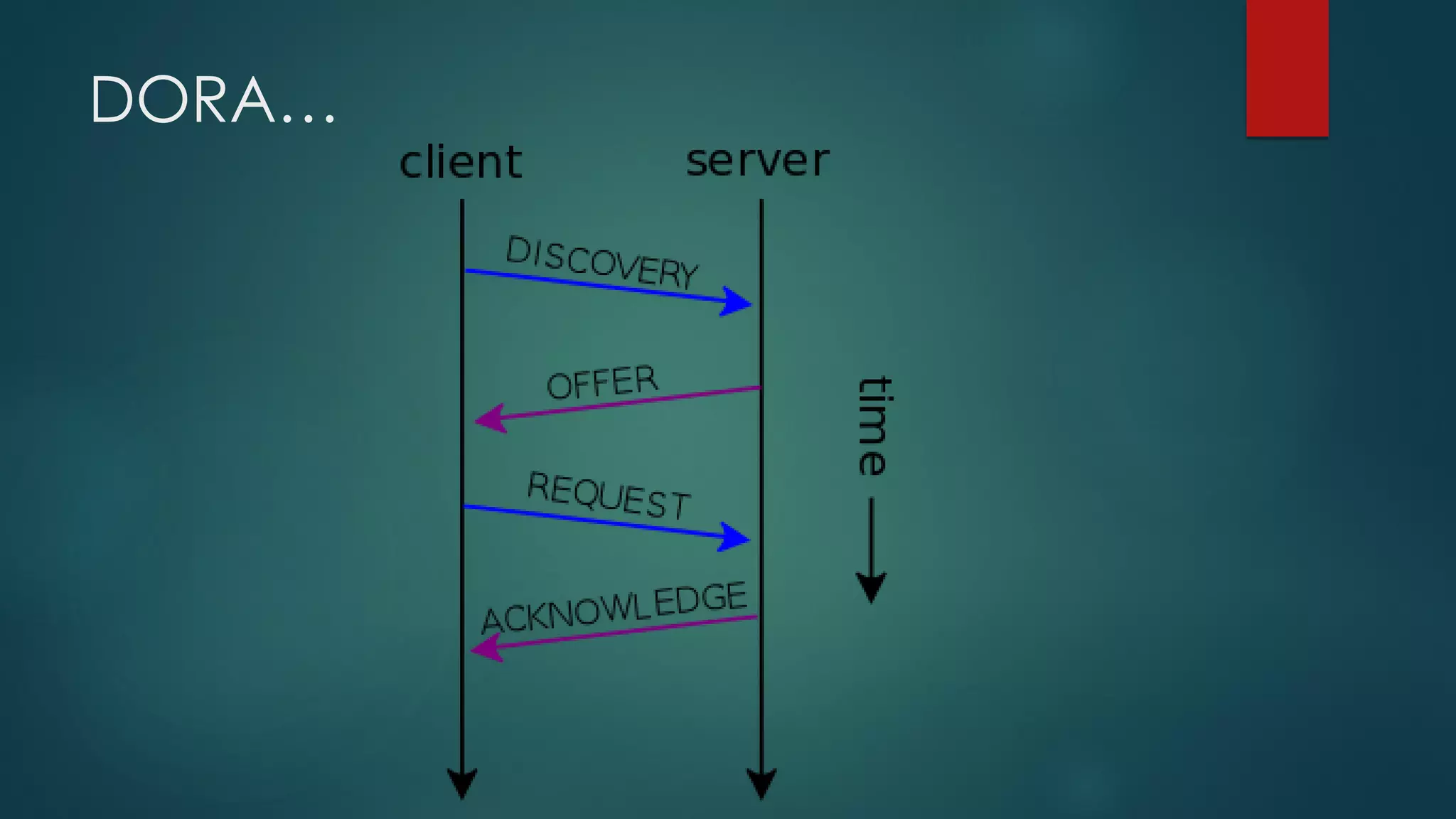
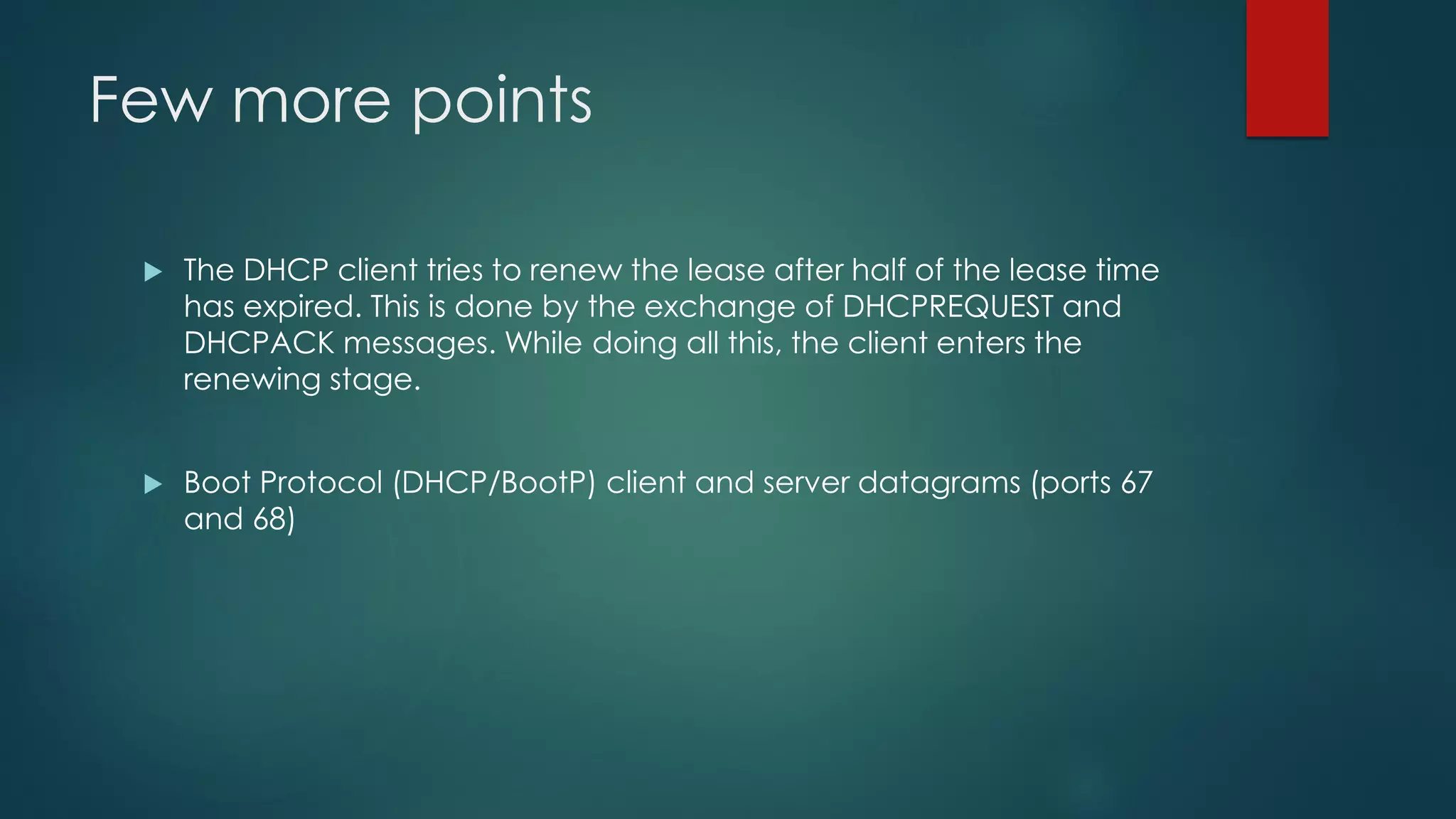
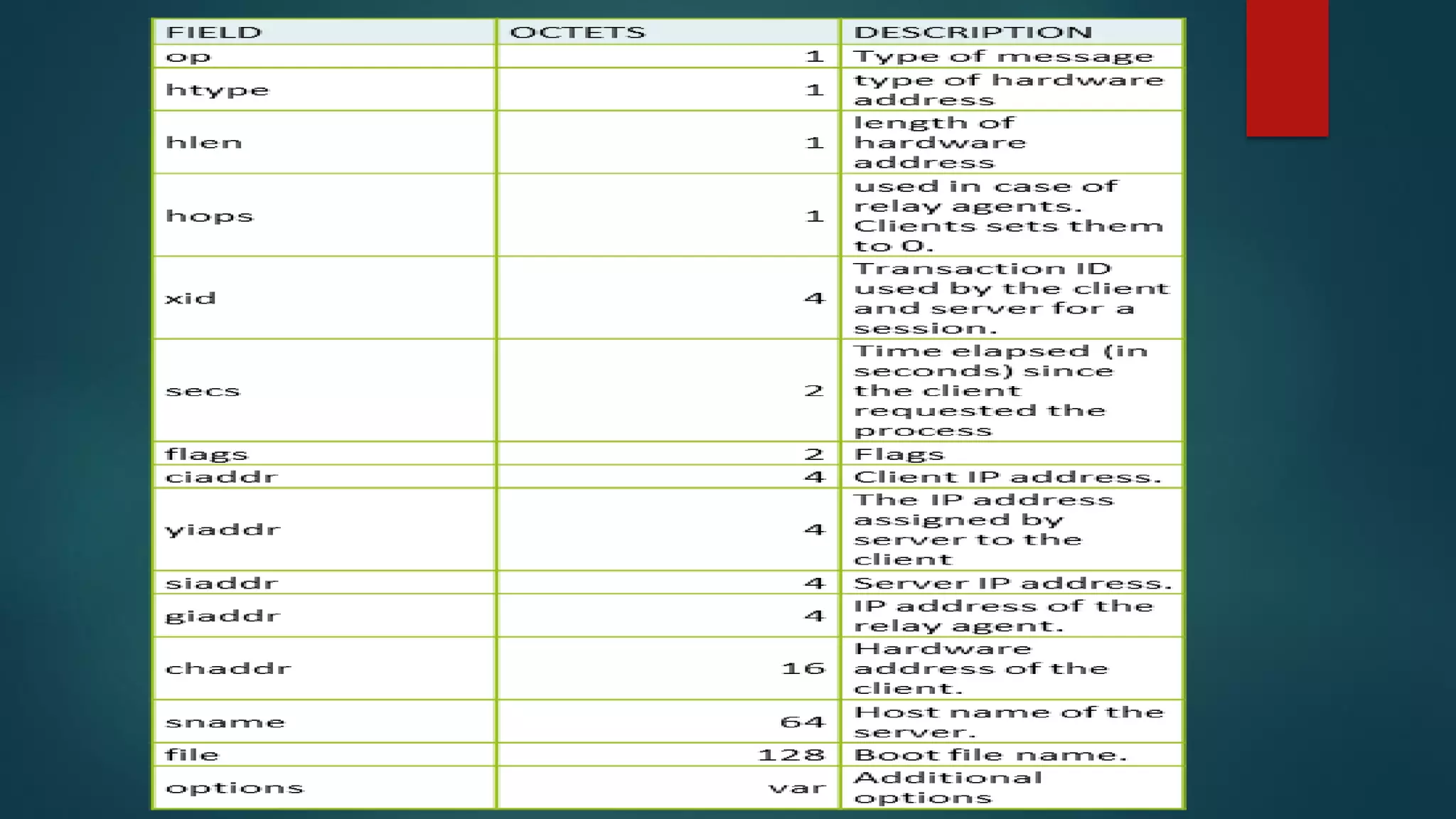
