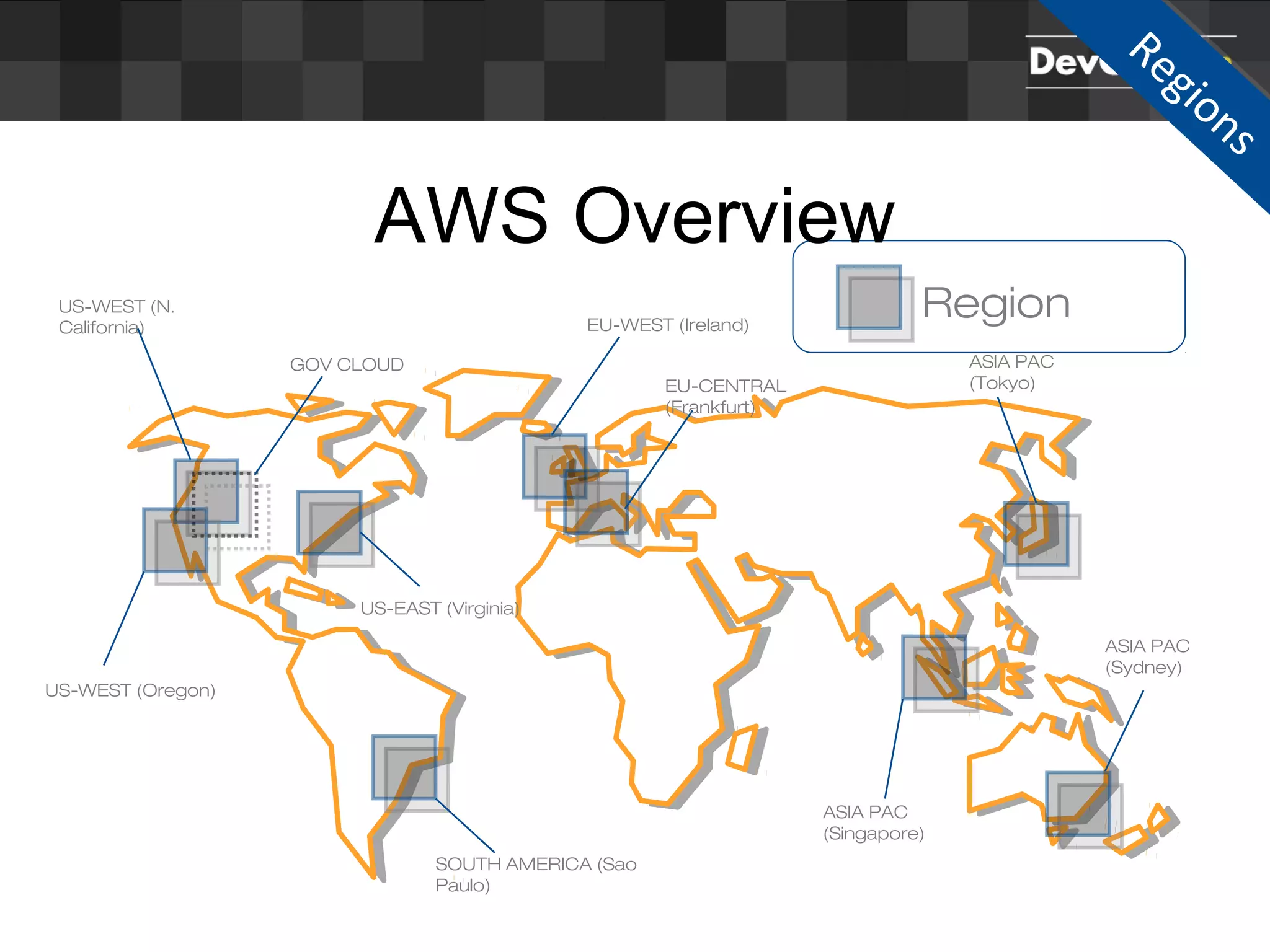
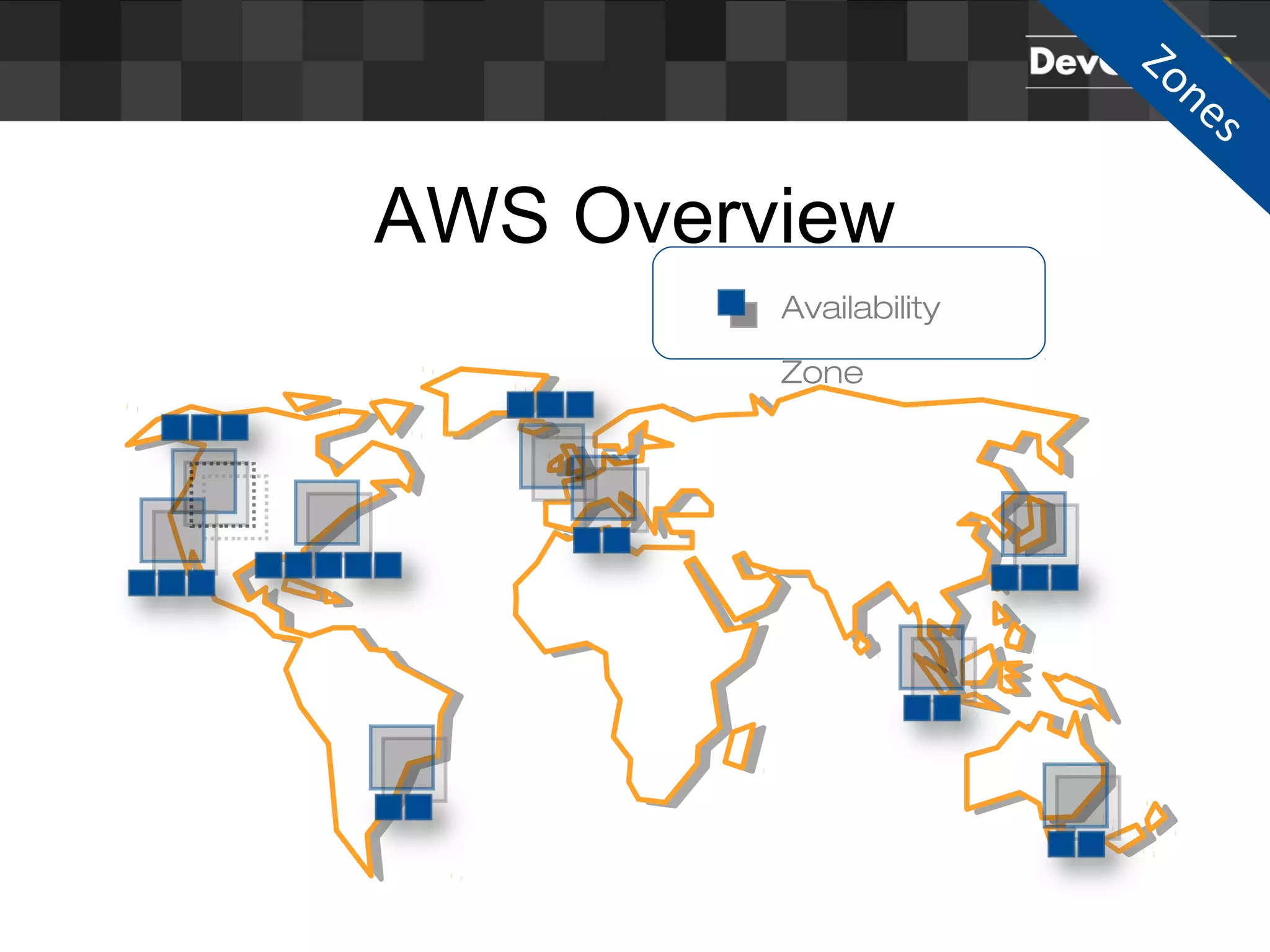
