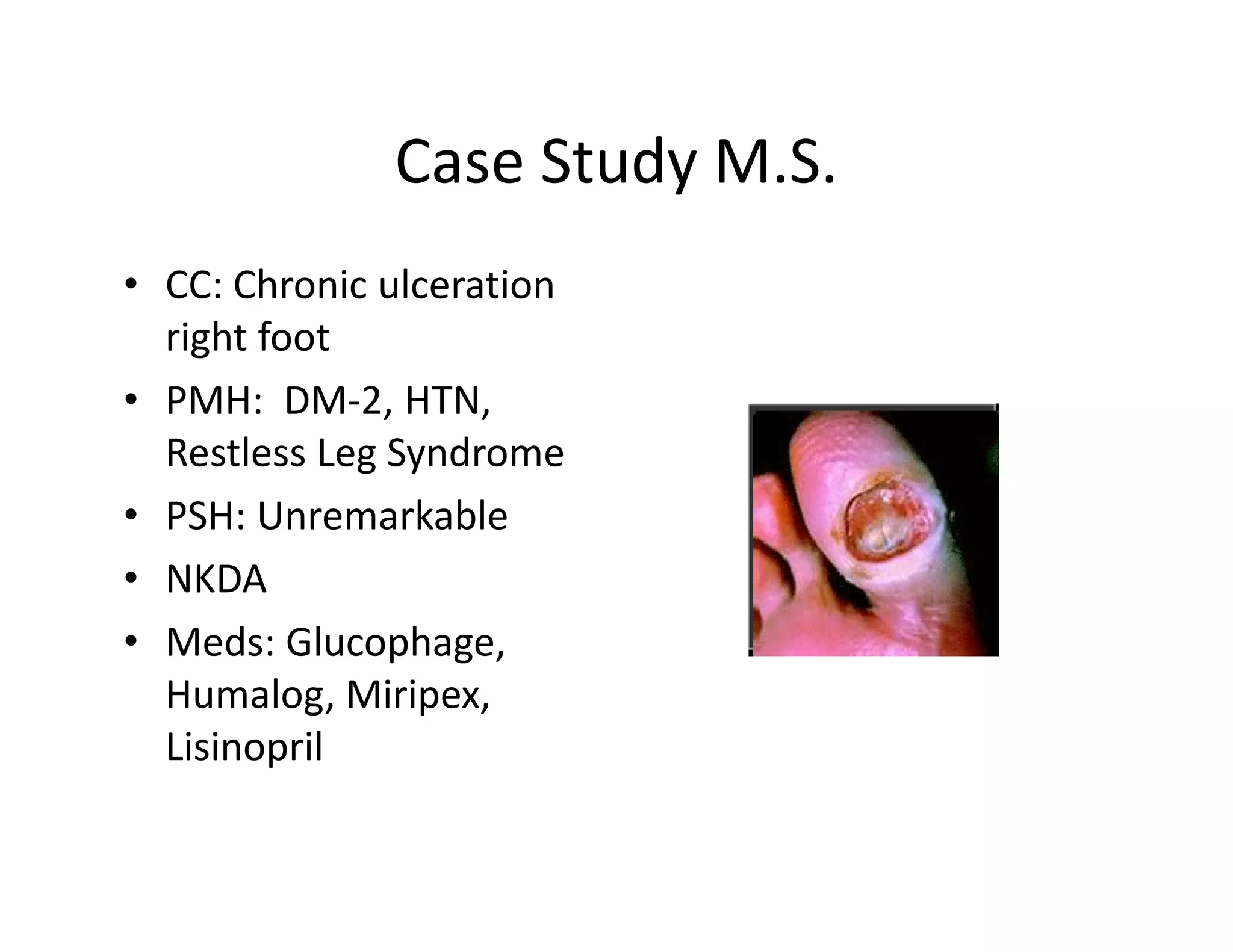
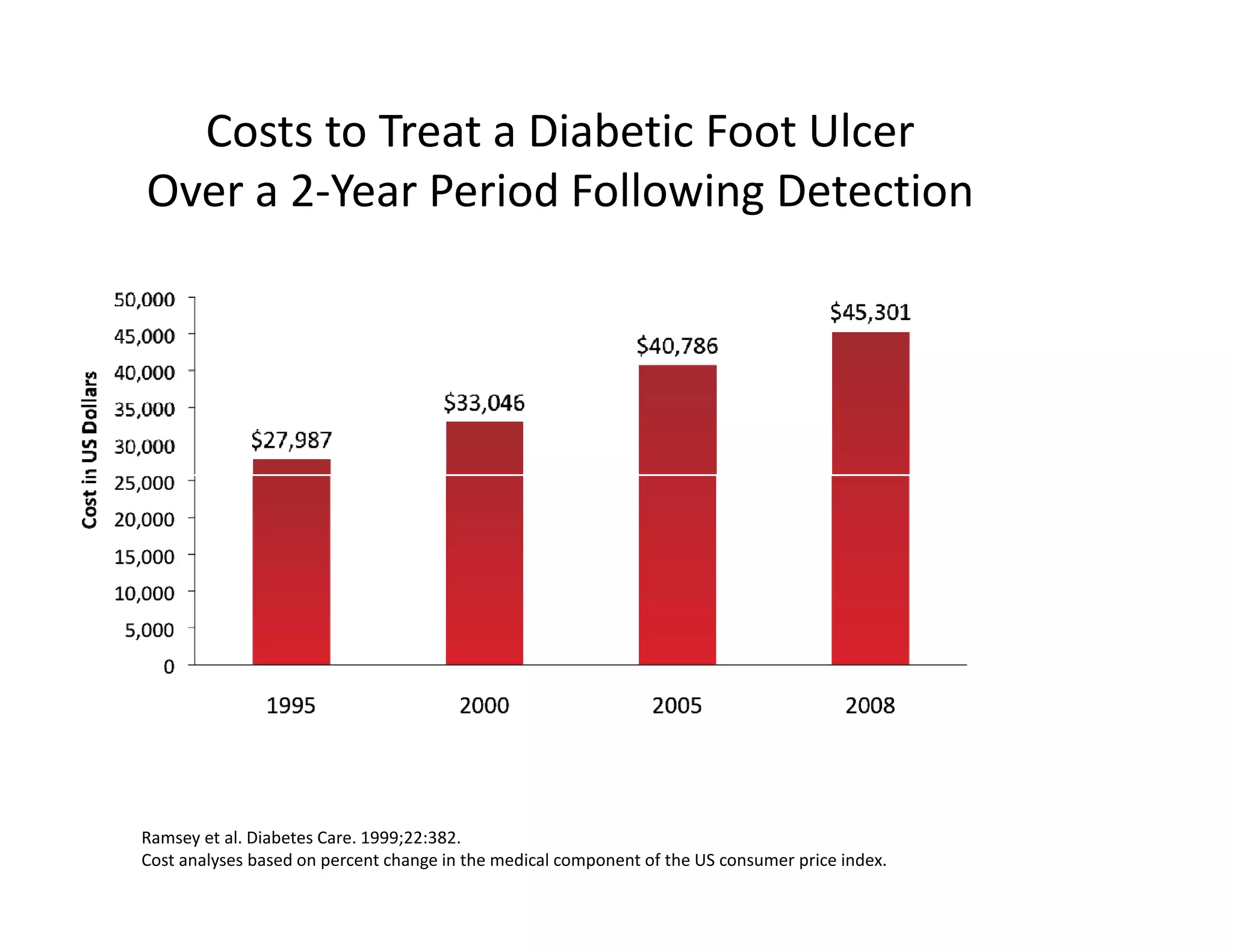
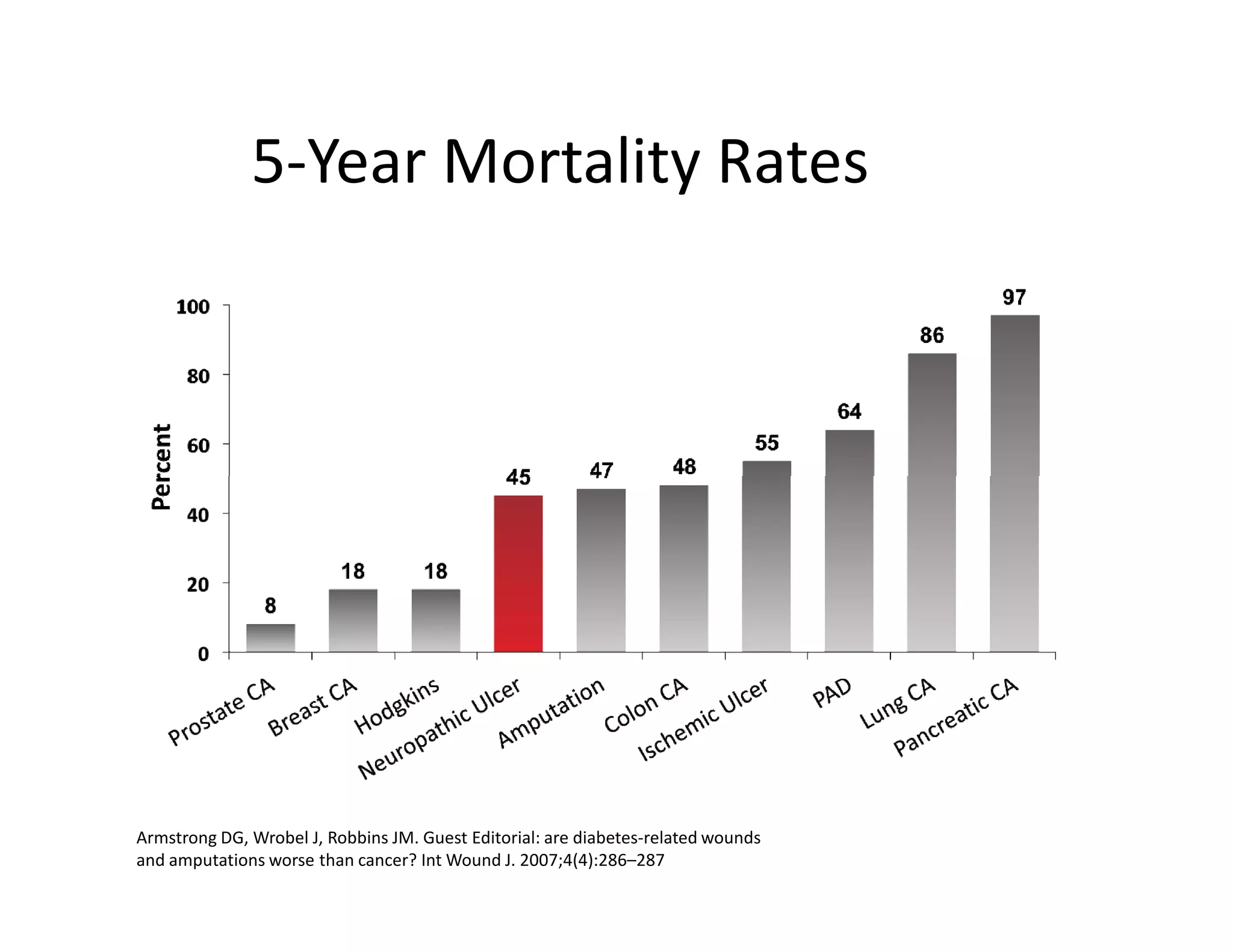
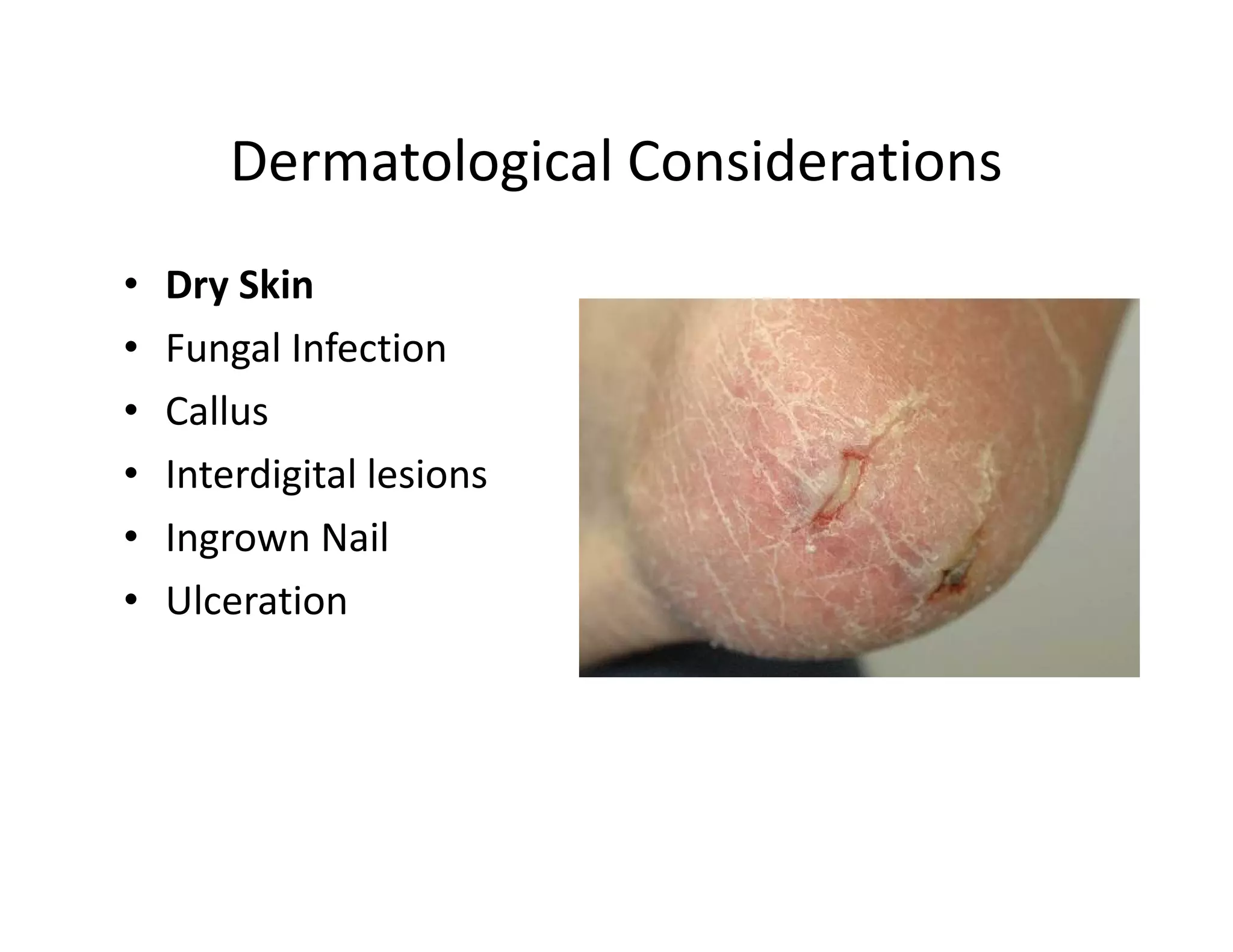
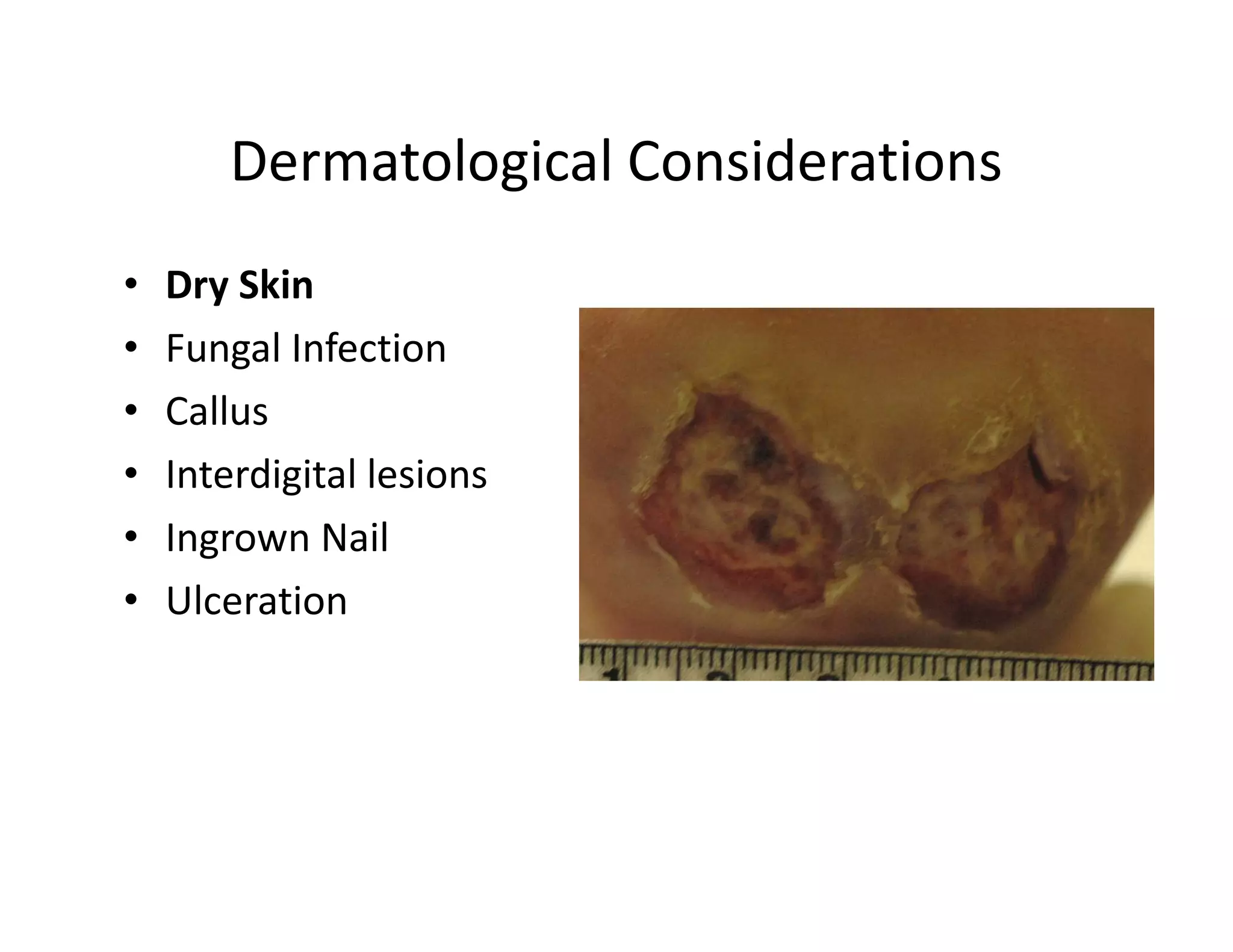
