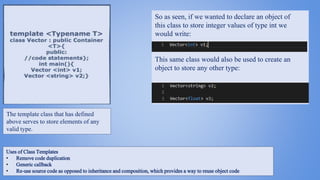
This document provides an overview of the C++ programming language, highlighting its evolution, key features, and applications. It emphasizes the importance and functionality of the C++ standard library, particularly the class template vector, which supports generic programming and efficient code reuse. The document also discusses the structure of C++ code and the benefits of class templates in reducing code duplication.