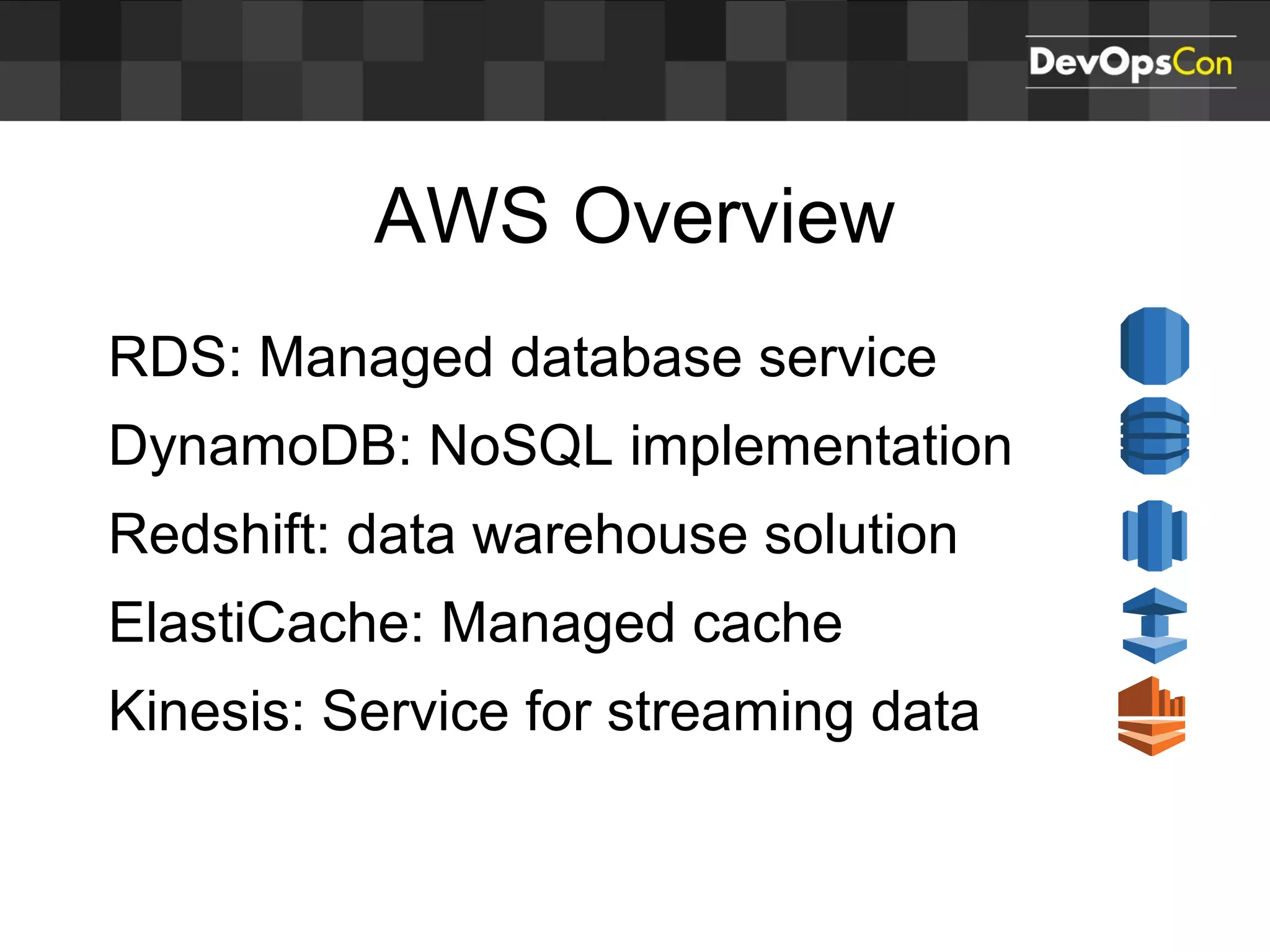
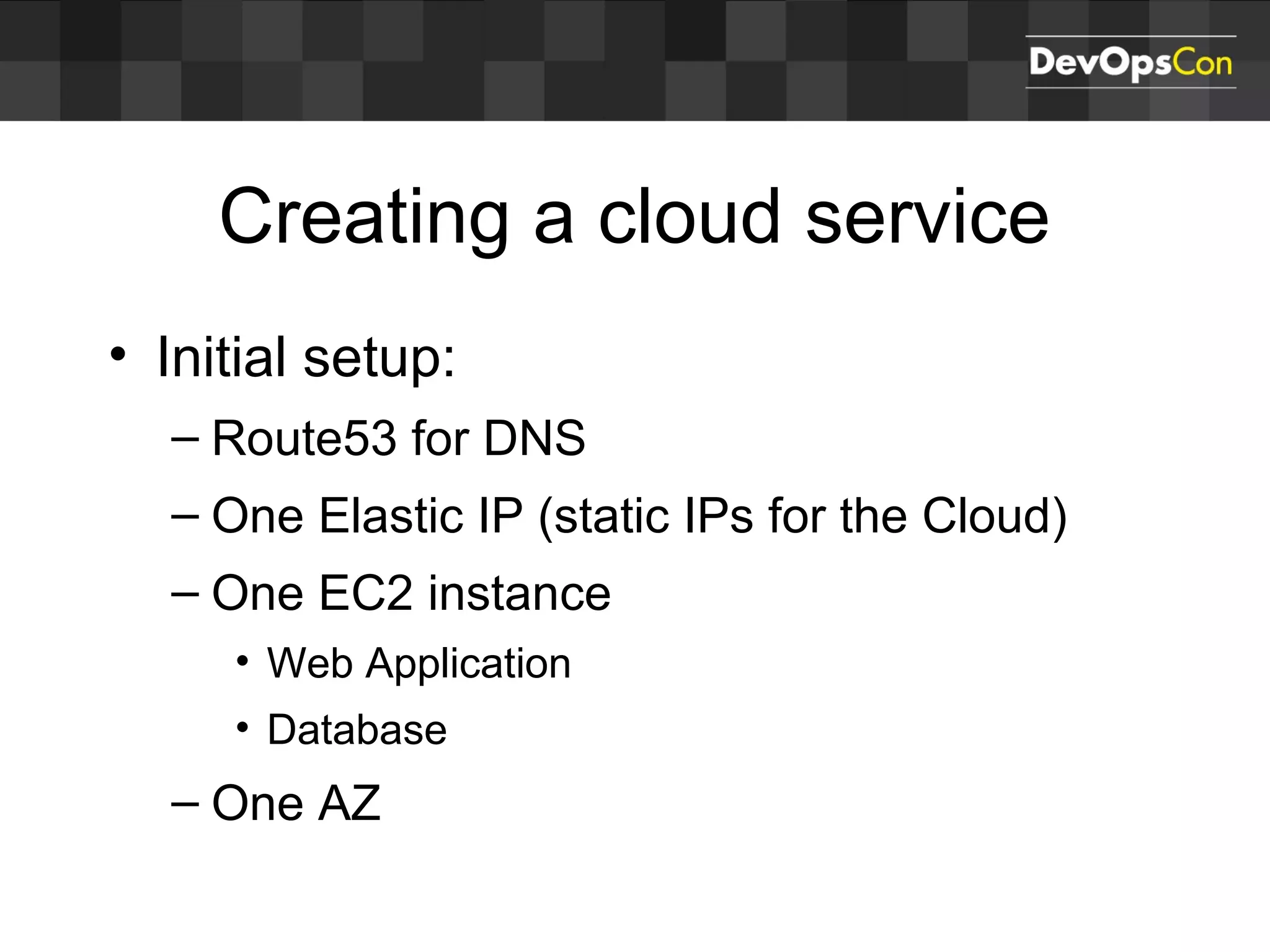
