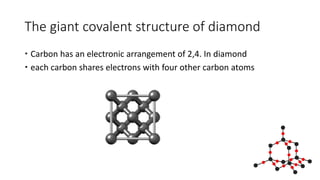
The document discusses the physical, optical, electrical, and thermal properties of diamonds, highlighting their hardness, high melting point, and non-conductivity. It also explains the formation of synthetic diamonds through various methods and their diverse applications in industries such as healthcare, electronics, and laser technology. Additionally, the document addresses the optical properties, including fluorescence and color variations caused by impurities.