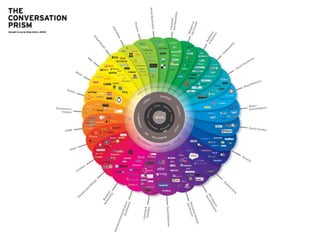
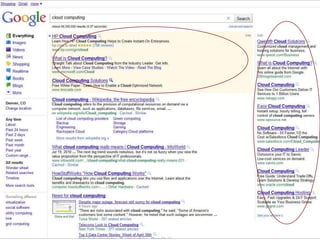
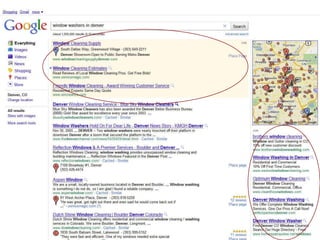
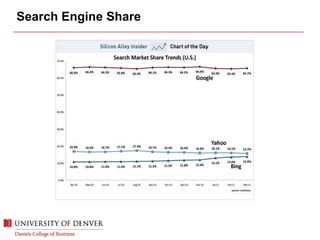
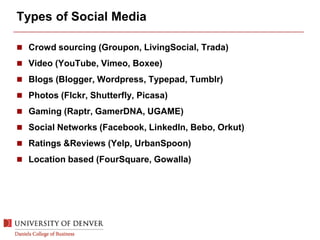
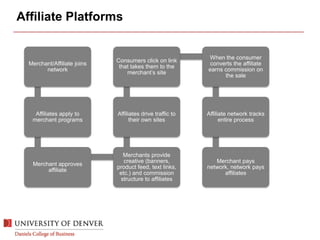
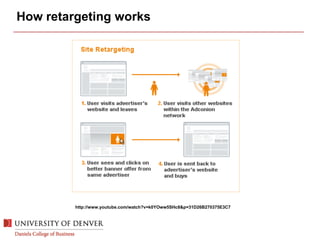
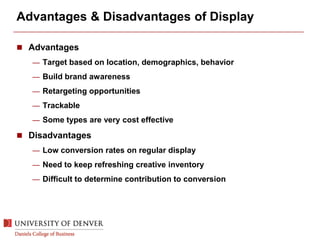
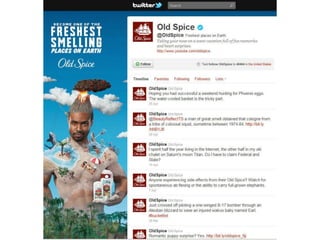
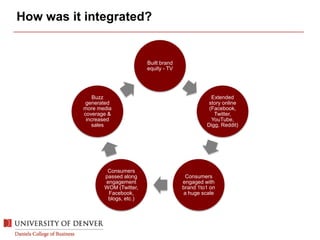
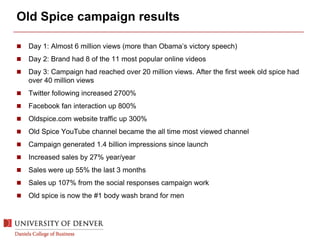
The document discusses digital marketing and integrated marketing communications, highlighting the importance of a cohesive strategy across various digital channels such as SEO, SEM, social media, email, and affiliate marketing. It emphasizes the need for relevant messaging, customer engagement, and the use of data to inform marketing decisions, alongside the advantages and disadvantages of each digital marketing method. The Old Spice case study showcases a successful integrated campaign that significantly increased brand awareness and sales, demonstrating the effectiveness of engaging consumers through multiple channels.