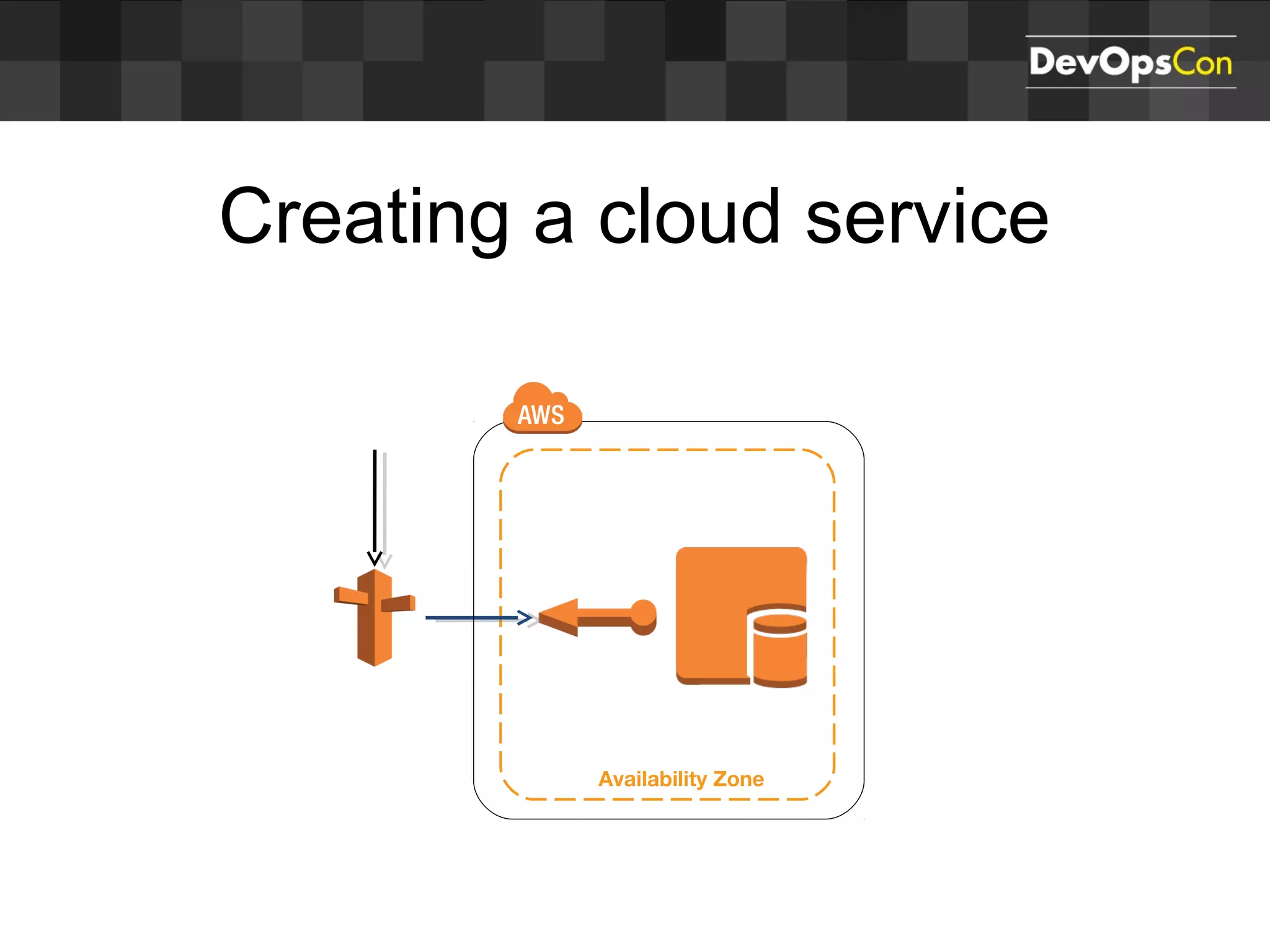
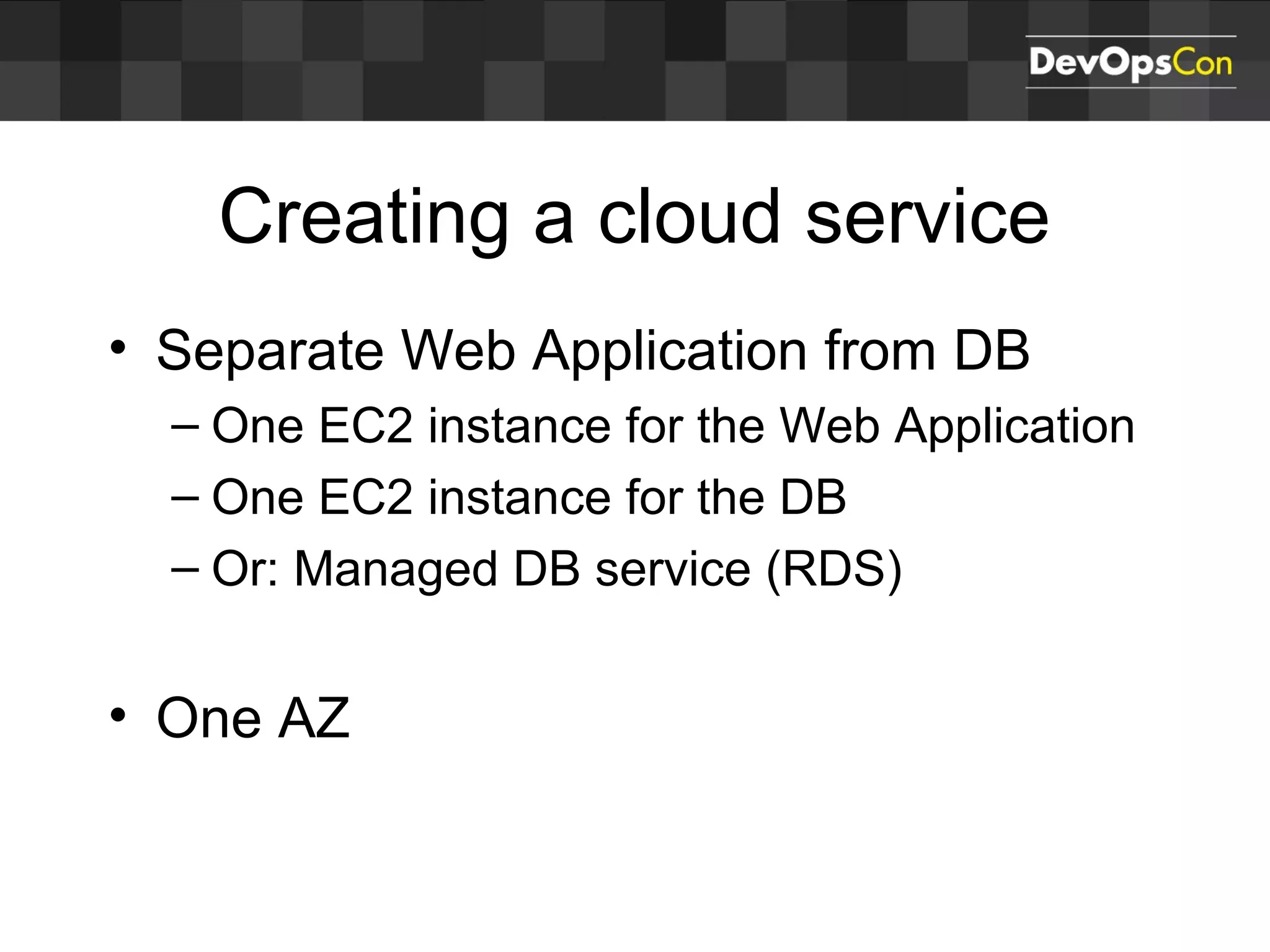