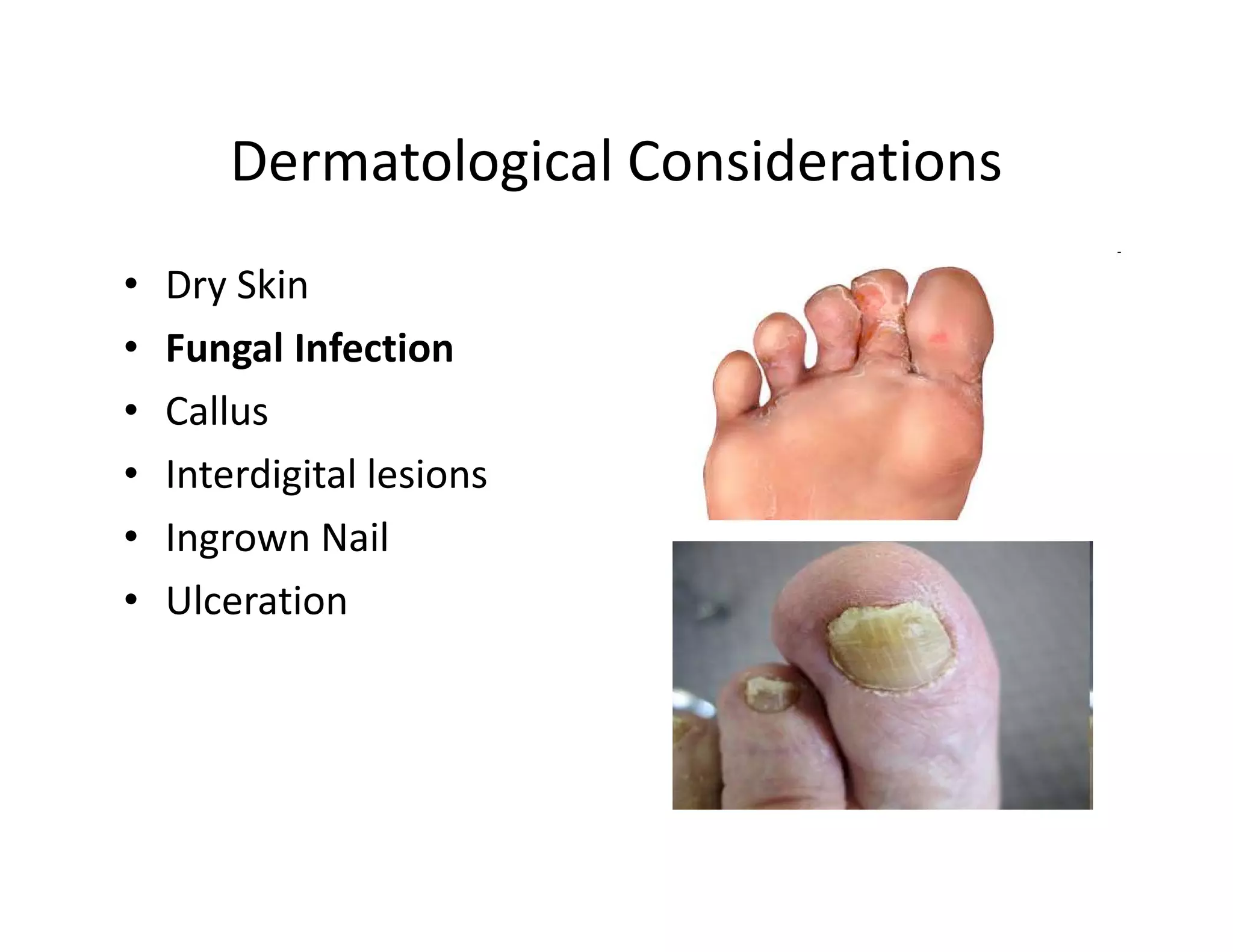
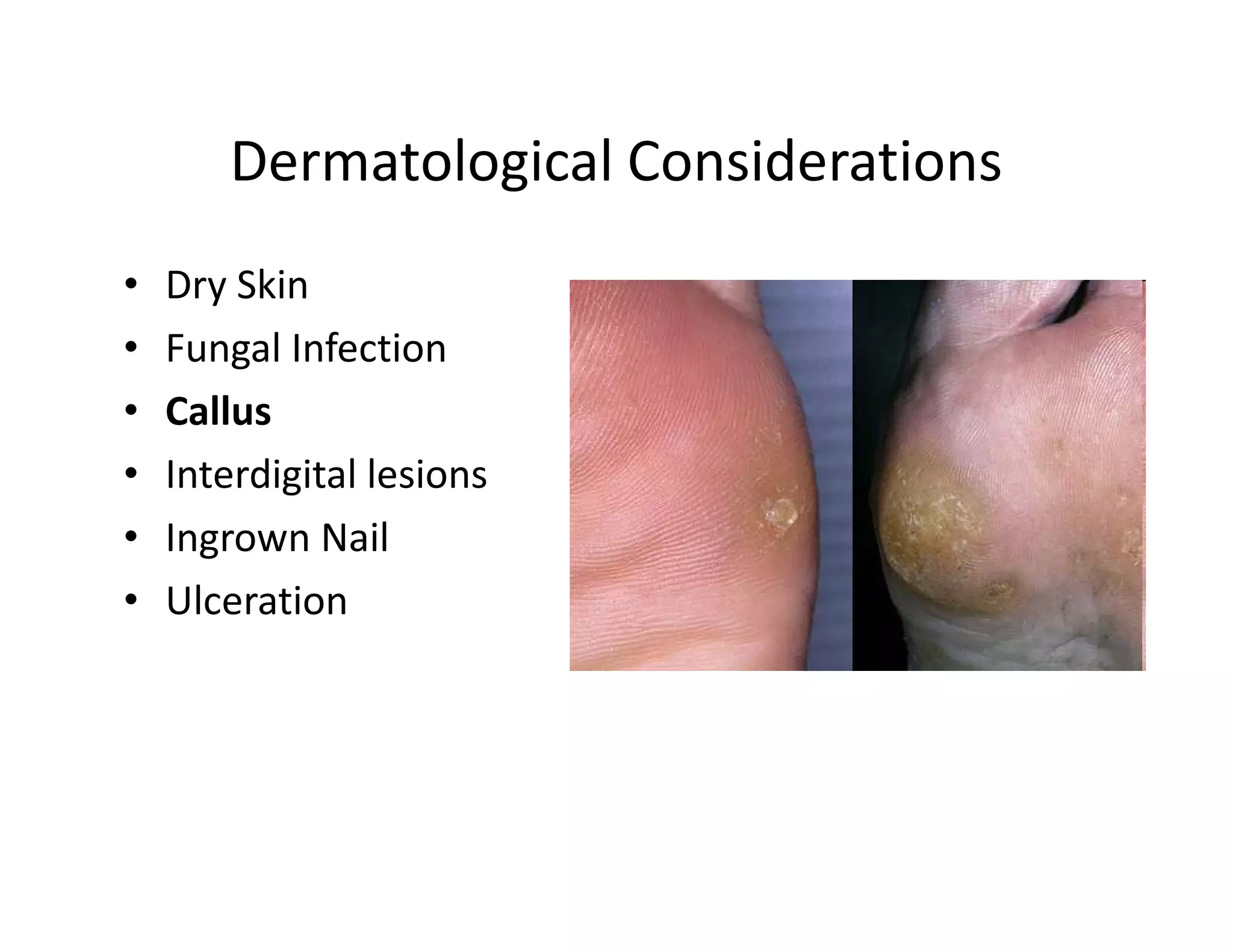
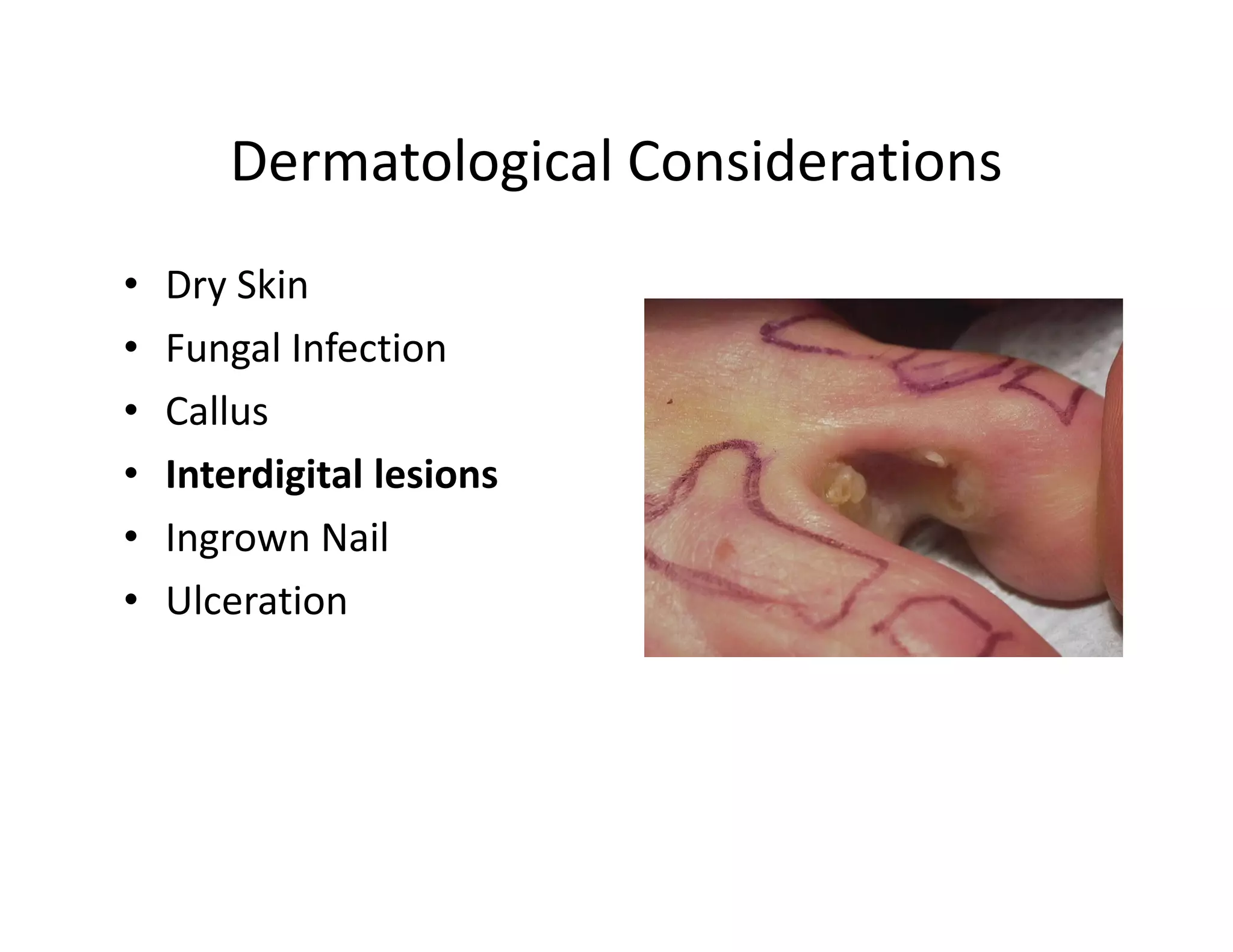
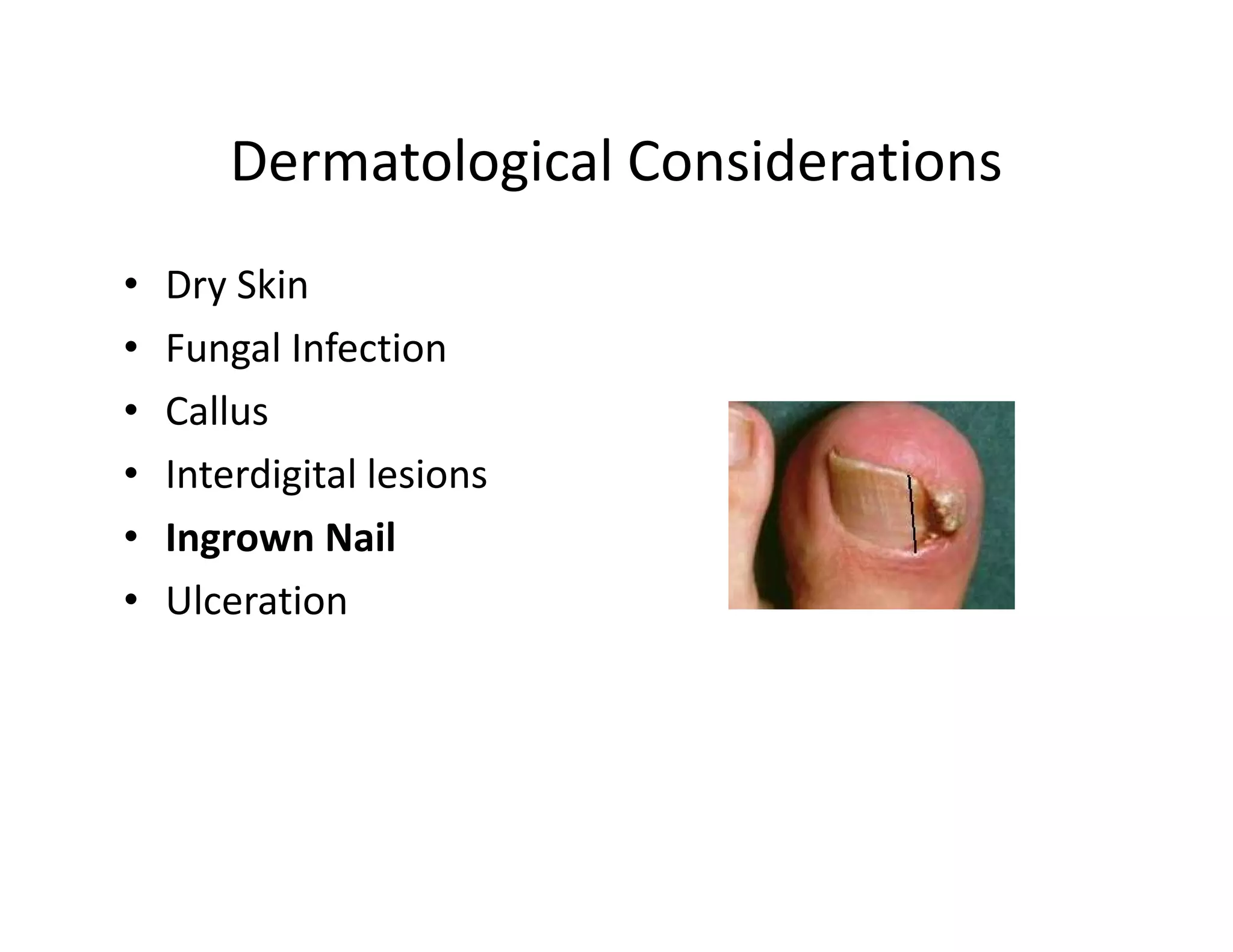
