Team Members: Ahmed Moawad, Ebtsam Abdul-Aziz Hassan, Shimaa Mohsen El-Sadik, Nora Abdul-Rahman, Nermin Abdul-Menaem Hassan.
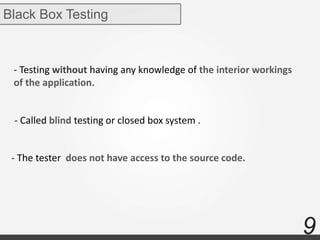
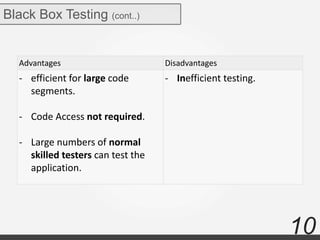
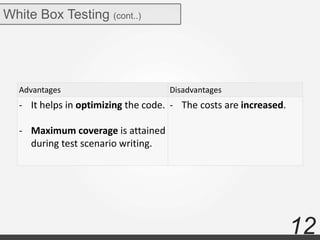
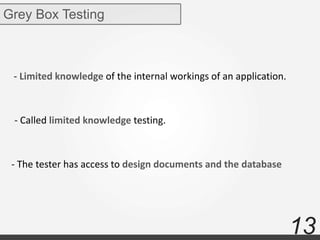
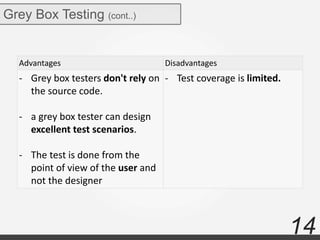
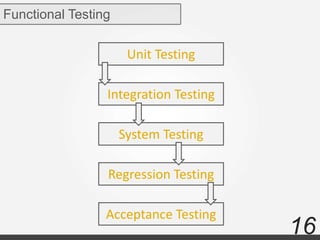
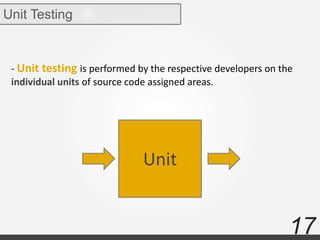
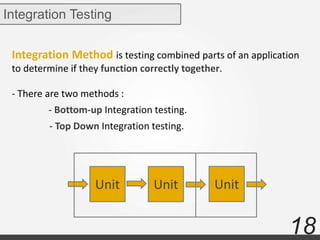
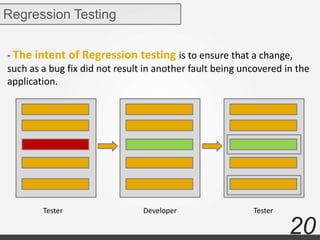
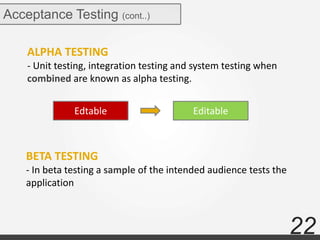
The document discusses various types of software testing including manual testing, automation testing, black box testing, white box testing, grey box testing, functional testing (unit, integration, system, acceptance, and regression testing), and non-functional testing (performance, security, usability, and portability testing).
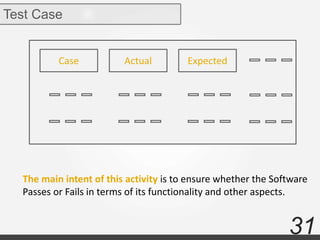
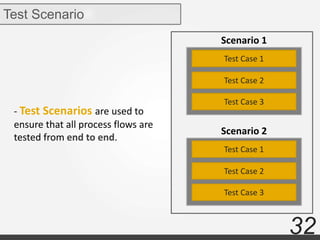
Testing documentation and the testing process are also summarized including test plans, test scenarios, test cases, when to start and stop testing, and references.