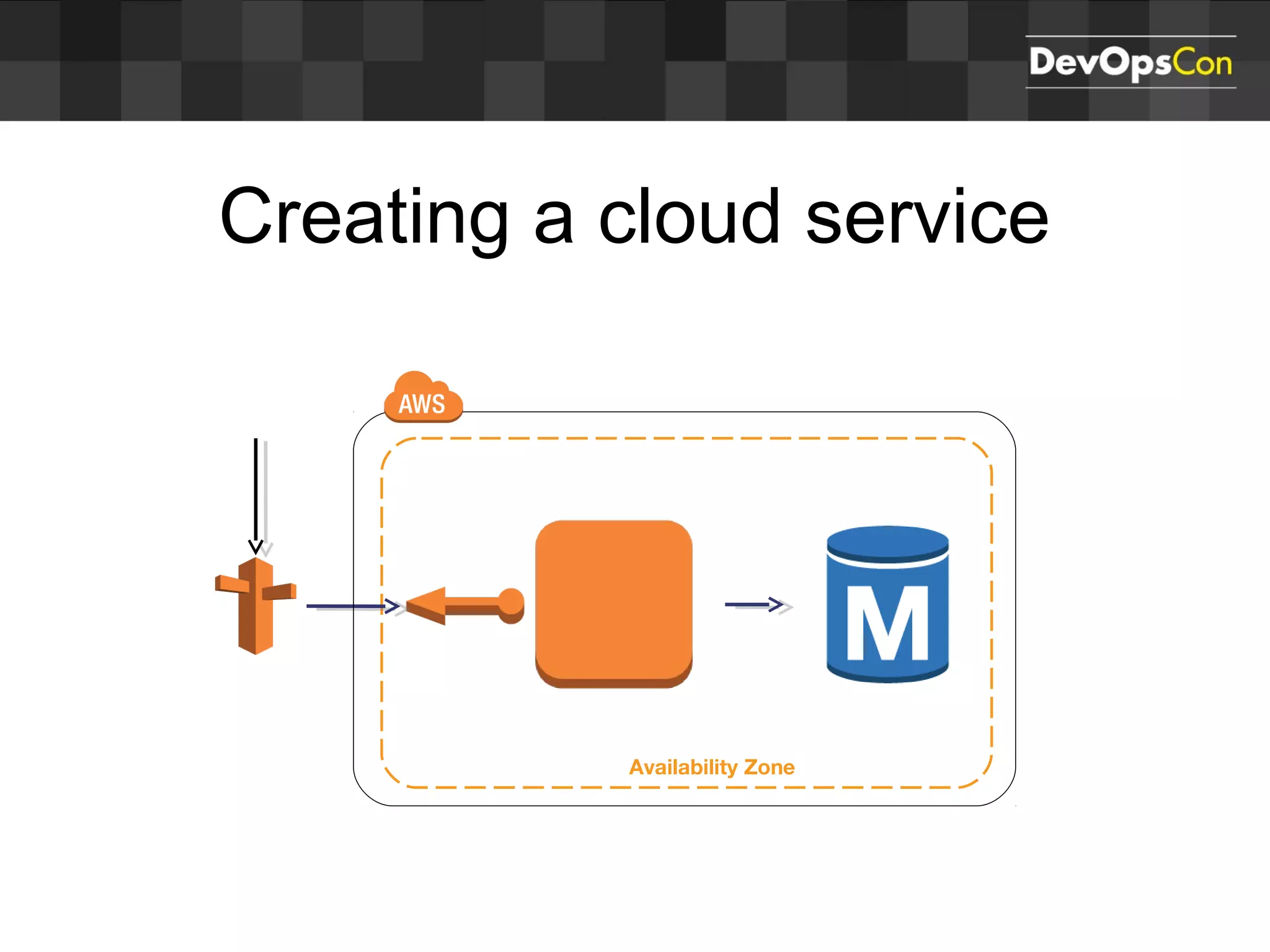
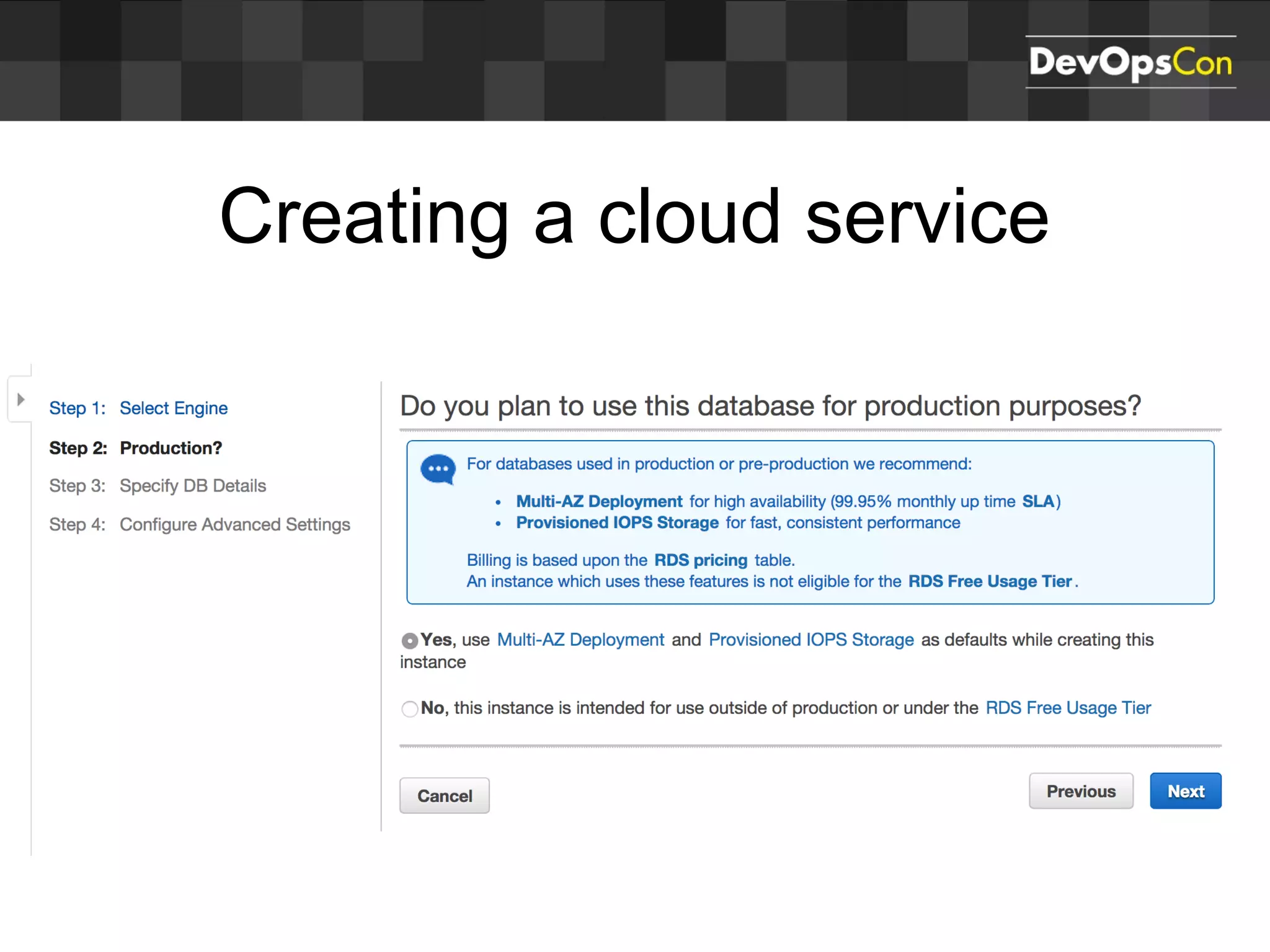
