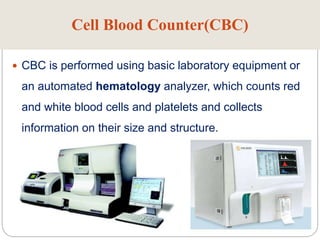
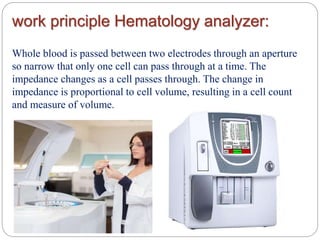
Diagnostic medical equipment is used in hospitals and clinics to diagnose patients' conditions. This includes laboratory equipment like cell blood counters, arterial blood gas analyzers, spectrophotometers, and microscopes. It also includes devices like electrocardiographs, electroencephalographs, electromyographs, patient monitors, pulse oximeters, pH meters, and thermometers. These devices help evaluate patients internally, detect any abnormalities, and allow doctors to precisely analyze organ function.