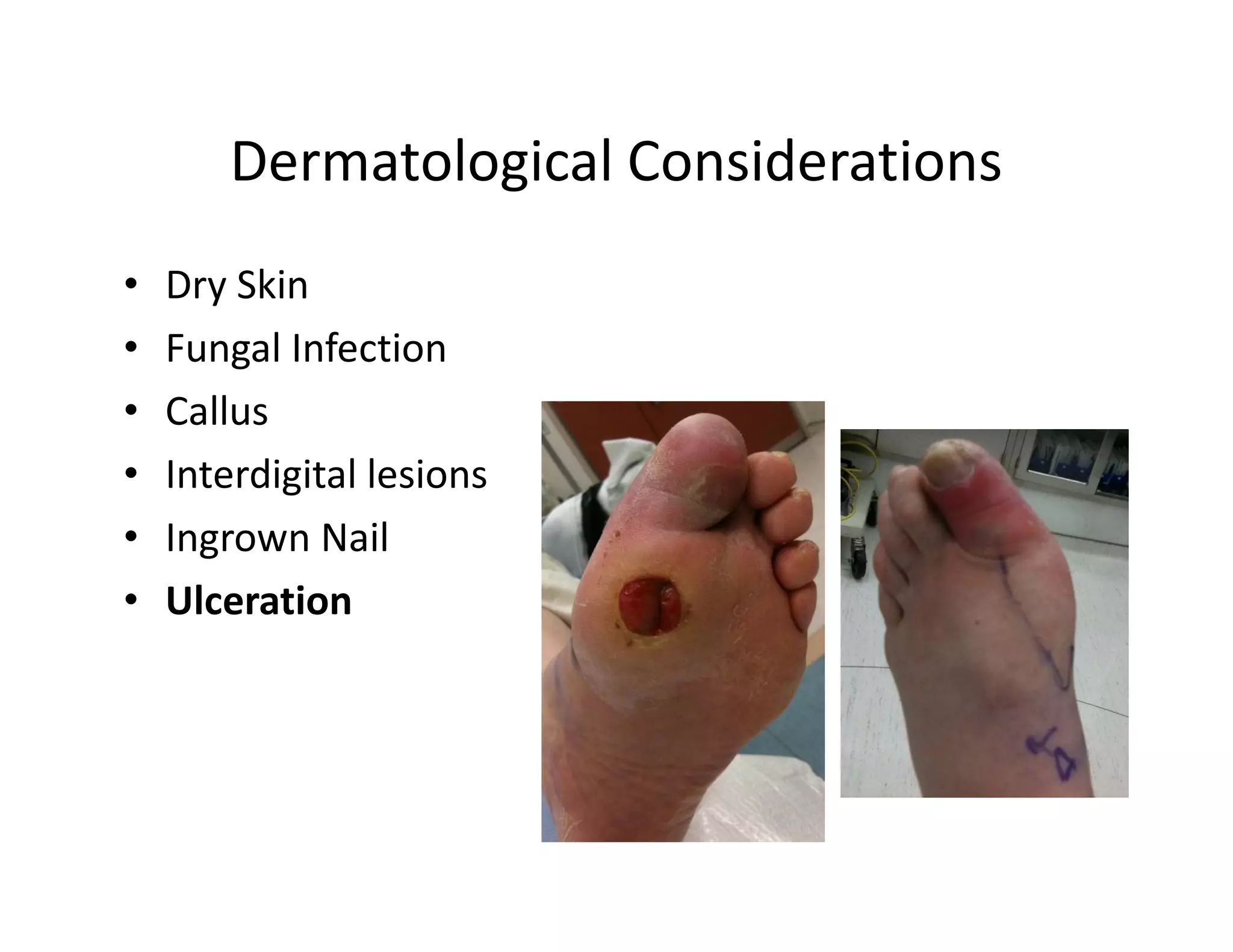
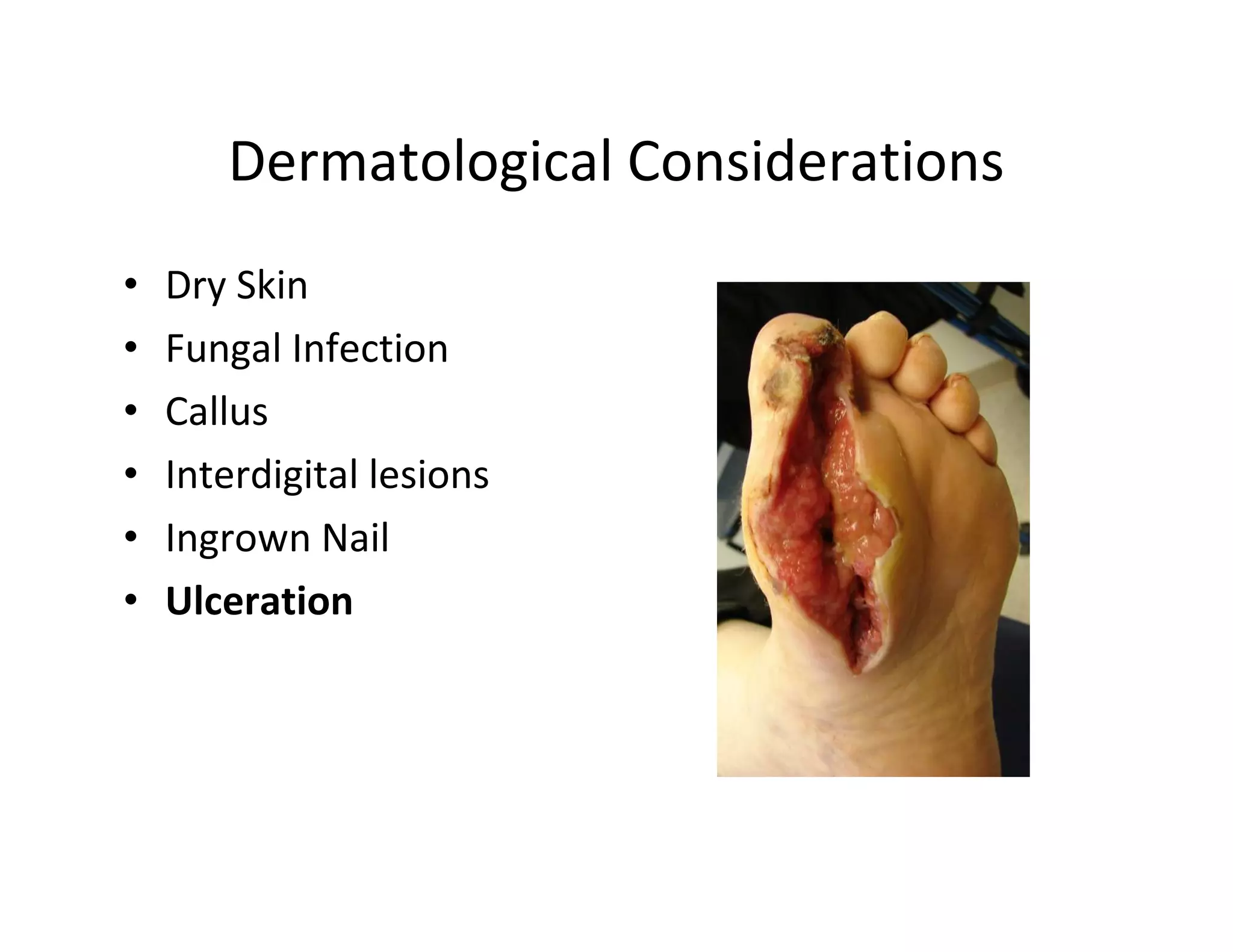
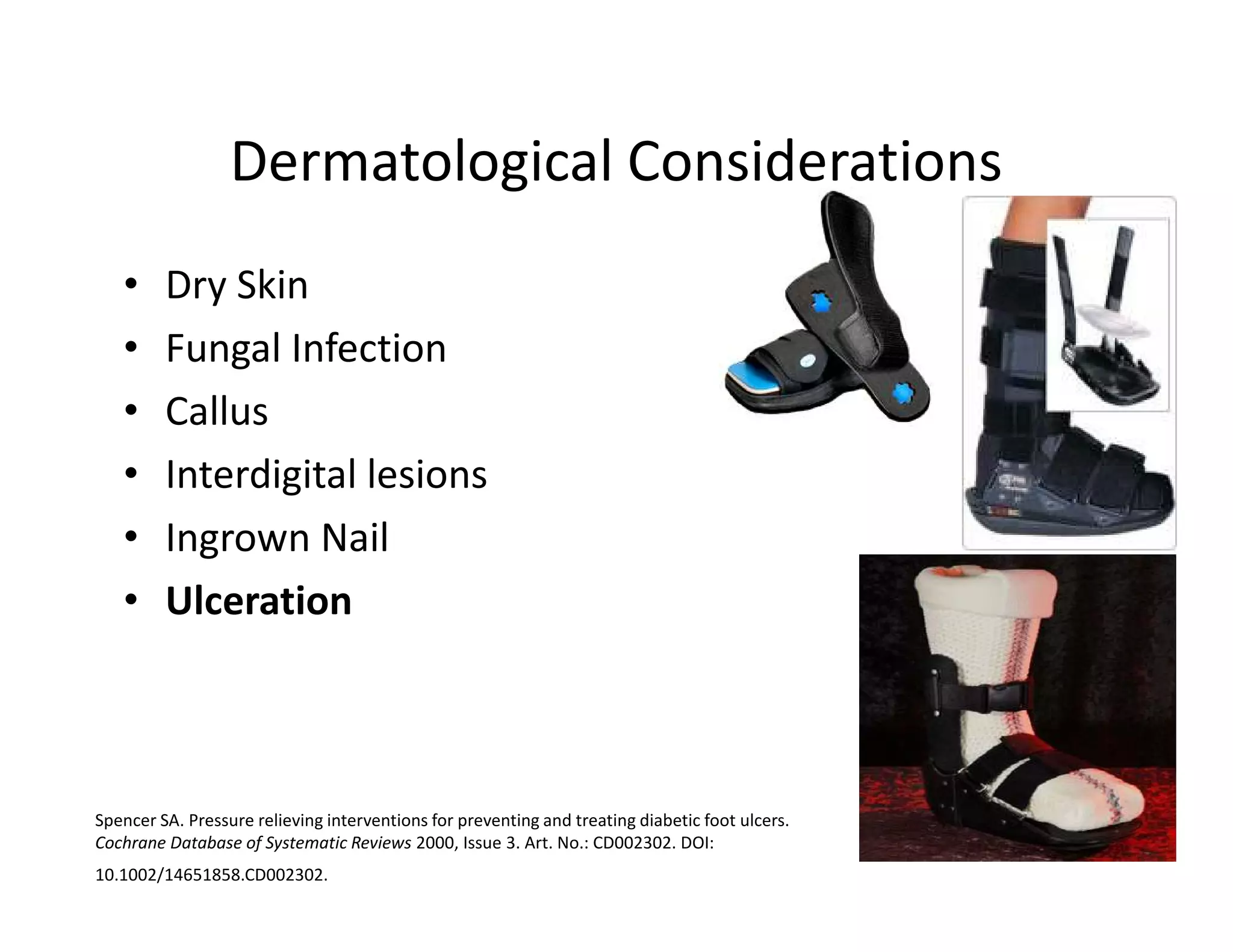
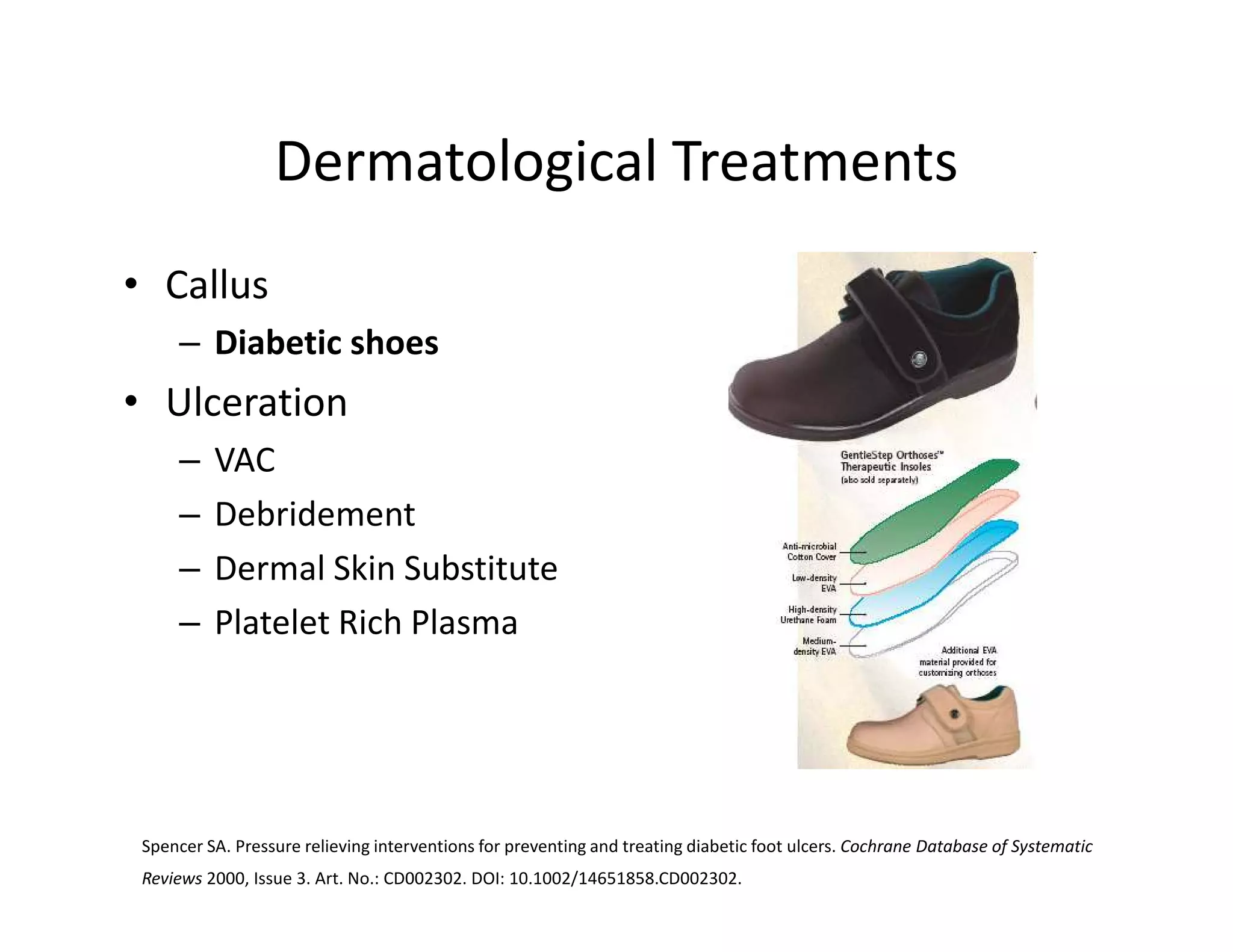
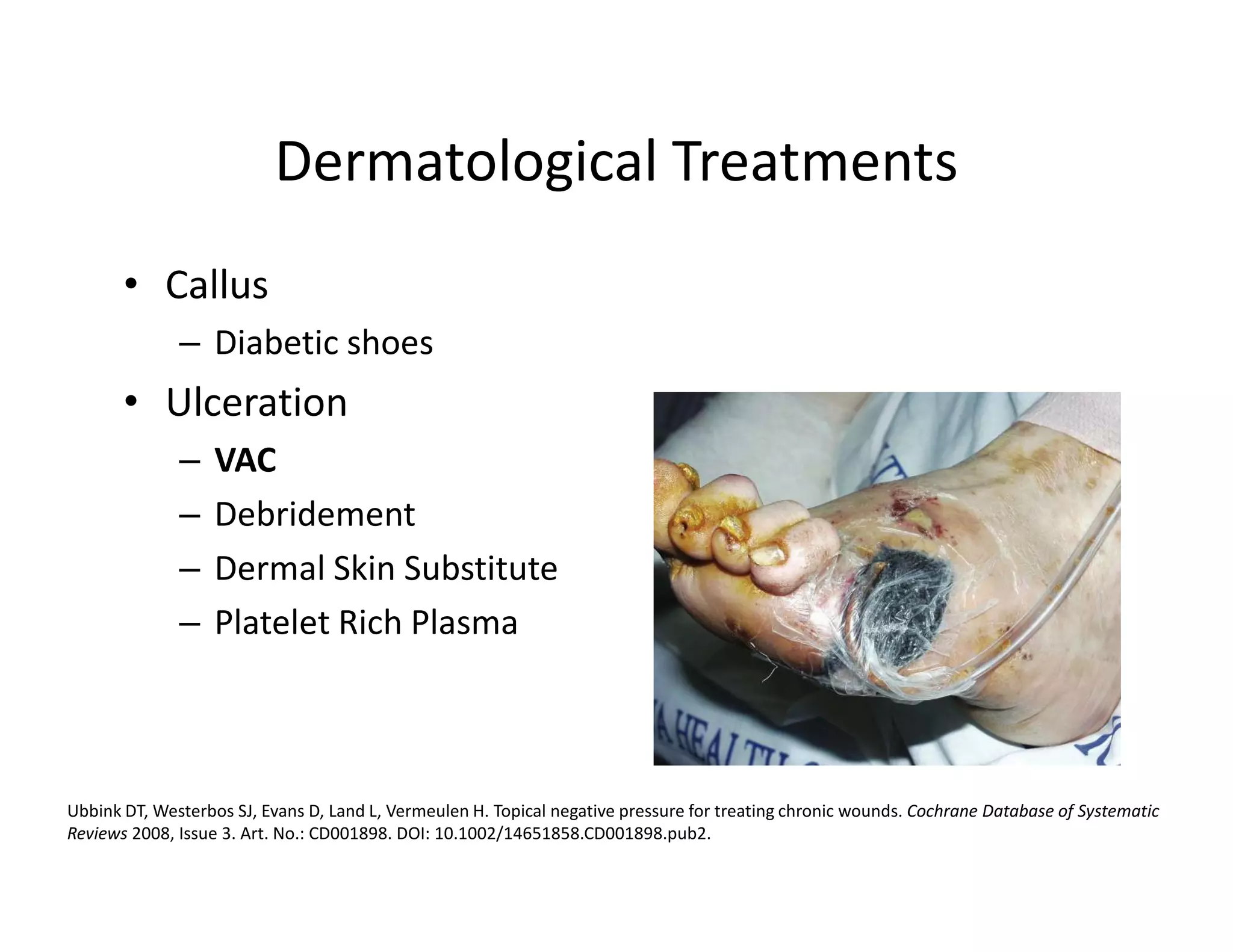