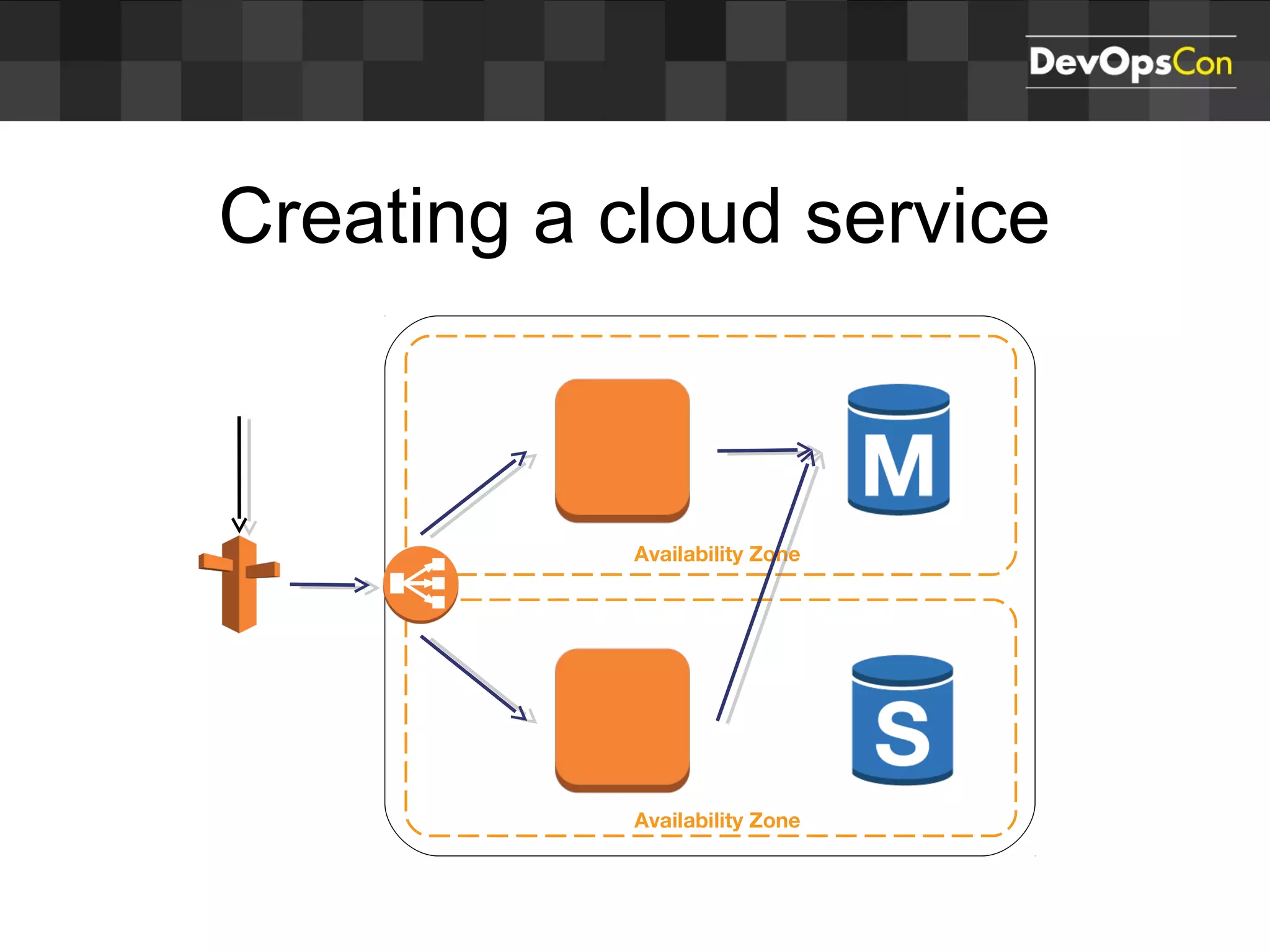
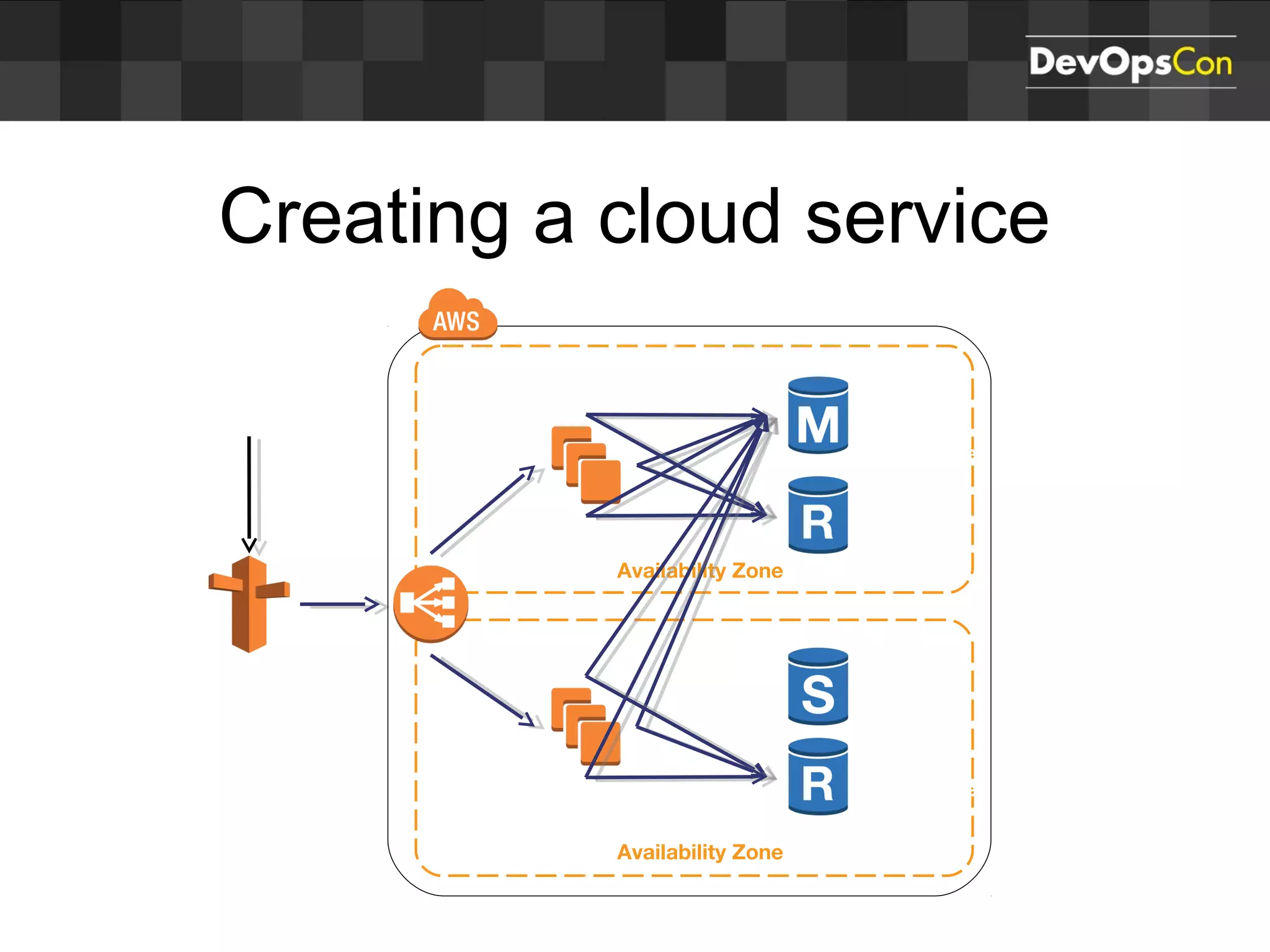
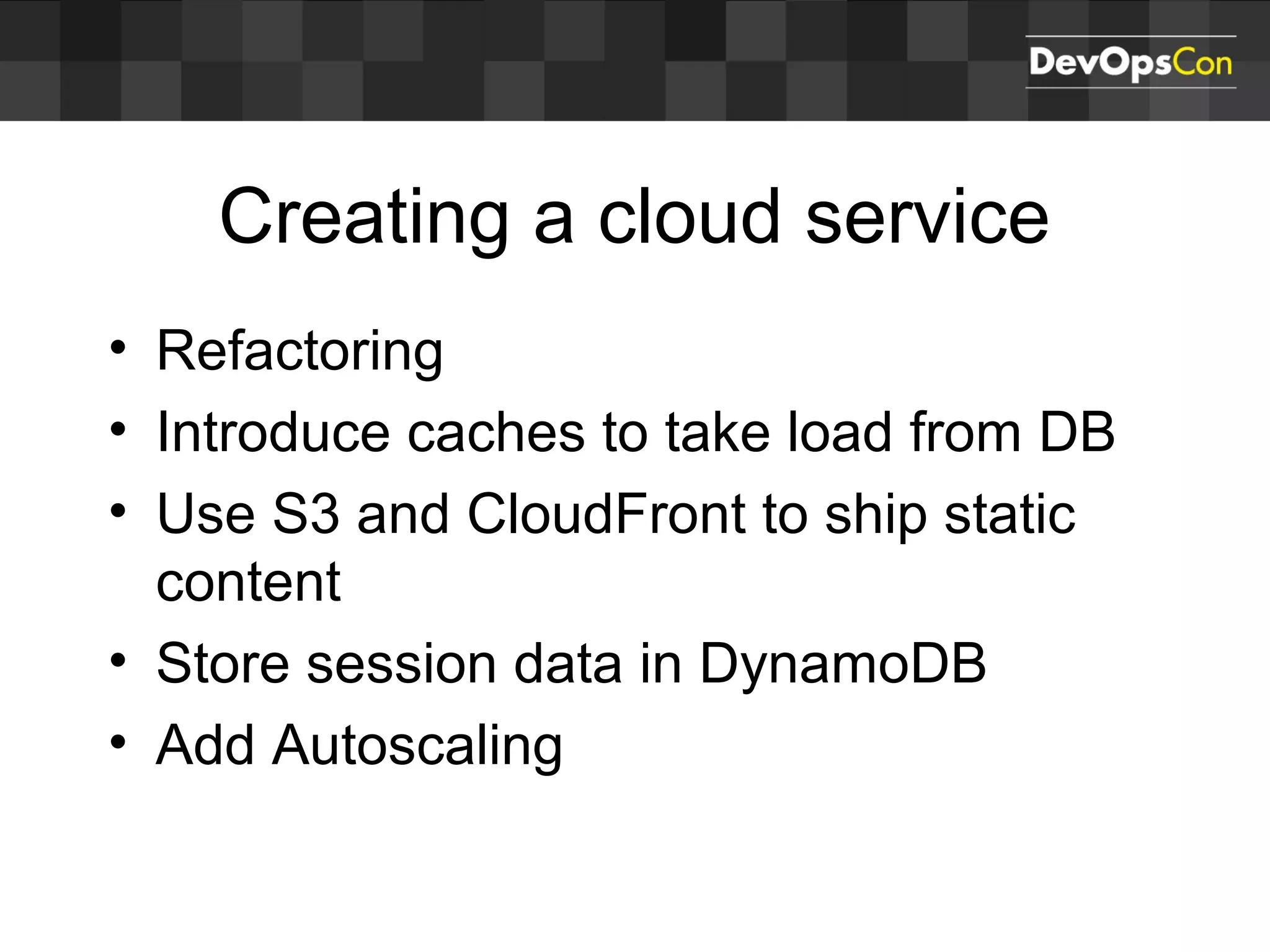
