map image fragments to phrases. It also discusses Vinyals et al (2015) and Mao et al (2015), noting common themes of joint embedding spaces and differences in image processing, inputs to RNNs, and recurrence types. Evaluation metrics like R@K and Med r are also introduced.









![Representing Sentences
Bidirectional RNN
input representation is based on word2vec
Produces an embedding at each position
of the sentence (𝒔𝒕)
Embedding also has dimensionality 𝒉
[don’t confuse this with hidden activity 𝒉!]
Key claim
𝒔𝒕 represents the concept of the words near position 𝒕](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/captions-220930084514-3da7a7c1/85/Image-captions-pptx-10-320.jpg)