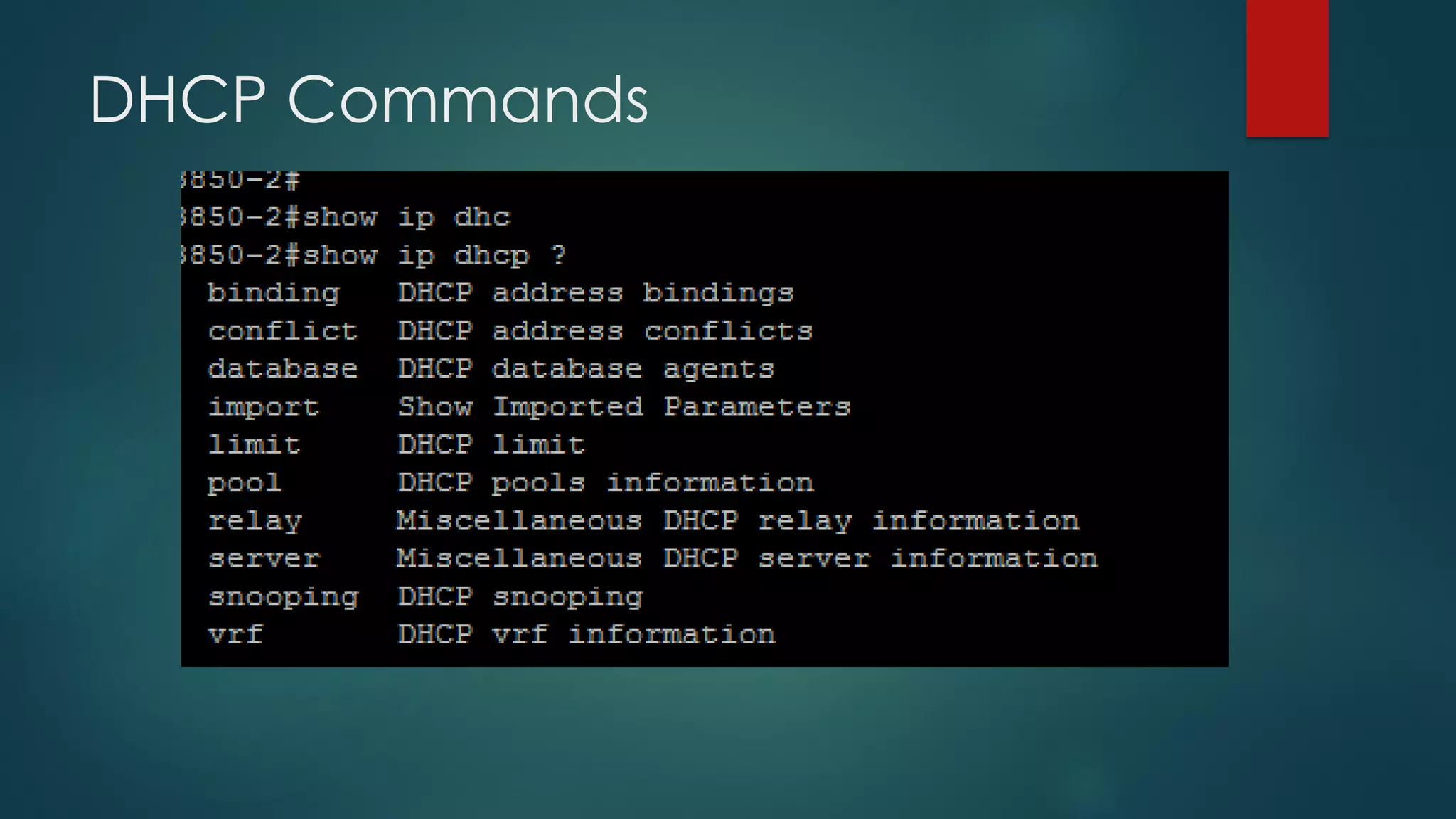
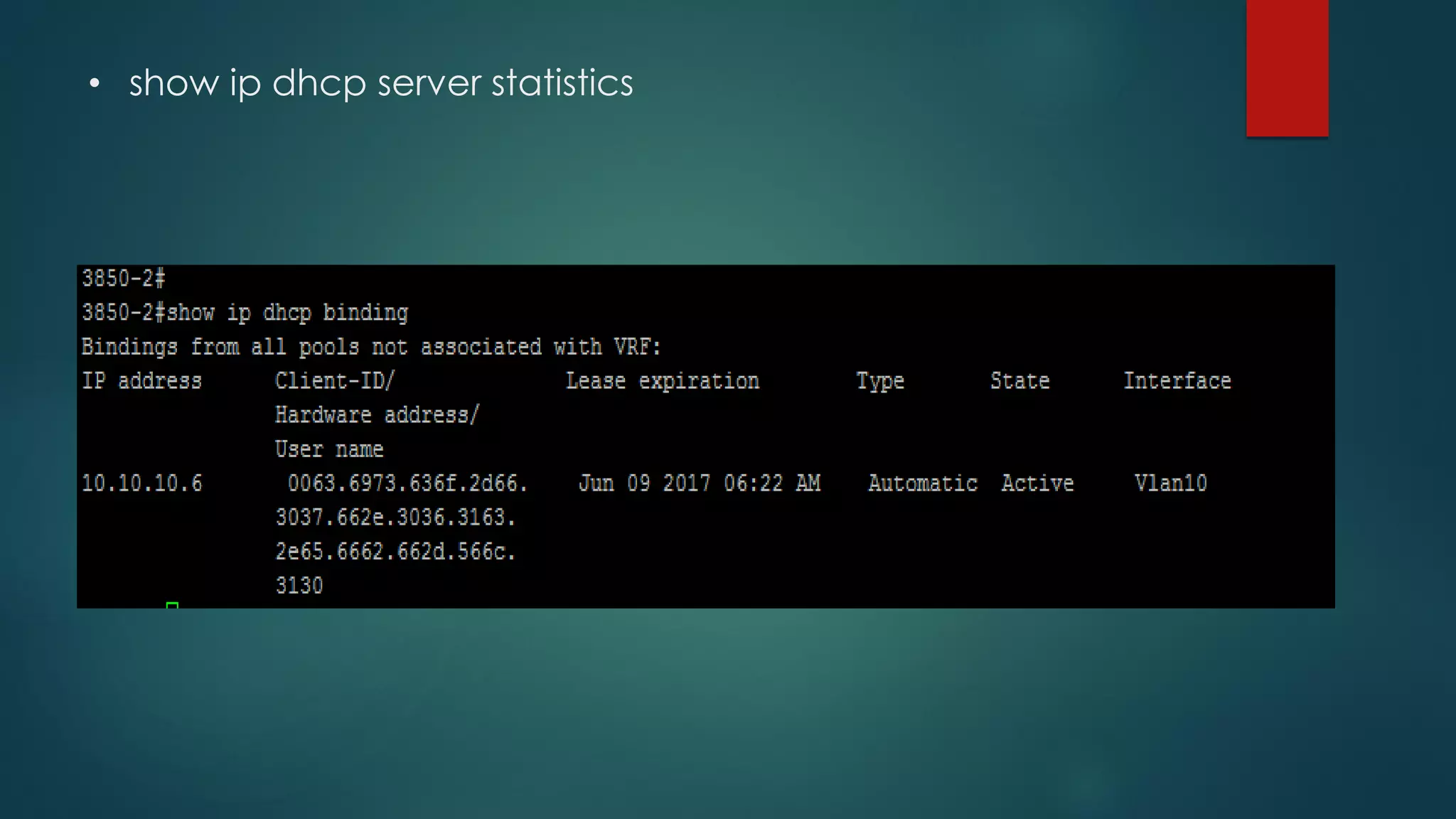
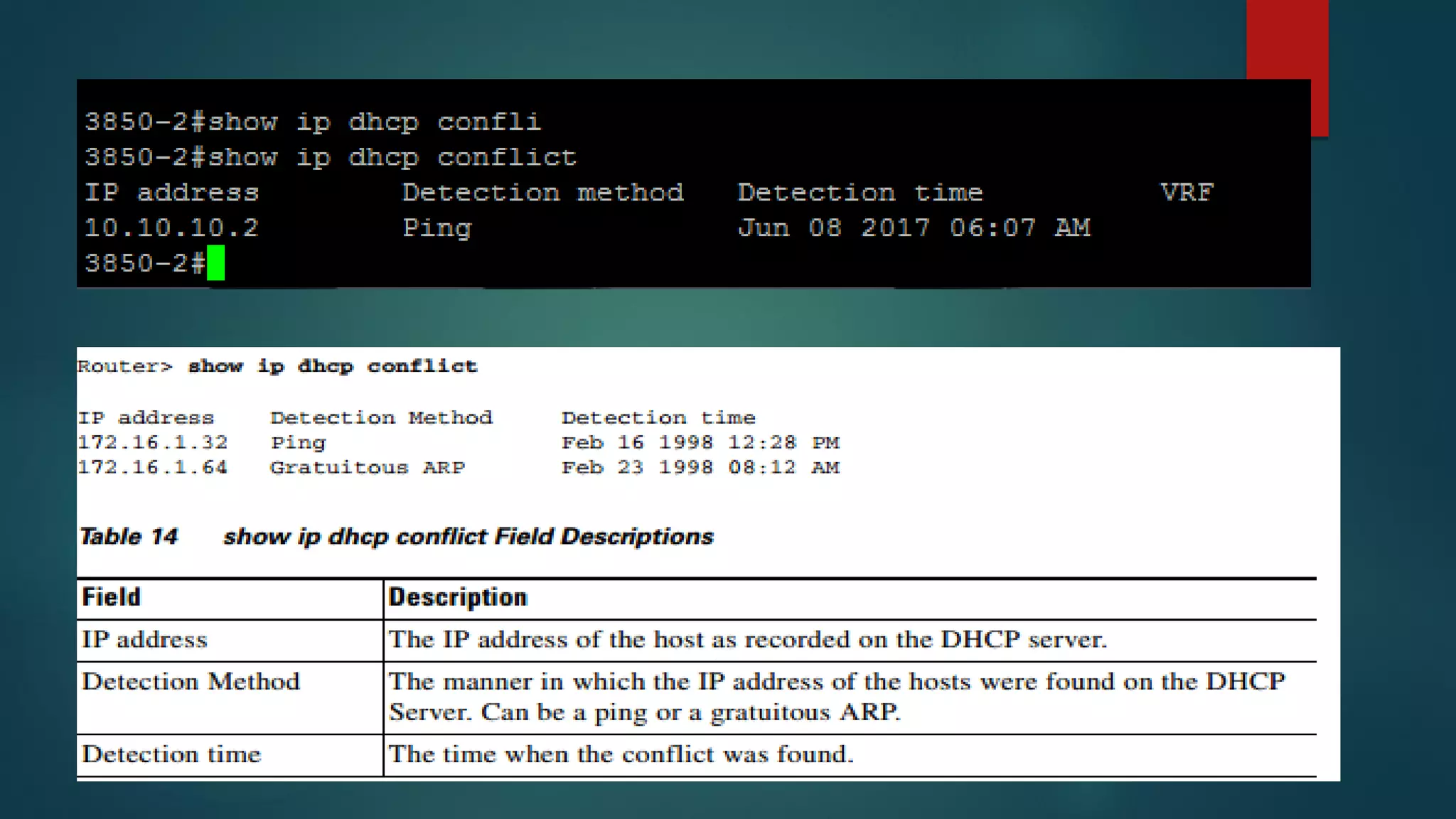