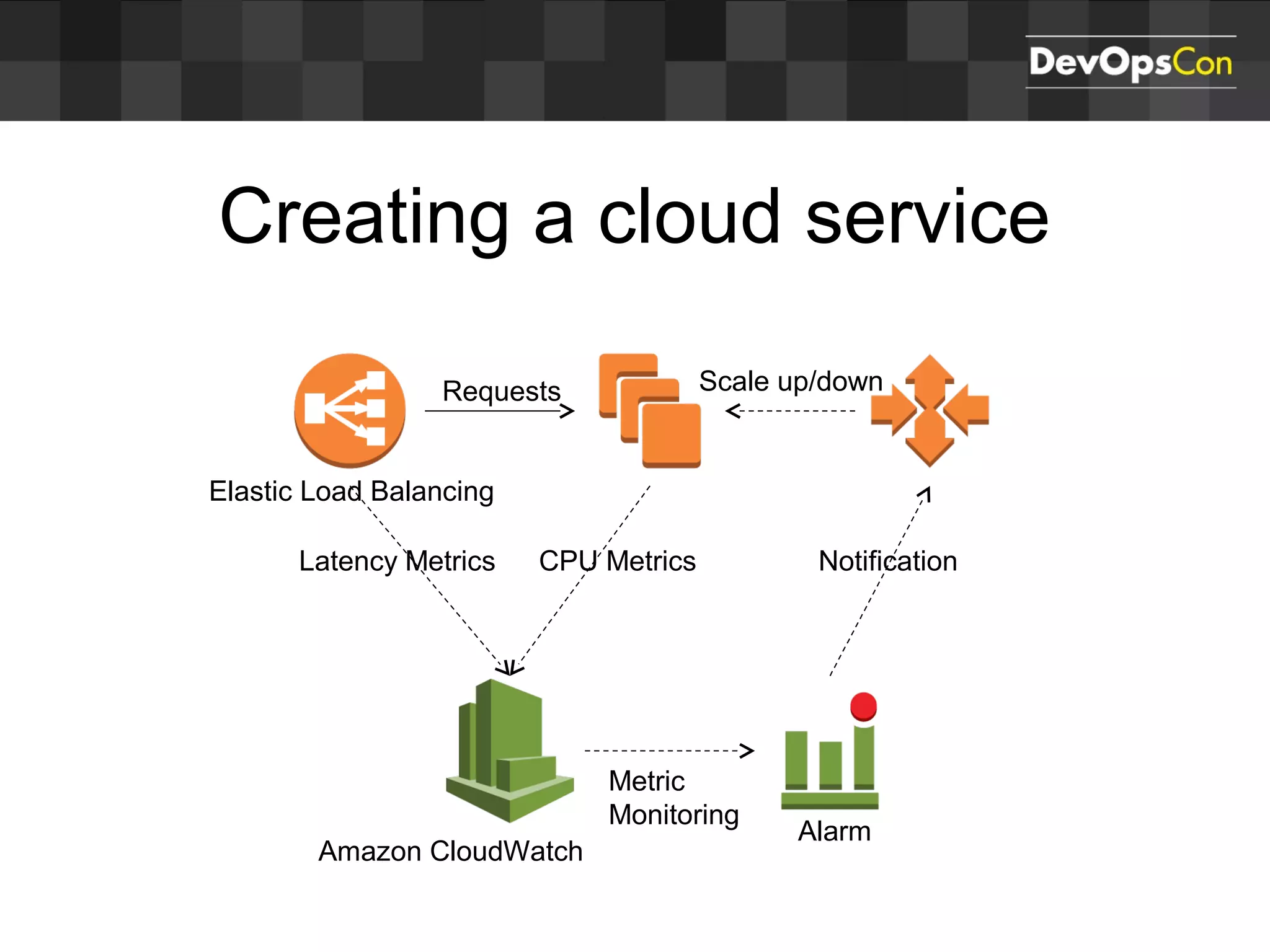
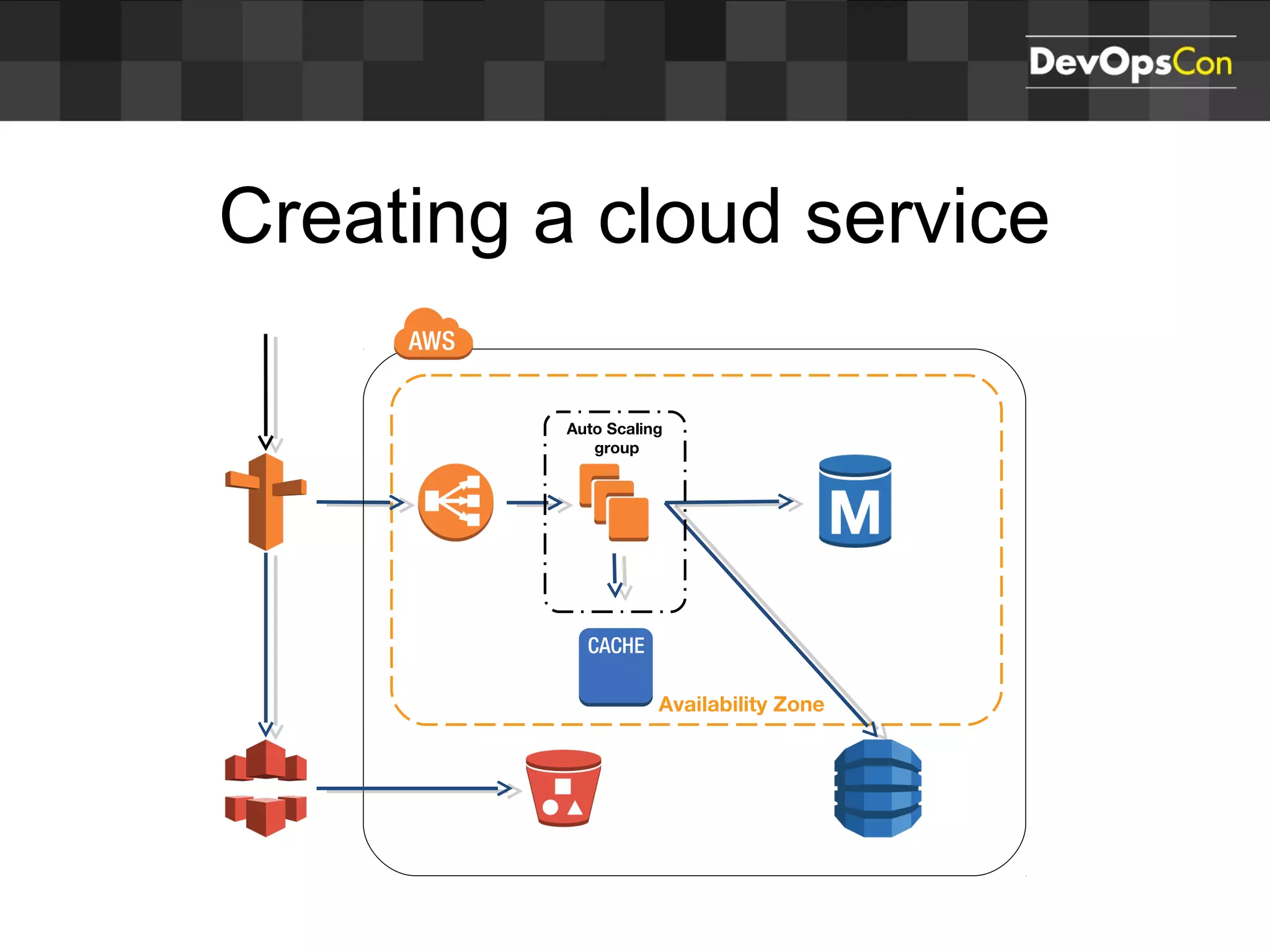