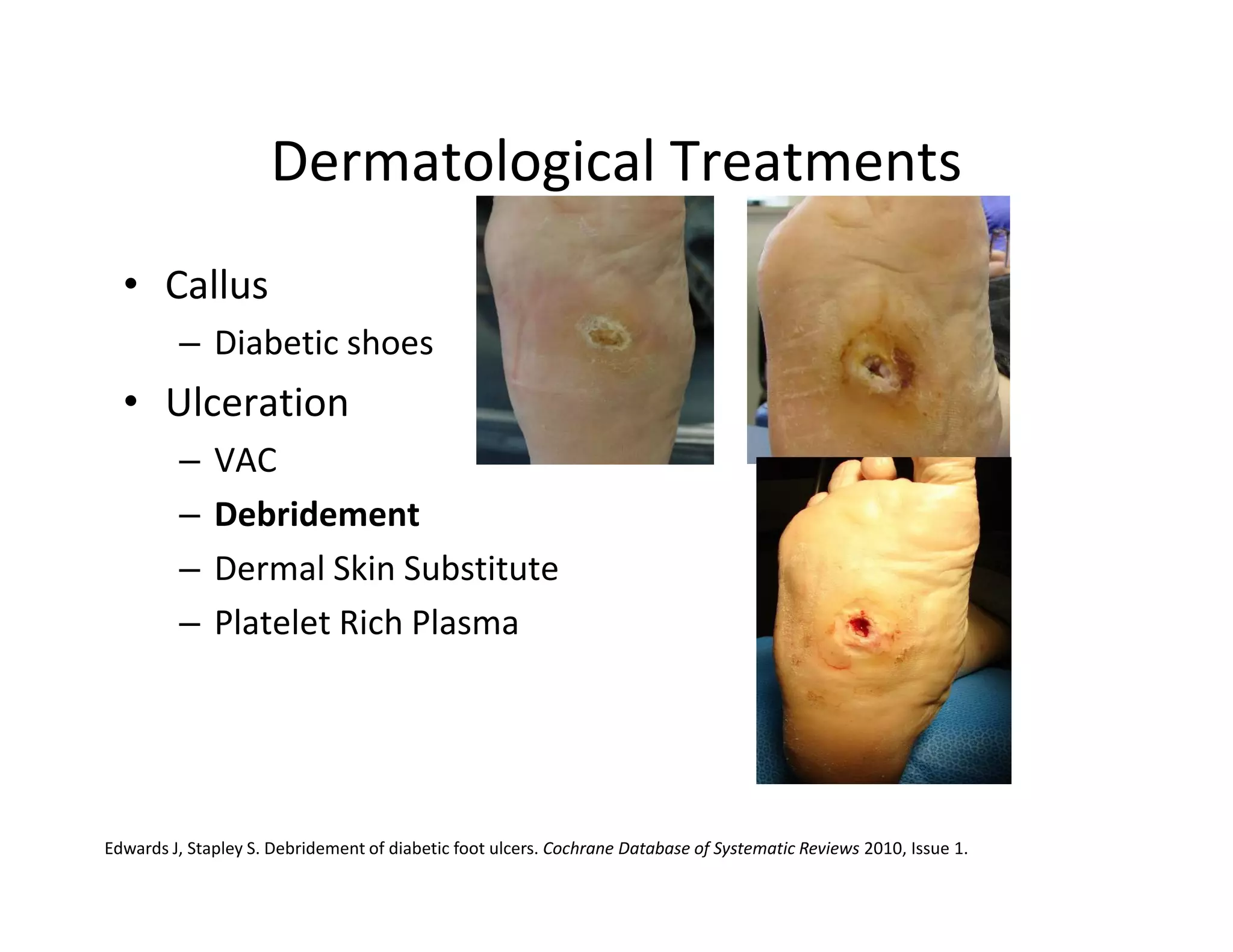
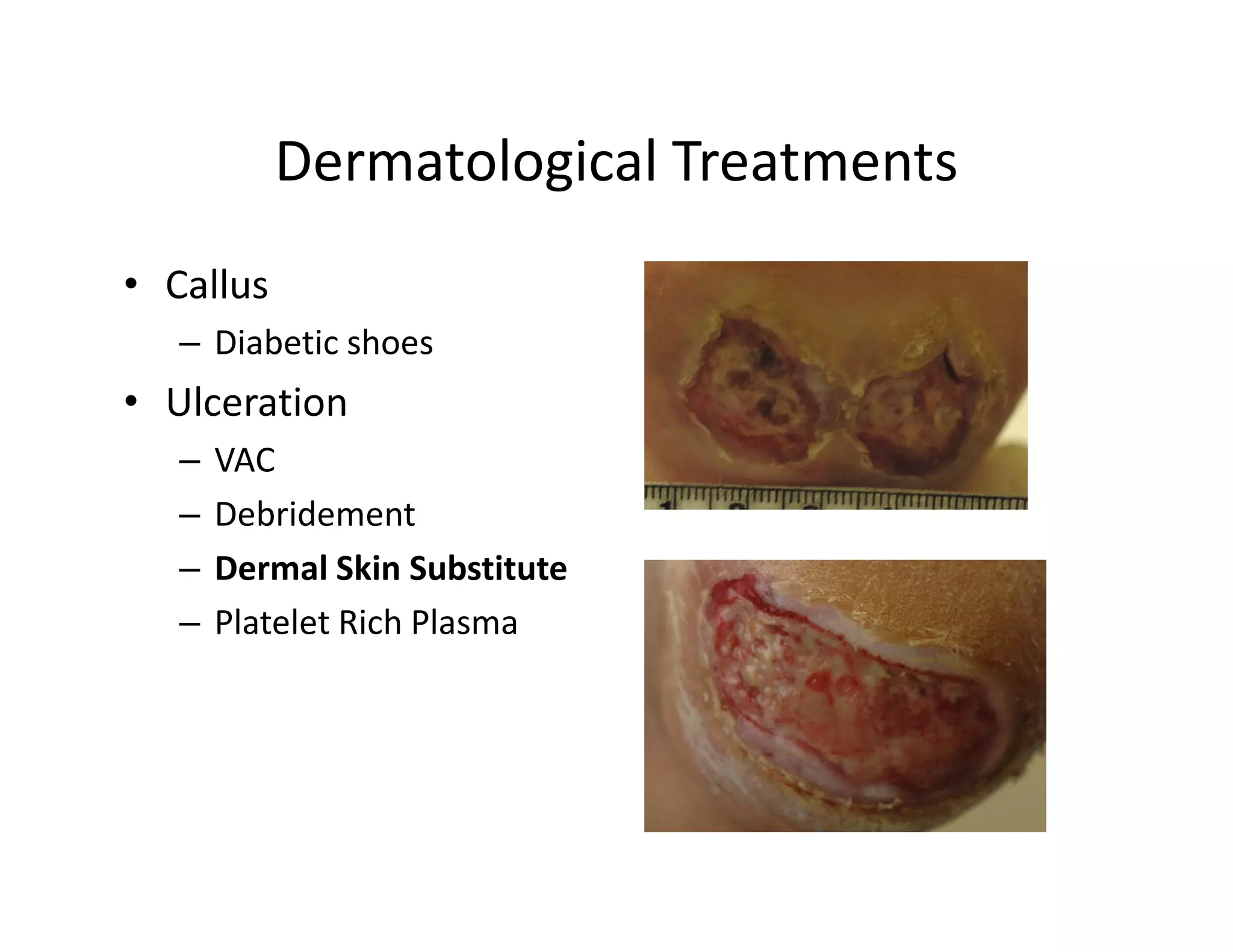
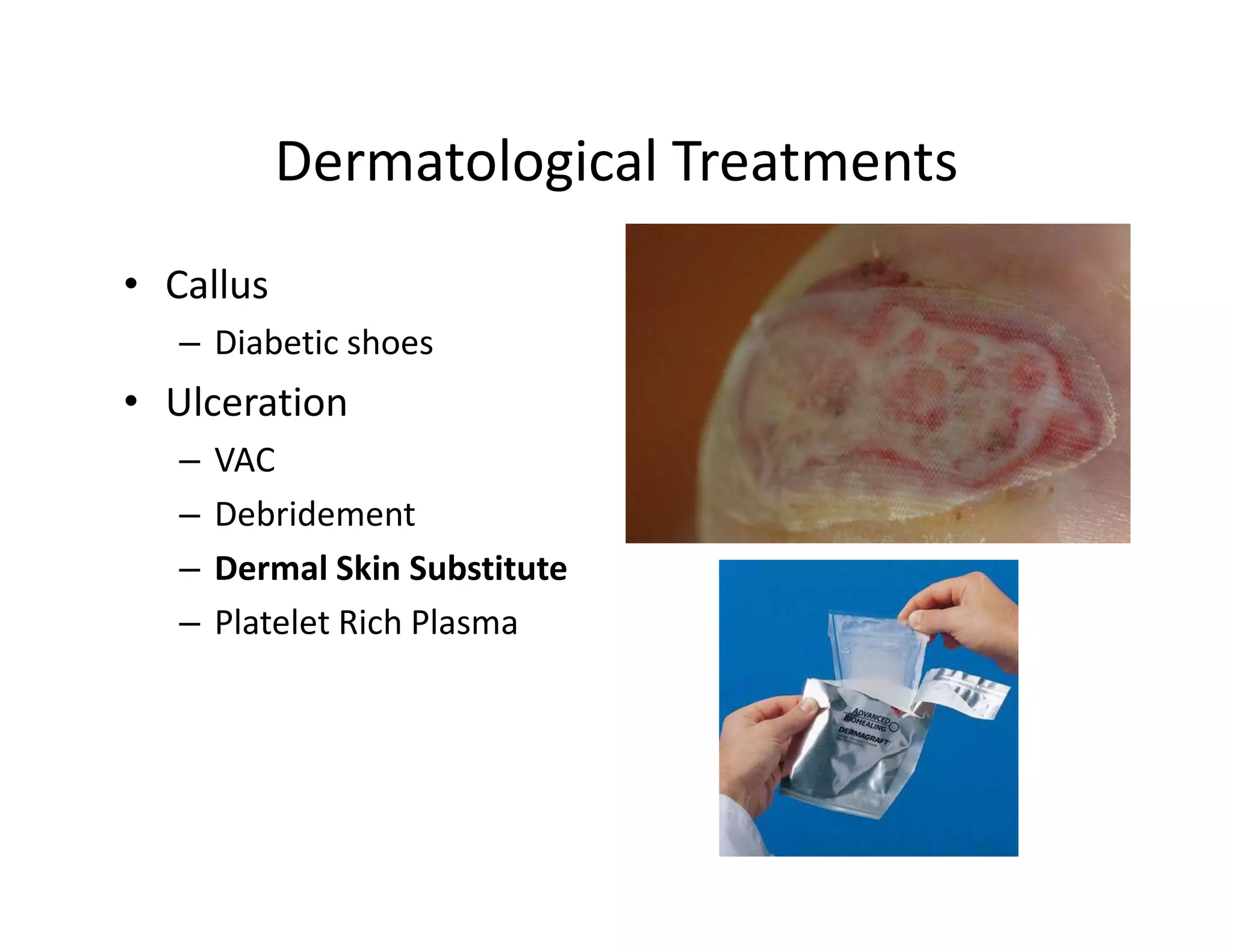
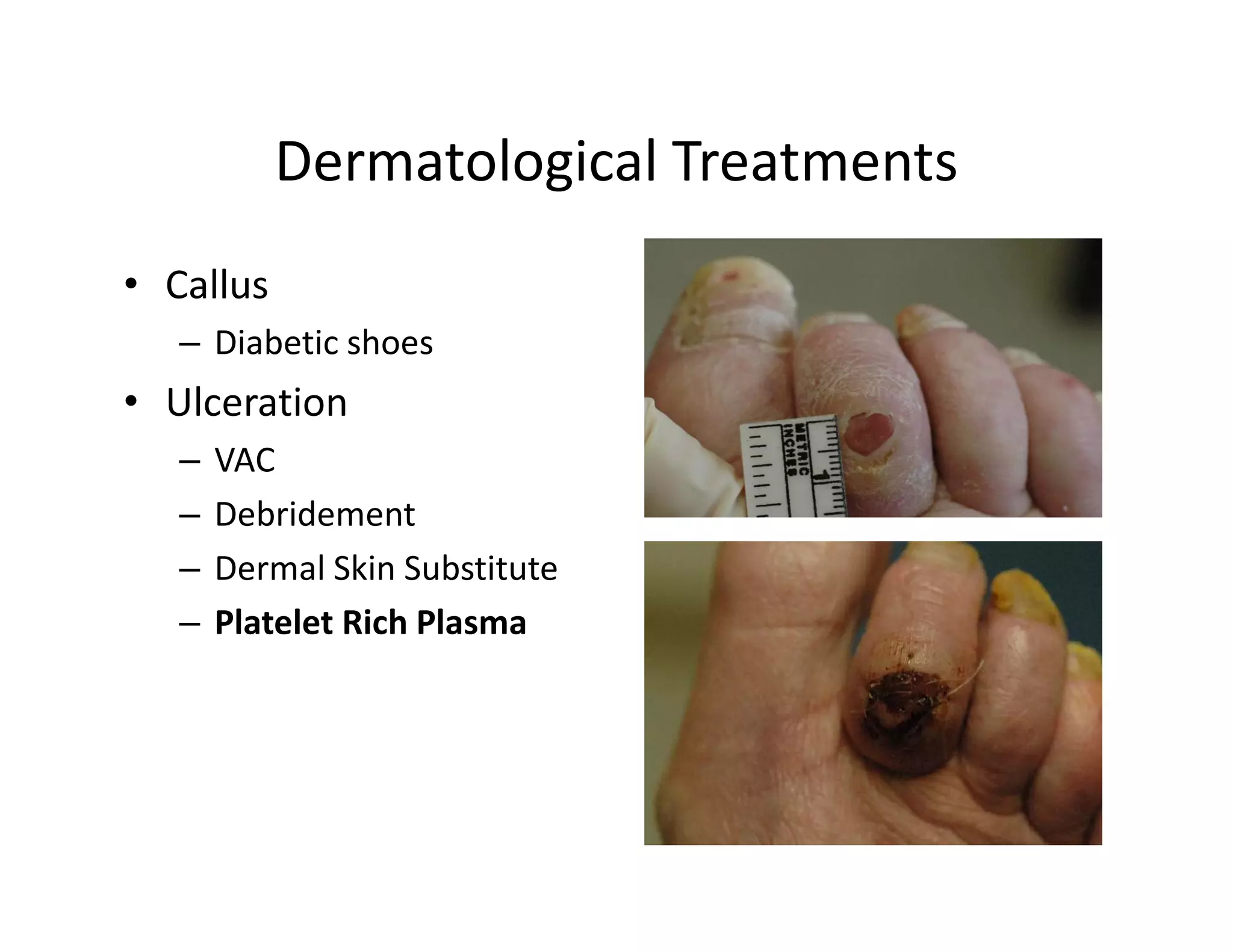
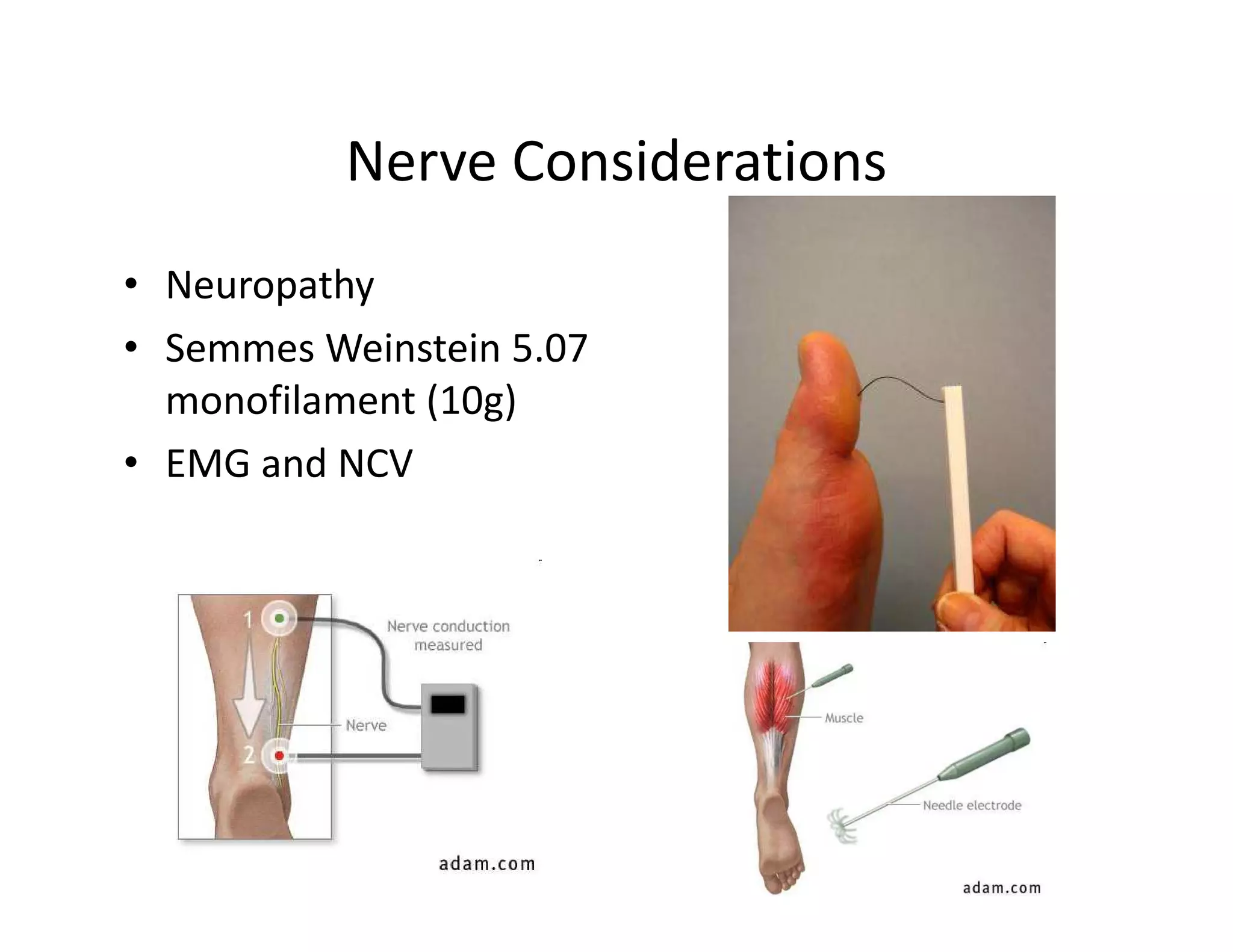
