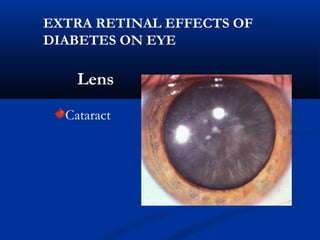
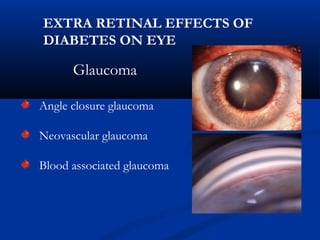
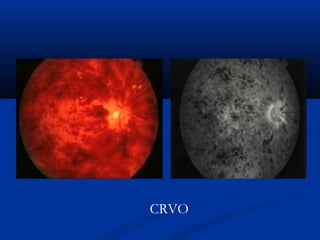
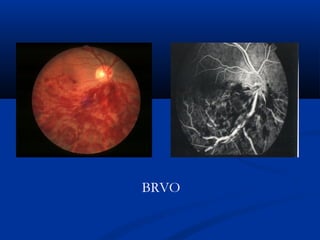
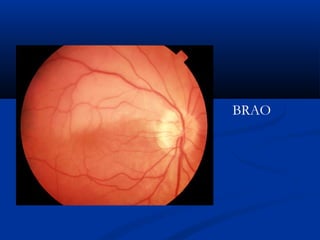
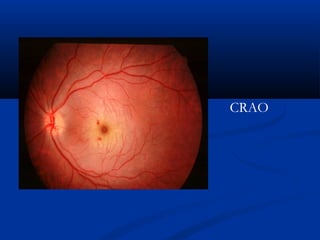
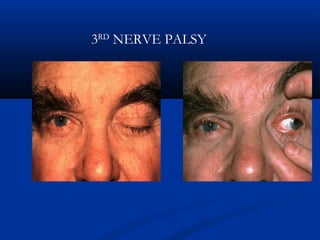
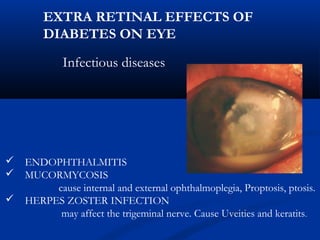
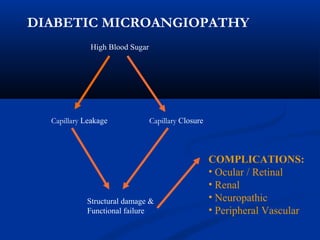
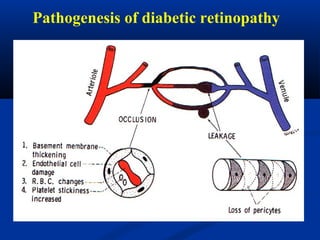
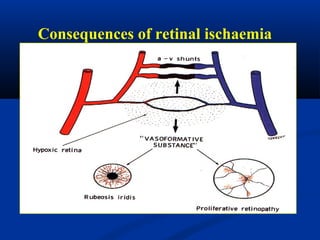
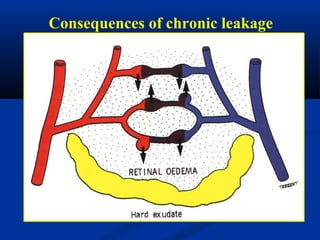
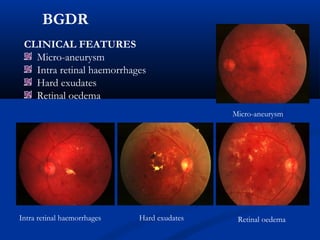
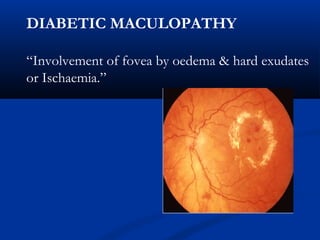
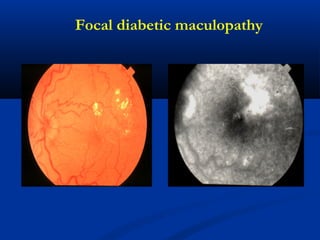
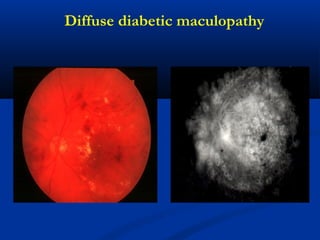
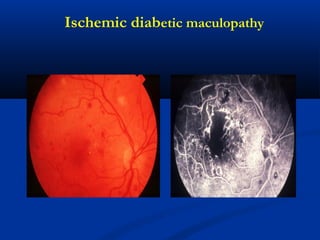
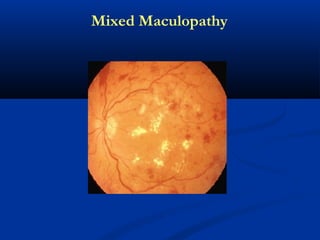
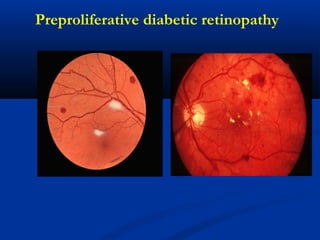
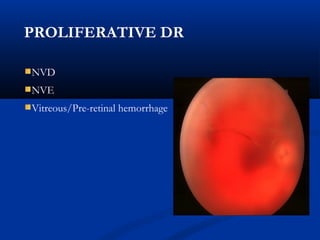
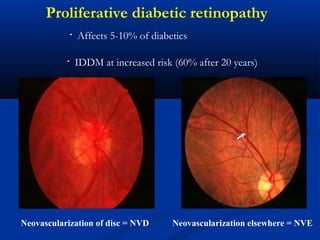
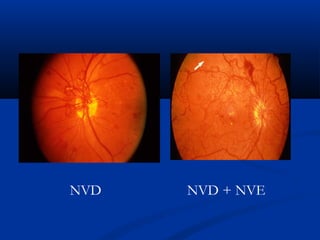
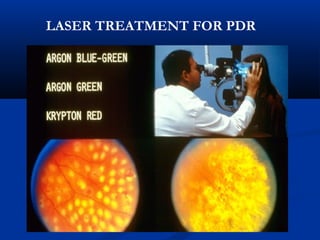
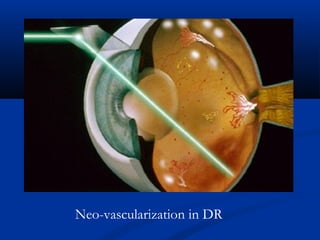