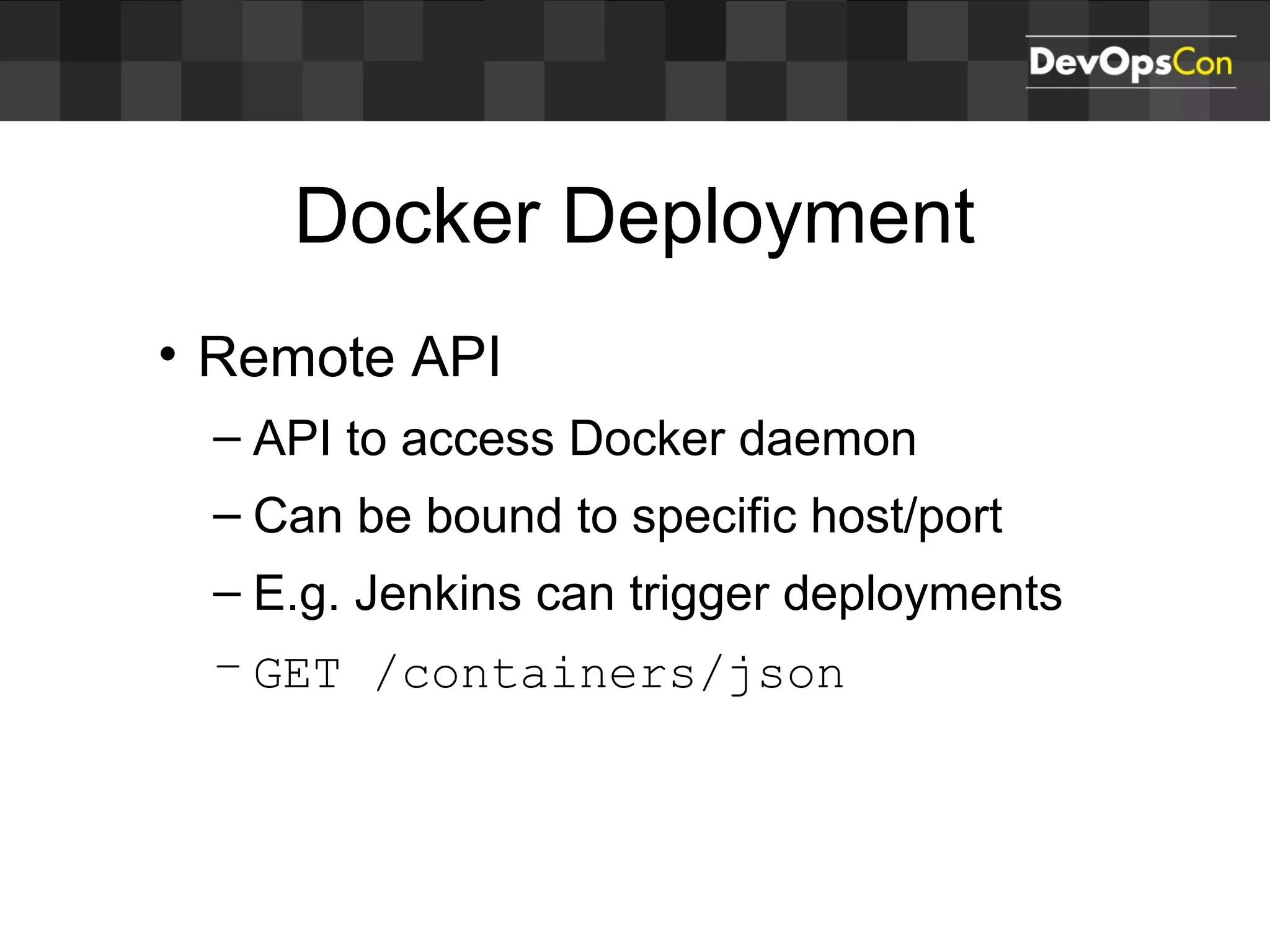
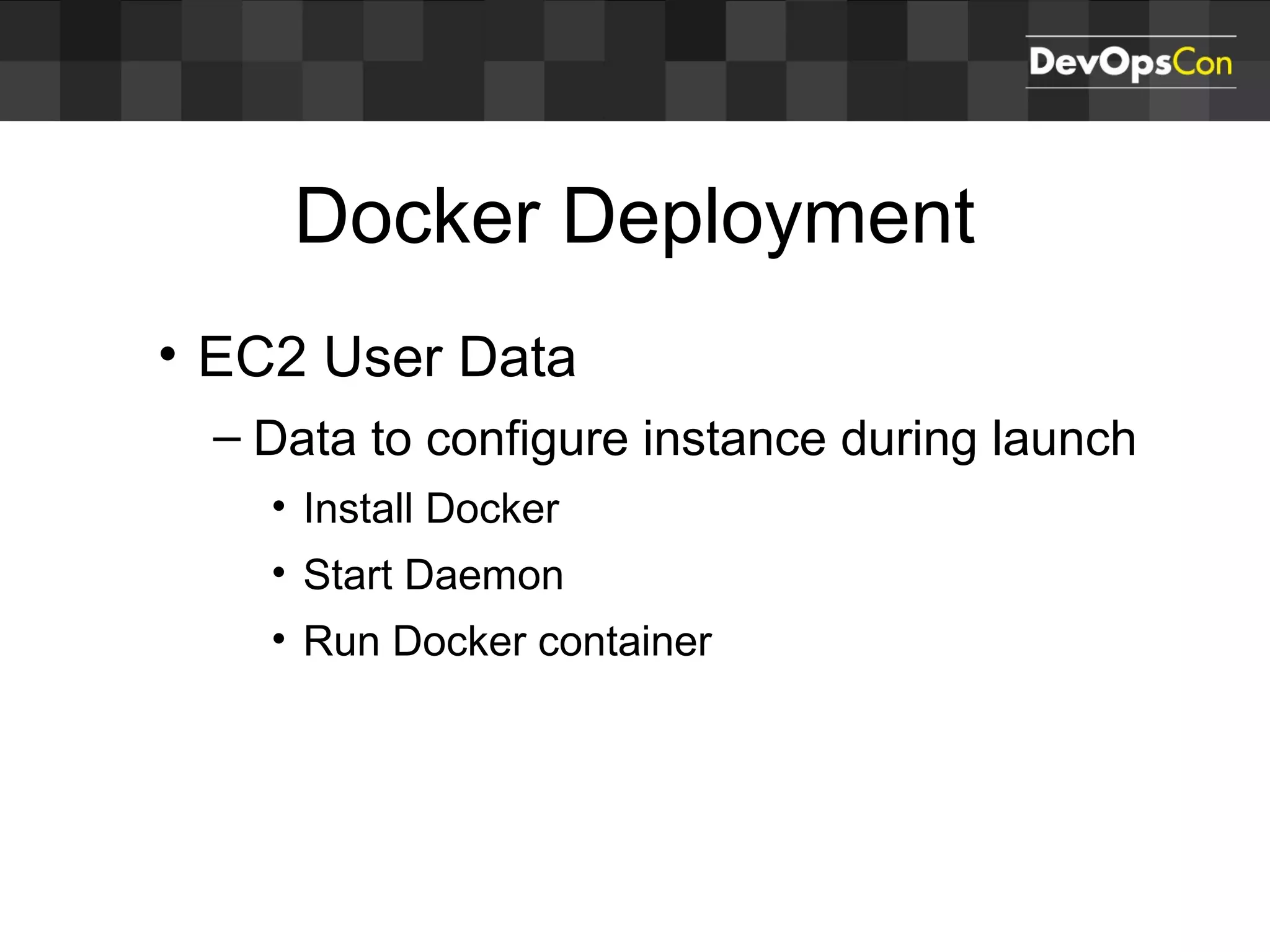
