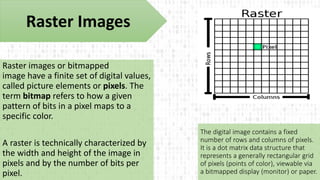
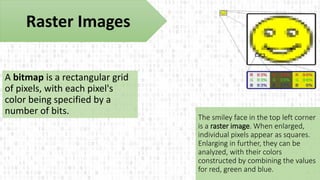
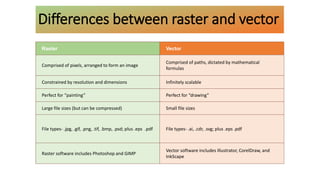
The document provides an overview of digital imaging, explaining the differences between raster and vector images, including their structures, scalability, file types, and applications. Raster images consist of pixels and are defined by resolution and color depth, while vector images are created using mathematical formulas, allowing for infinite scalability without loss of quality. Additionally, it discusses the RGB and CMYK color models used for digital screens and print materials, respectively.