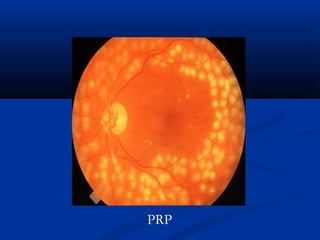
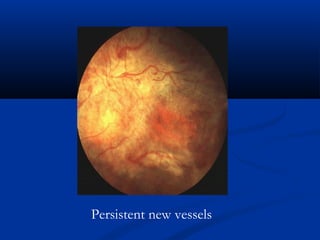
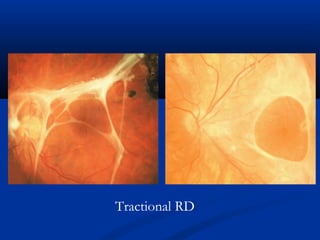
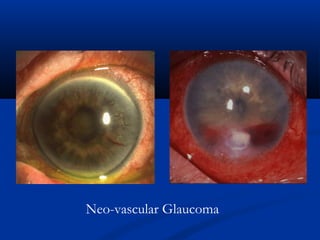
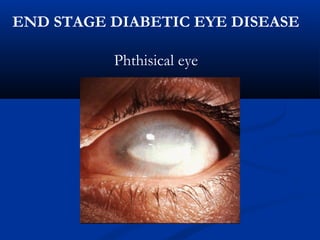
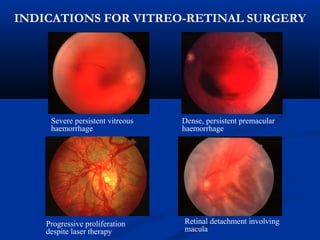
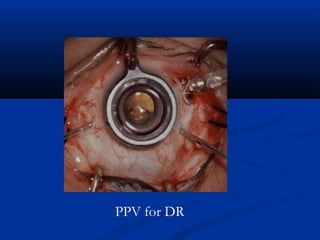
This document discusses diabetic ophthalmopathy, a common sight-threatening complication of diabetes. It begins by stating that diabetes affects about 3% of the global population. Next, it describes the various extra-retinal effects diabetes can have on the eye, including cataracts, glaucoma, retinal vascular diseases, and infections. A major section then focuses on diabetic retinopathy, including its pathogenesis, risk factors, various stages from non-proliferative to proliferative, and management through careful monitoring, laser treatment, and in advanced cases, vitreo-retinal surgery. The document aims to outline the ocular effects of diabetes and treatment approaches for associated conditions like diabetic retinopathy.