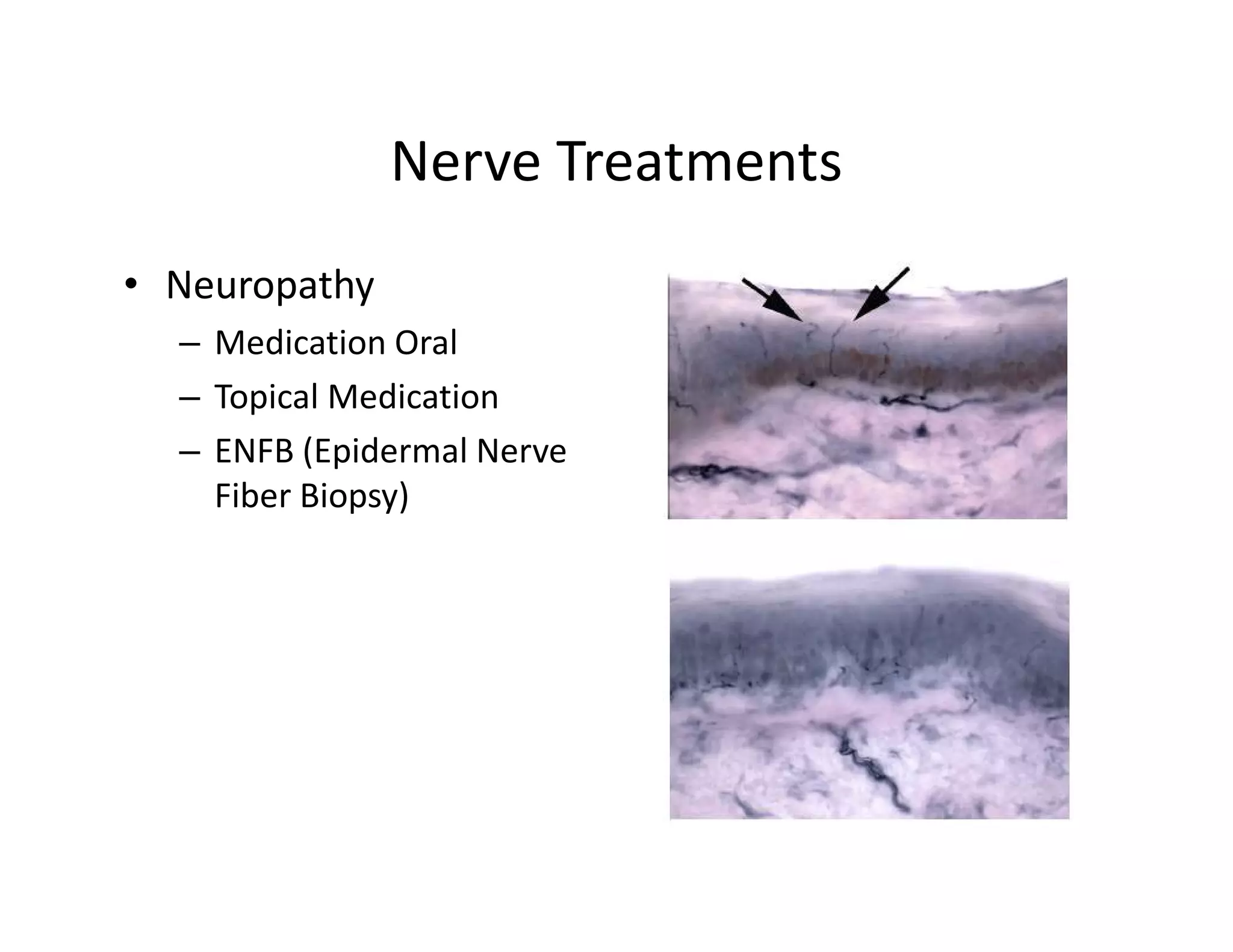
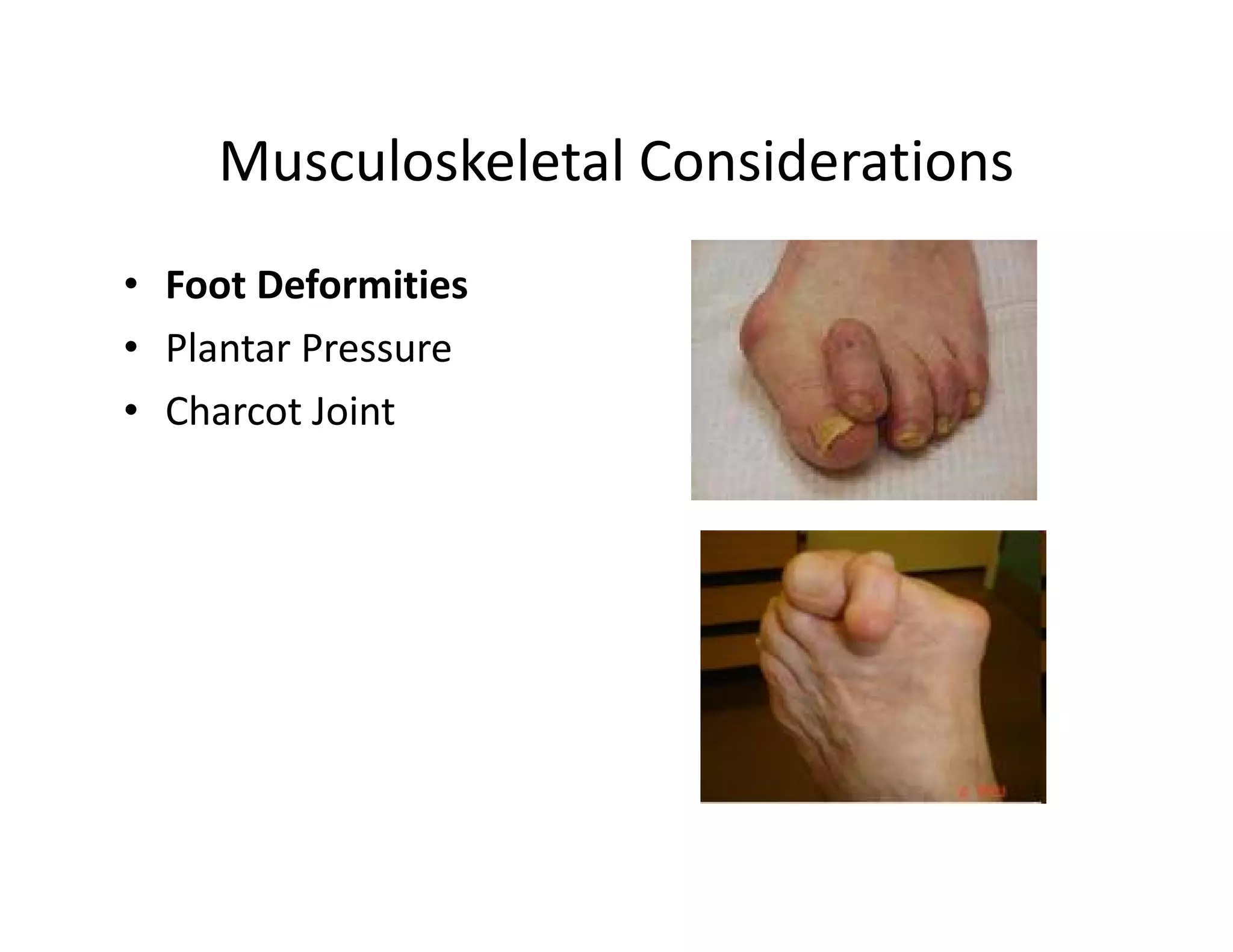
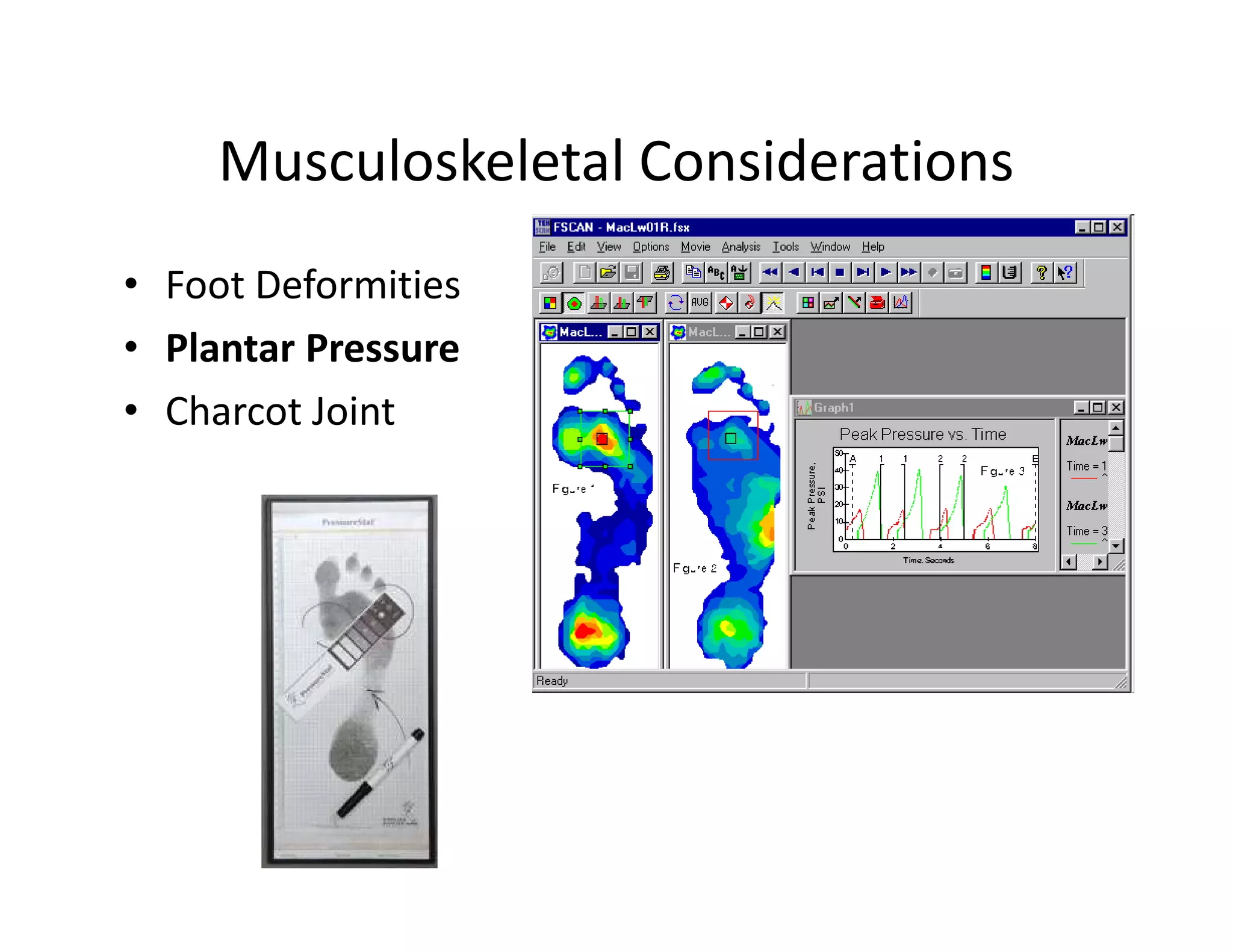
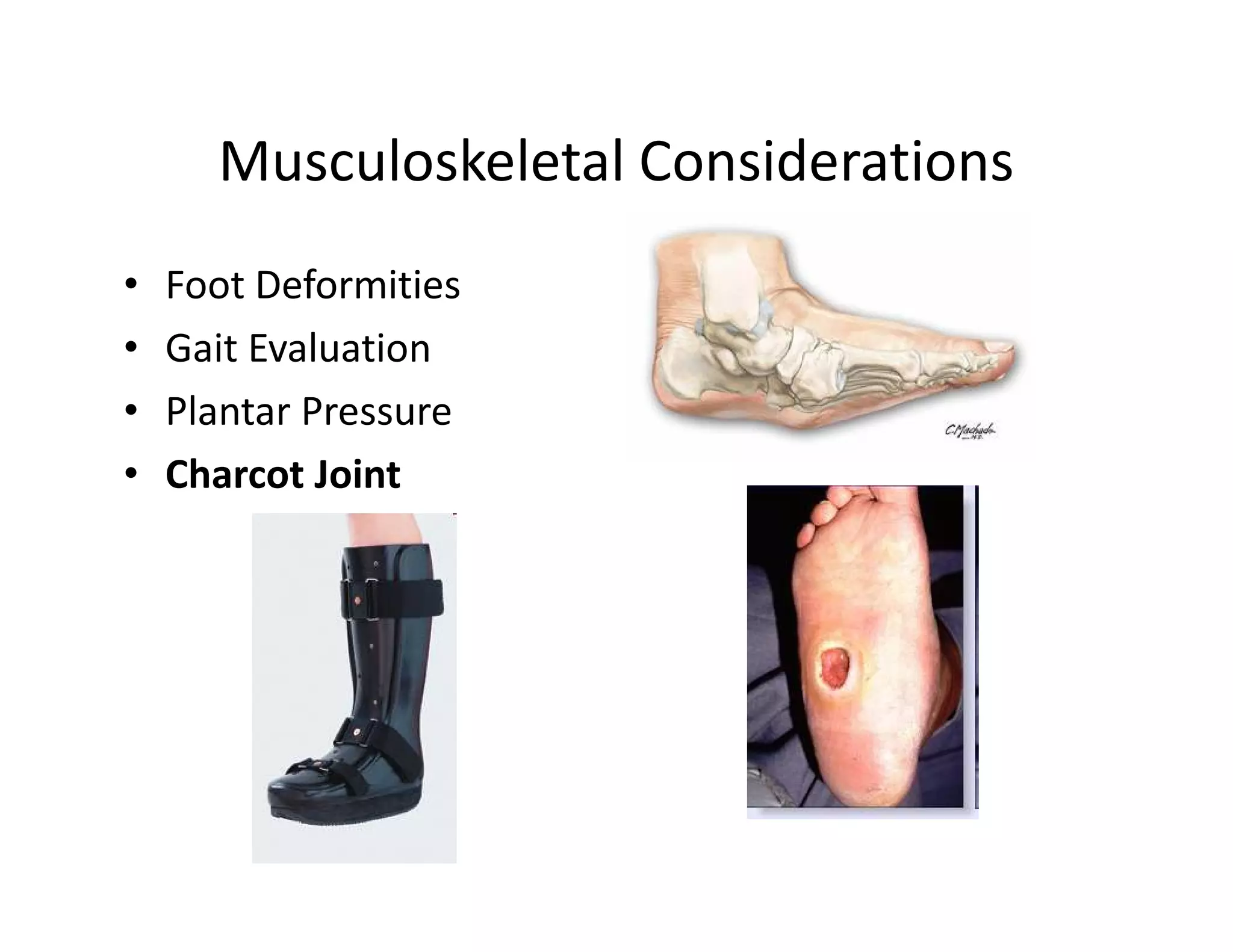