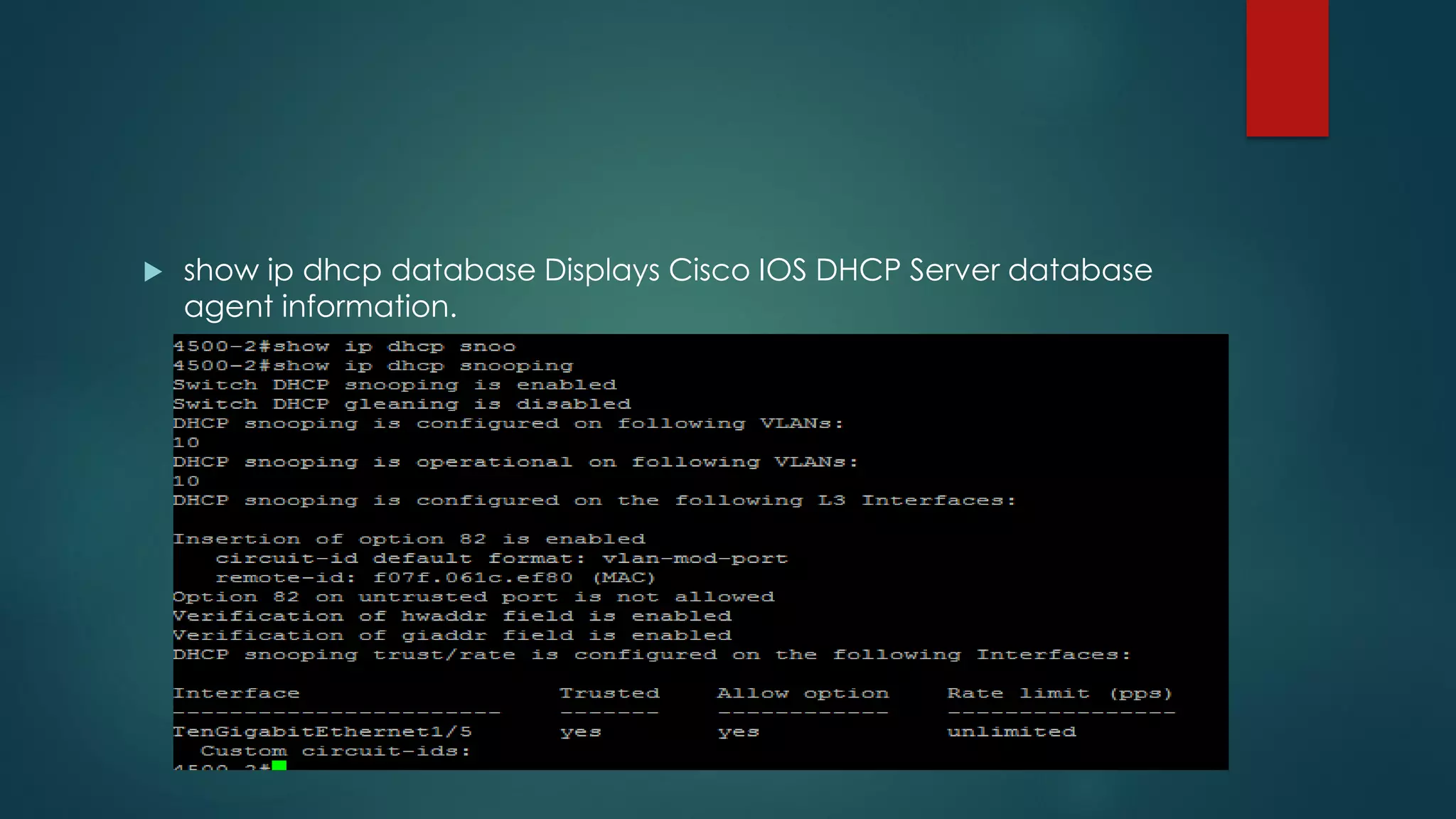
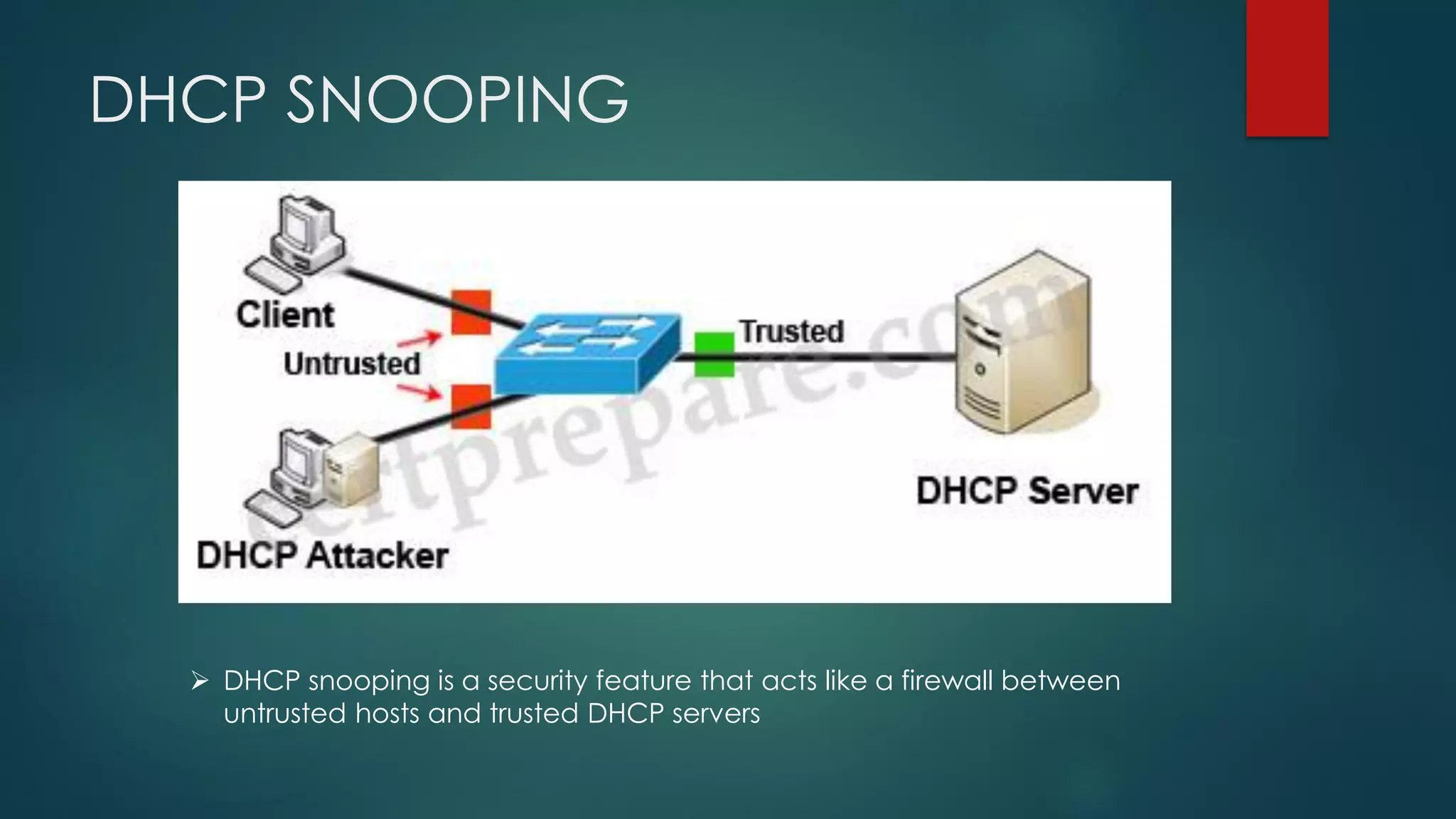
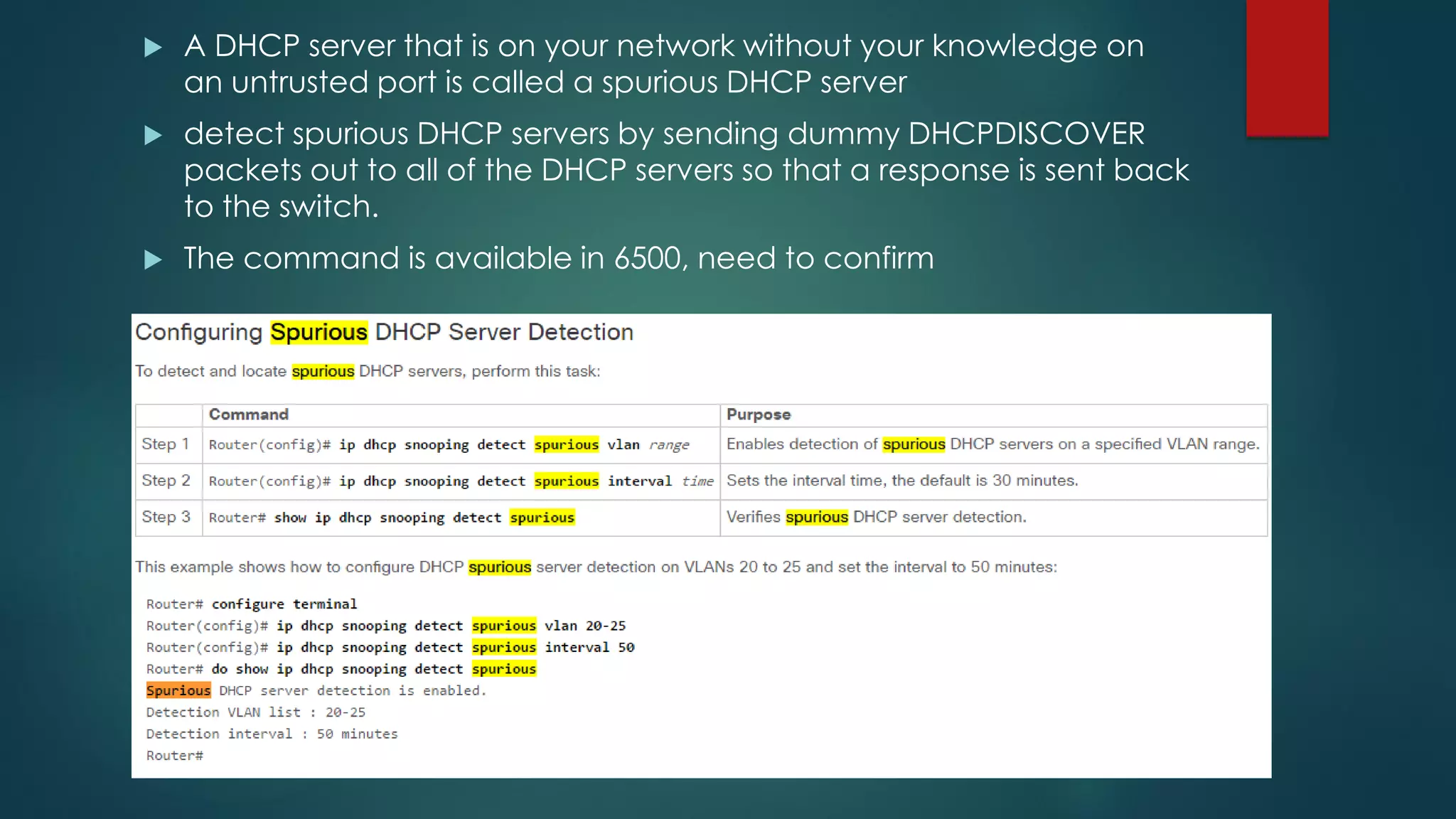
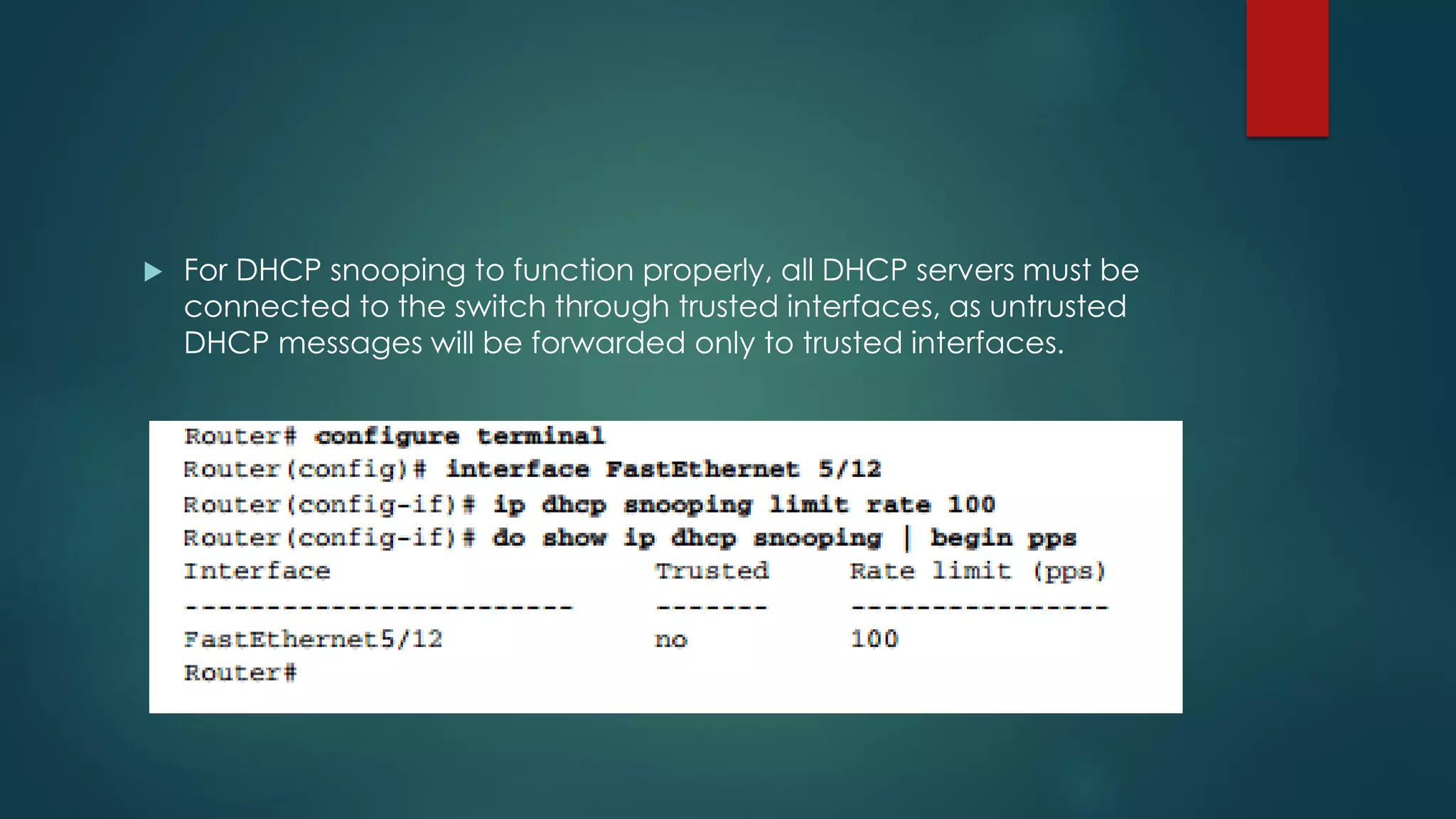
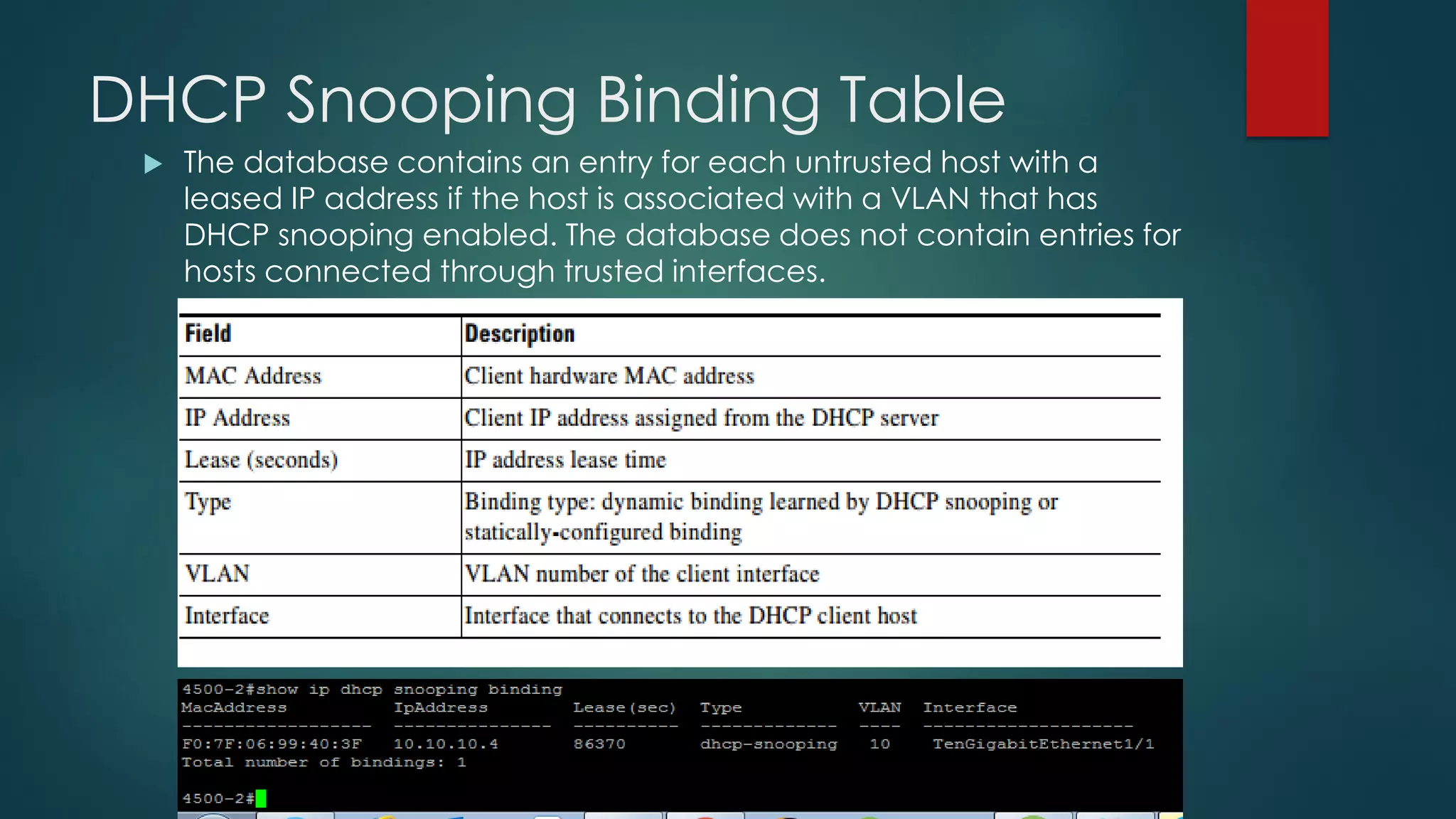
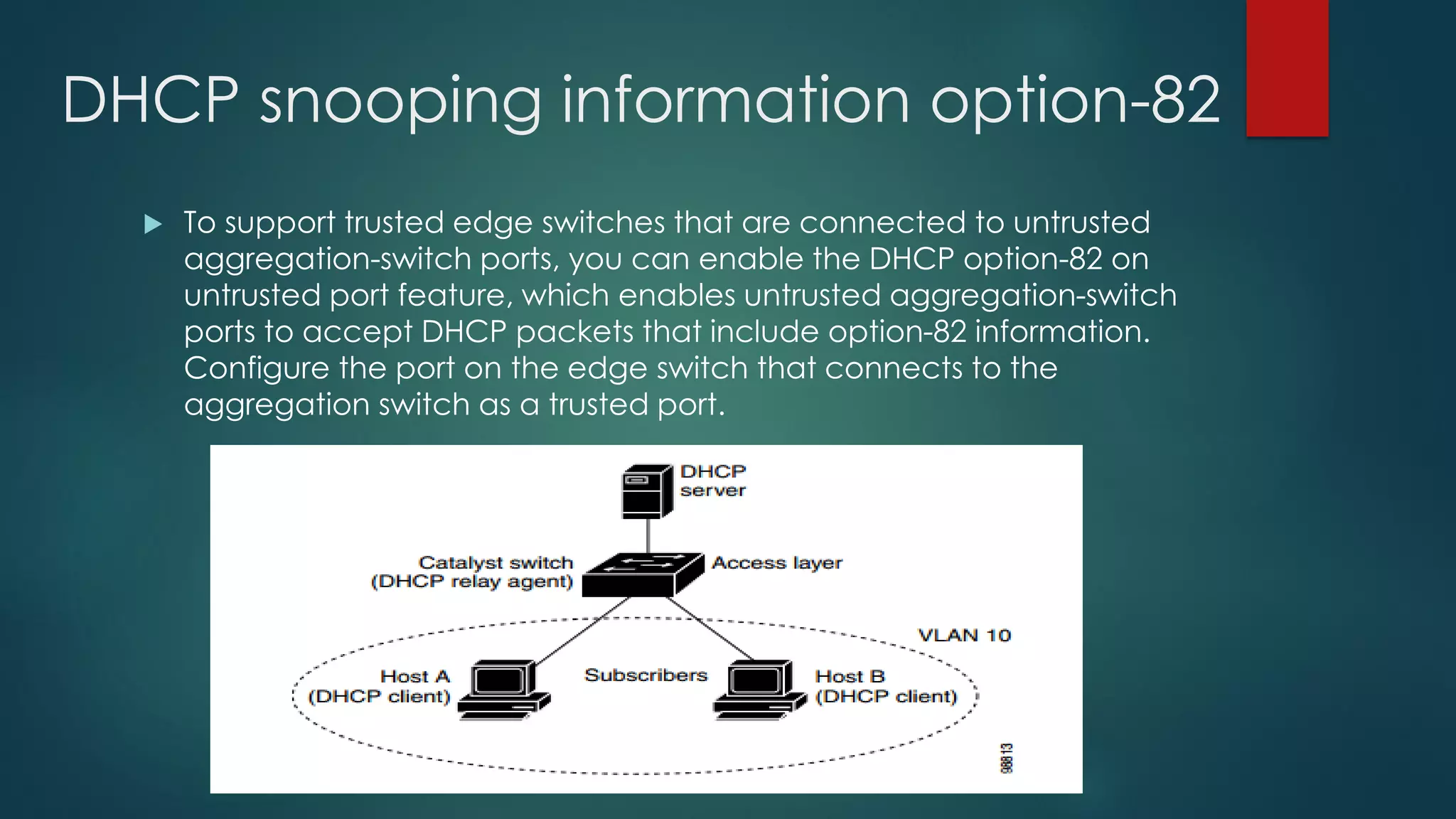
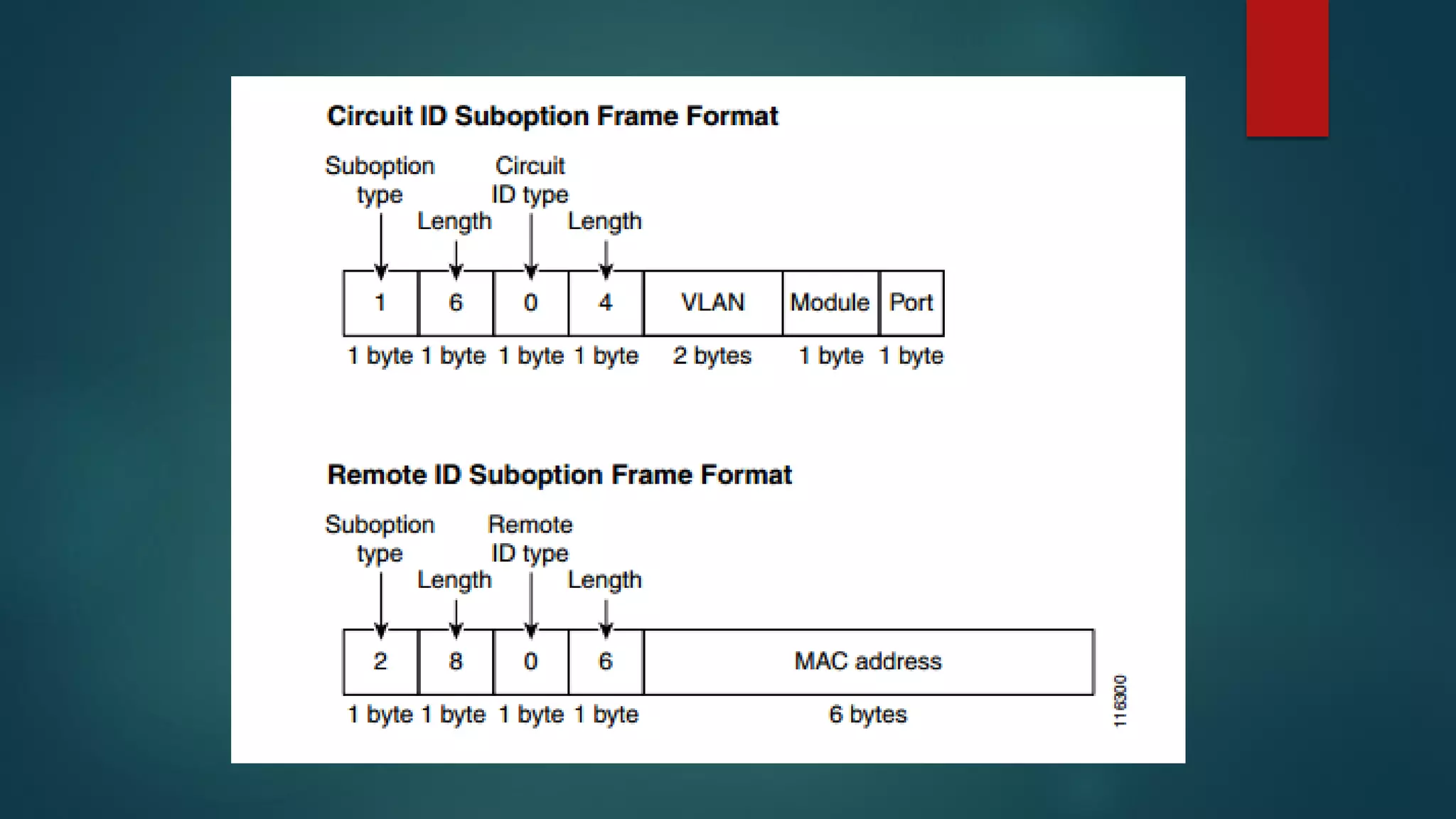