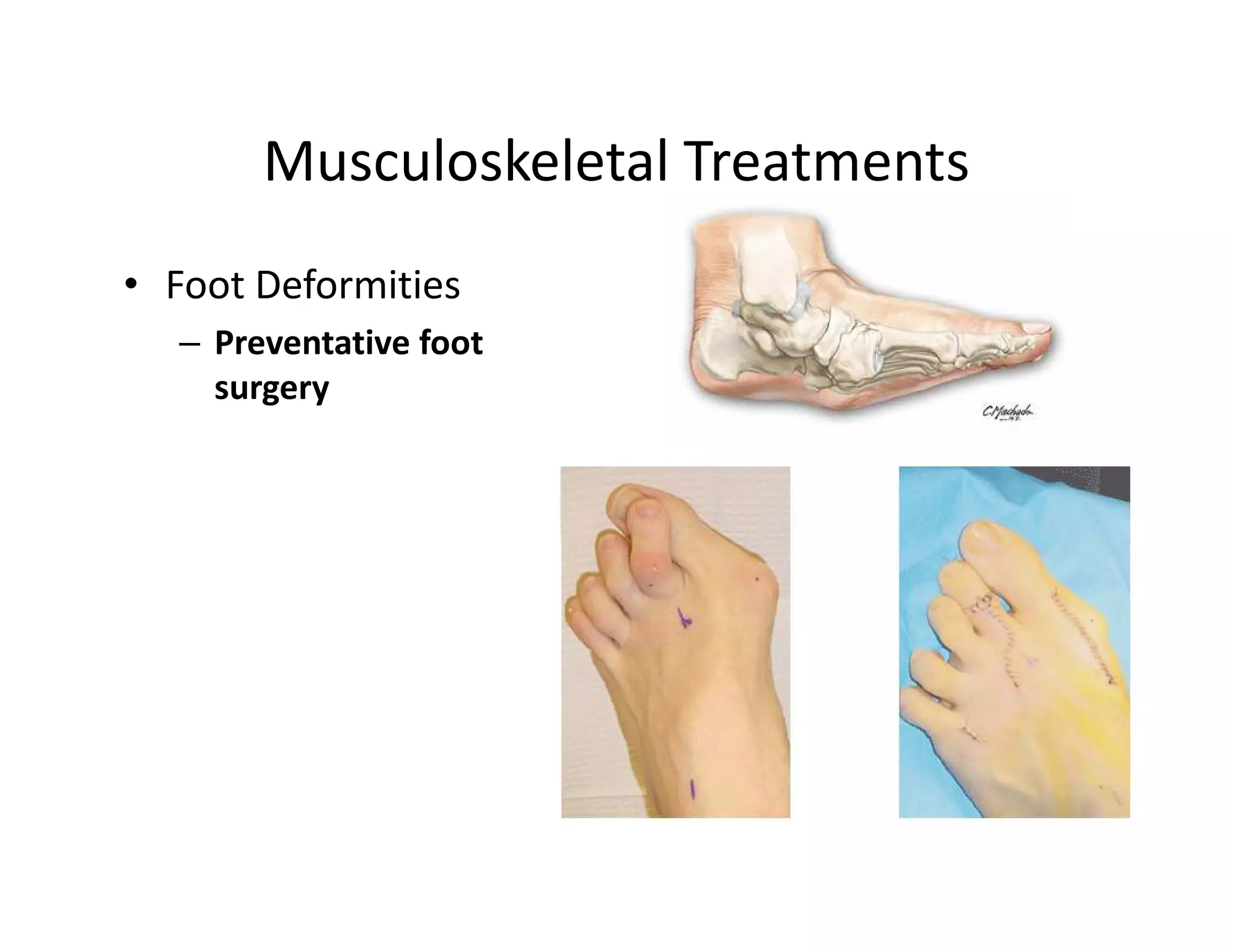
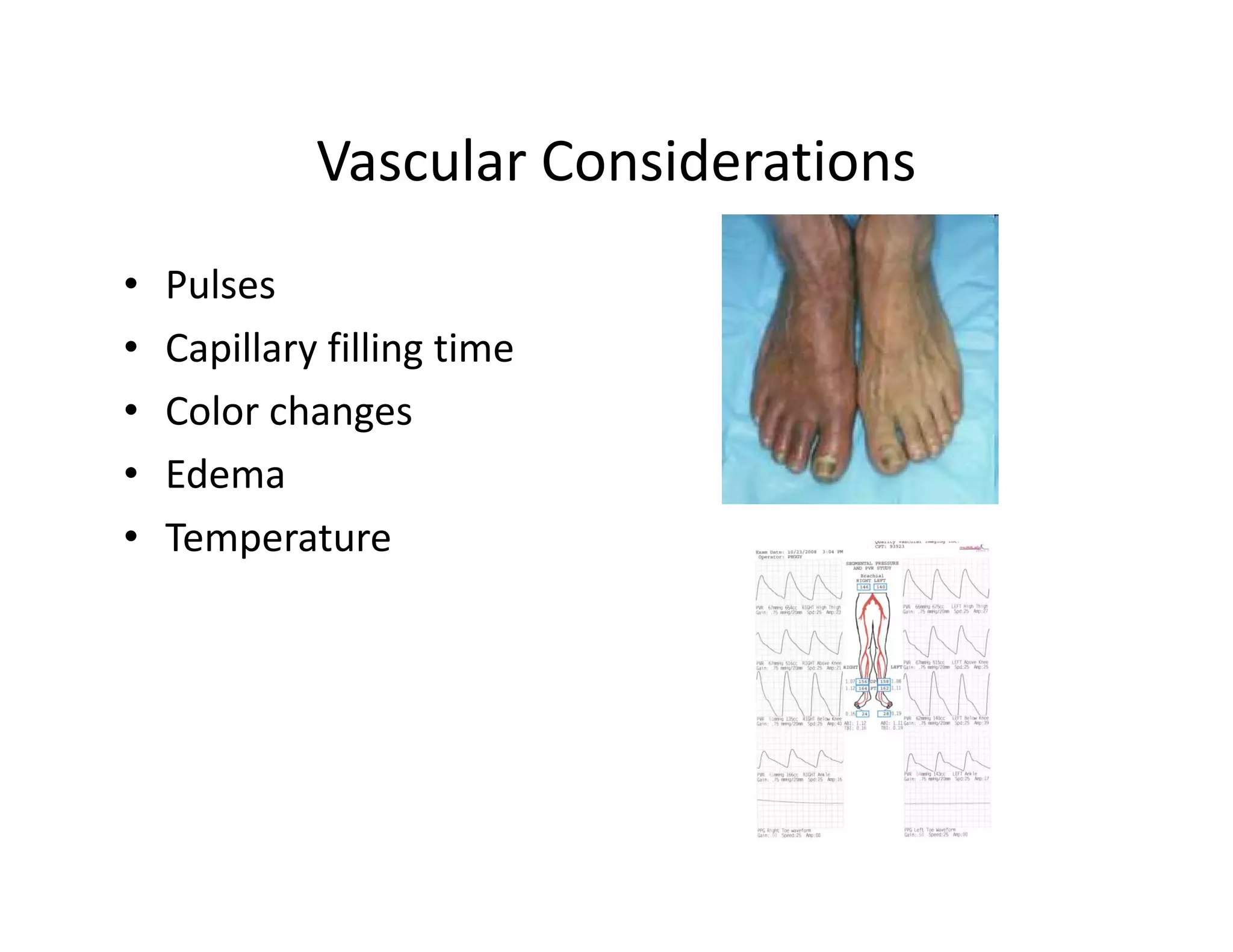
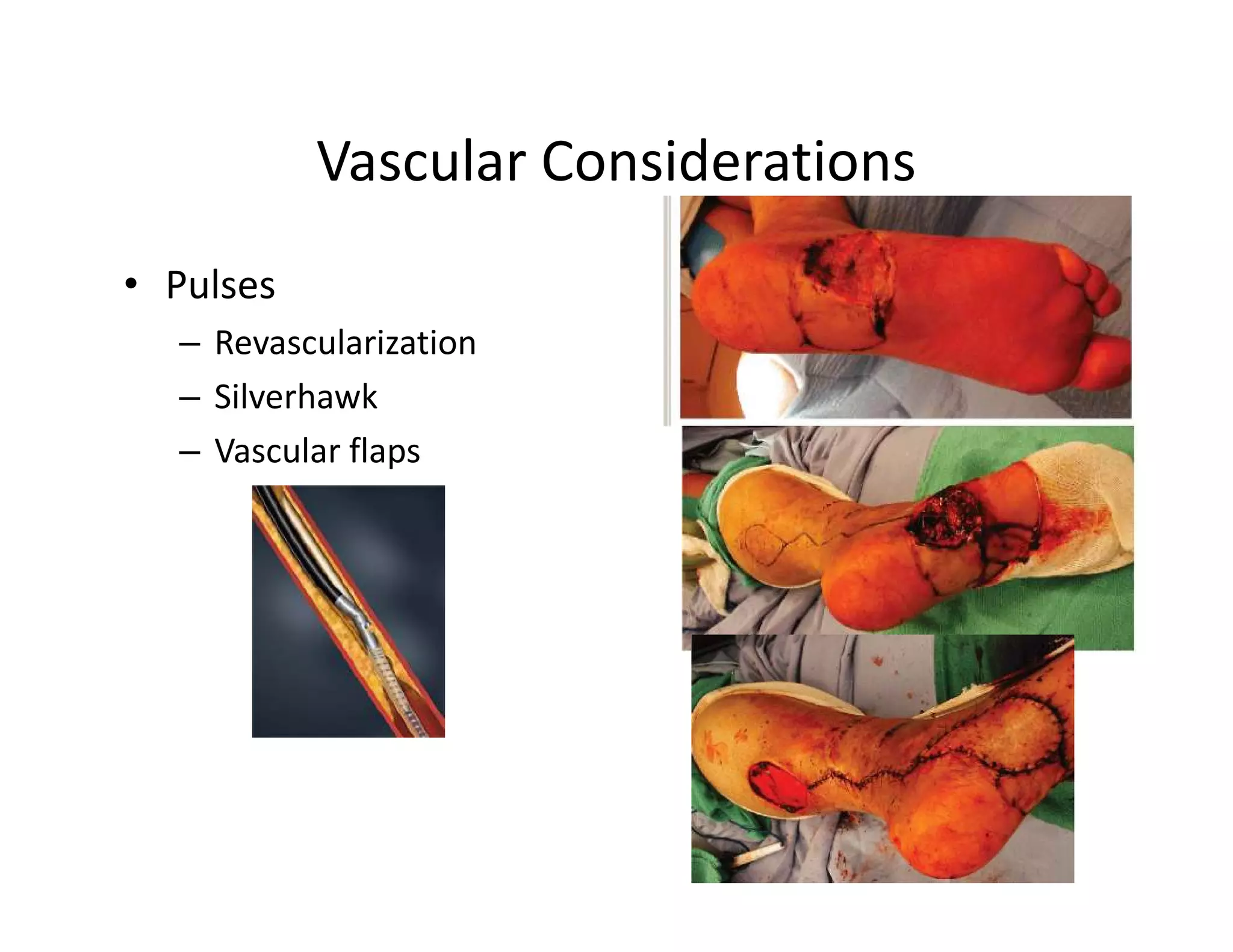
The document discusses current treatments and advanced therapies for diabetic foot complications, outlining risk factors like neuropathy and vascular issues that can lead to foot ulcers, and describing approaches to managing dermatological issues, nerve damage, musculoskeletal problems, vascular challenges, and proper shoegear through treatments like VAC therapy, debridement, dermal substitutes, revascularization, and diabetic footwear modifications.