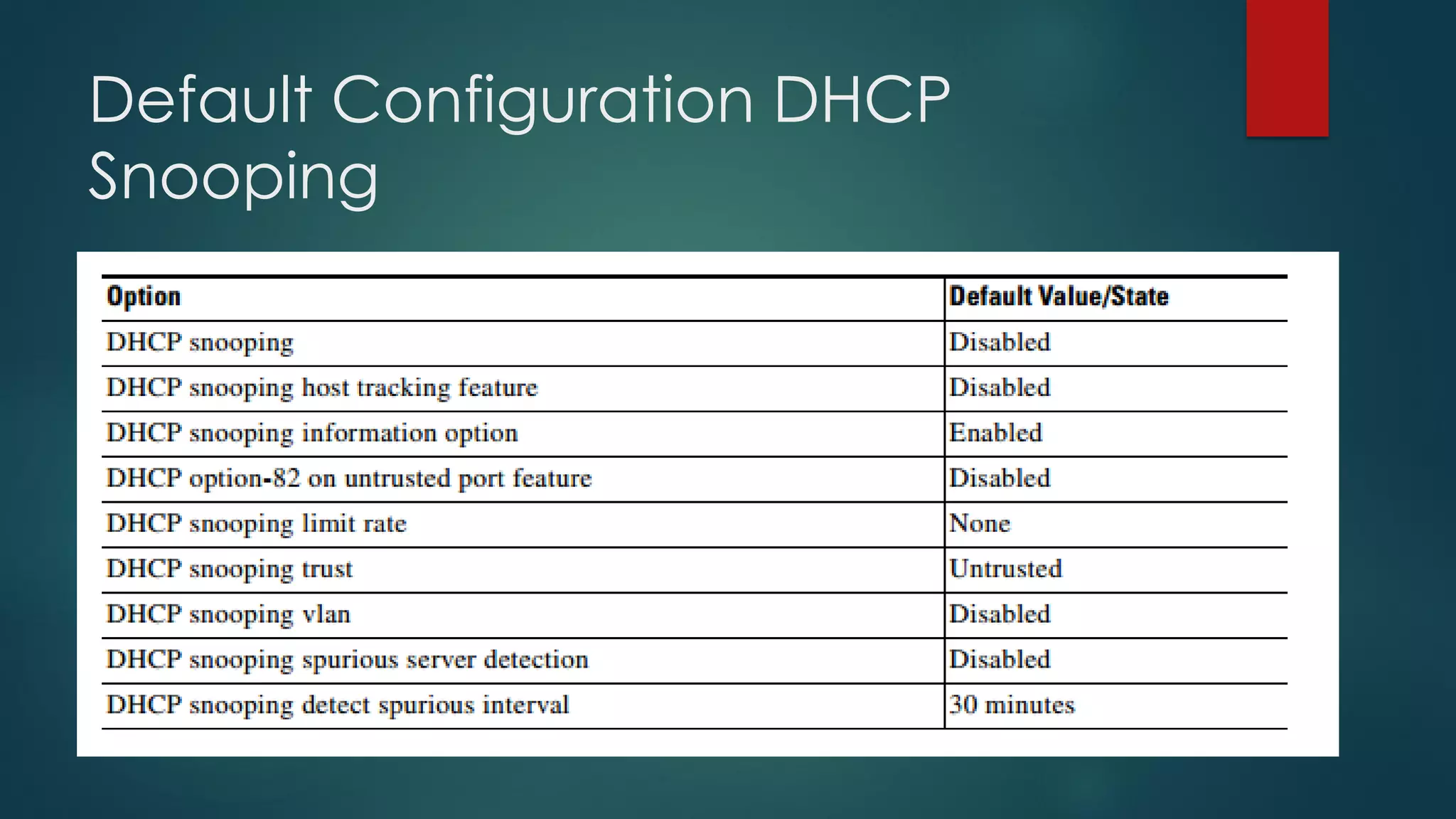
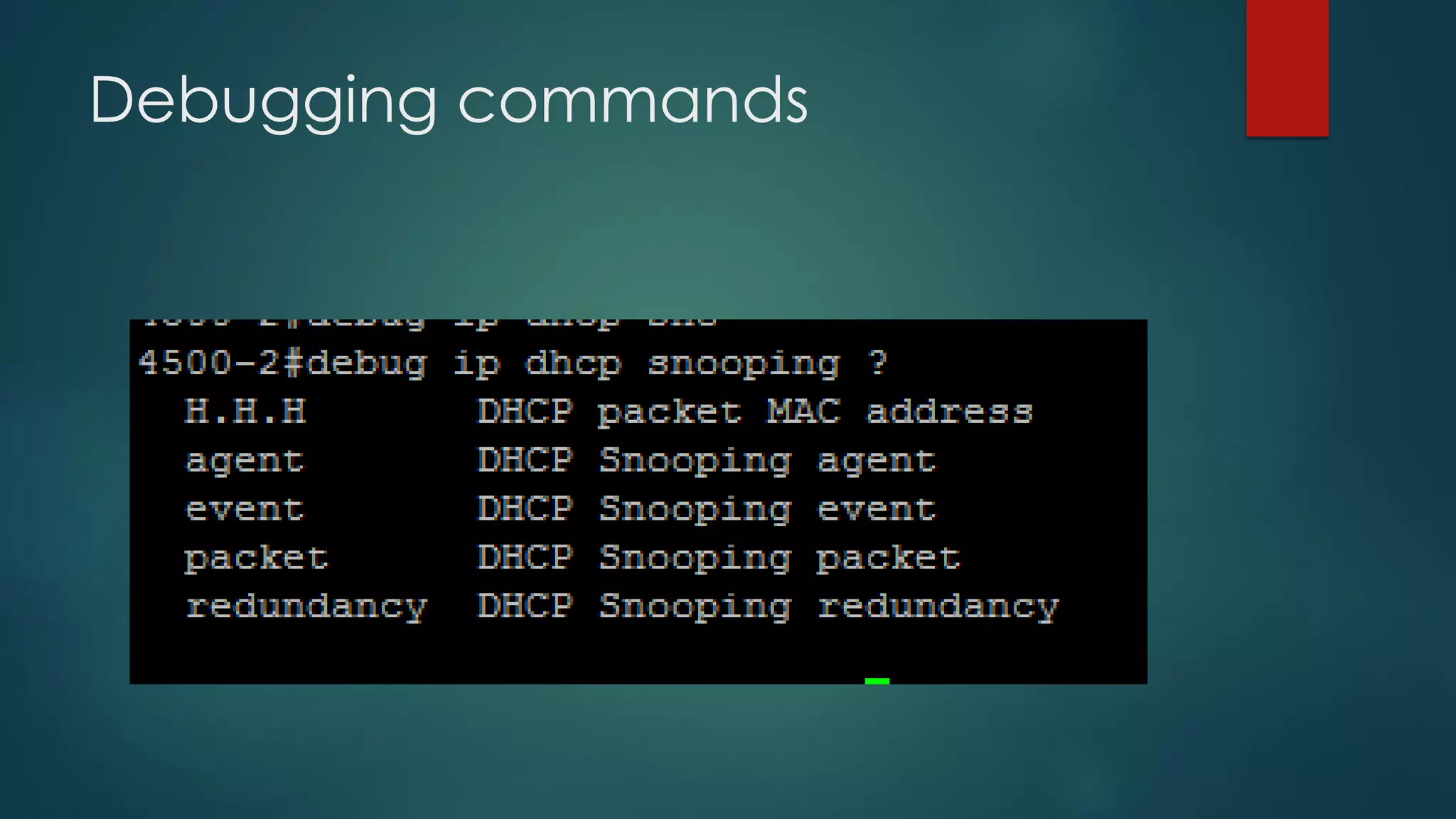
DHCP allows devices to obtain IP addresses and other network configuration dynamically. It uses a series of packet exchanges between DHCP clients and servers. The document discusses the DHCP packet types, client-server conversation process, DHCP snooping for security, and commands used to configure and monitor DHCP. It also covers Dynamic ARP inspection and IP Source Guard which work with DHCP snooping to provide additional network security.