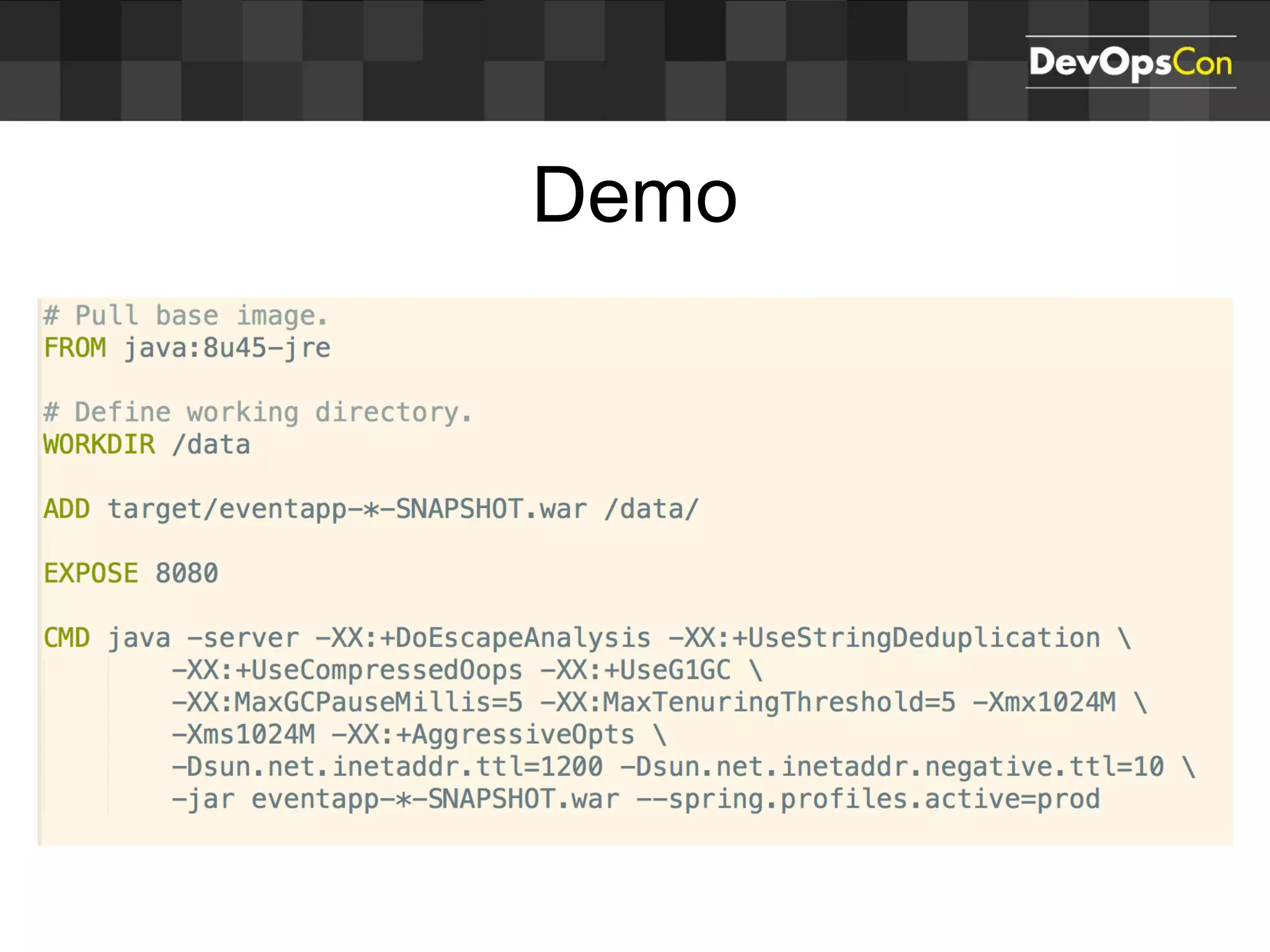
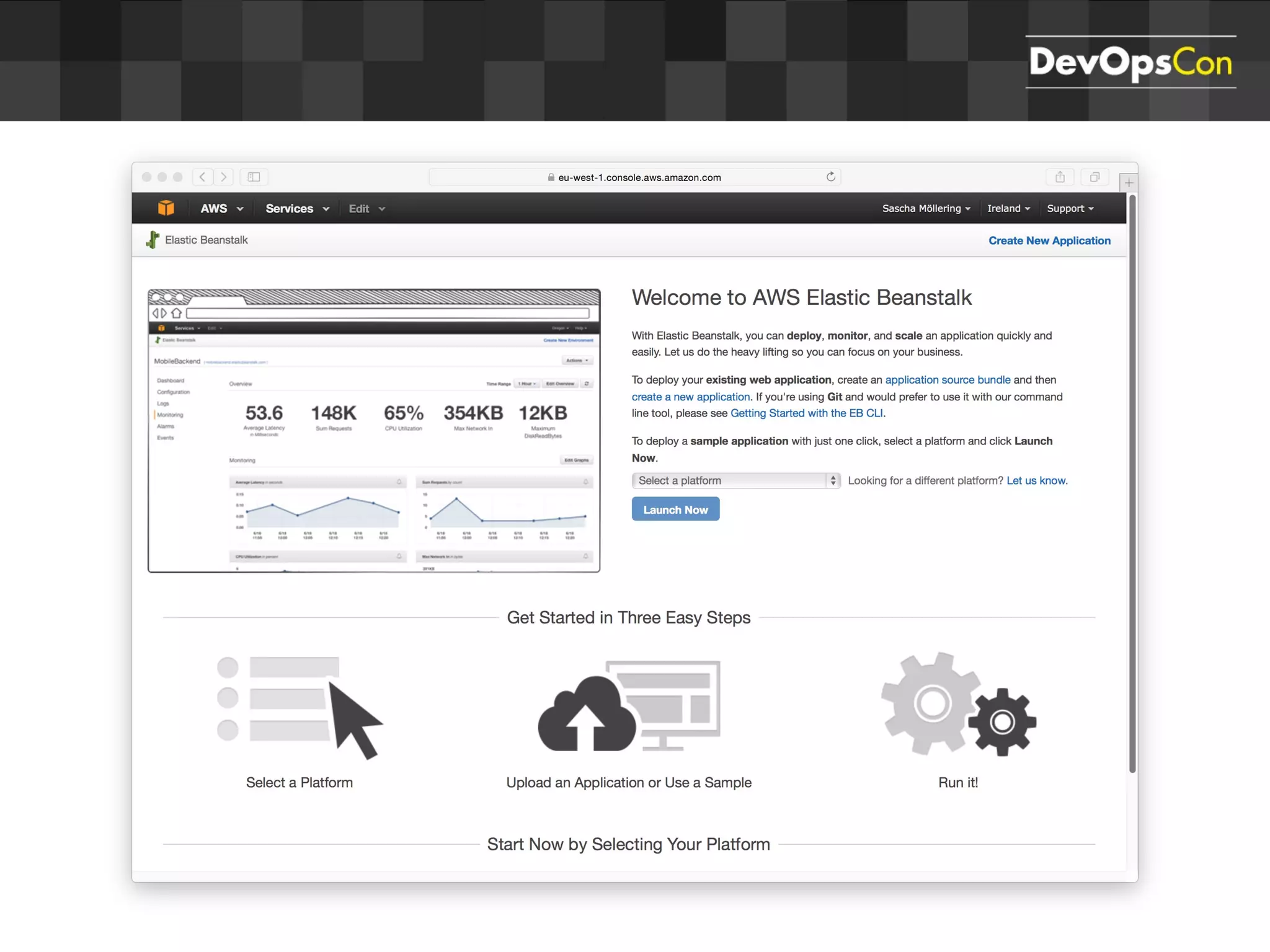
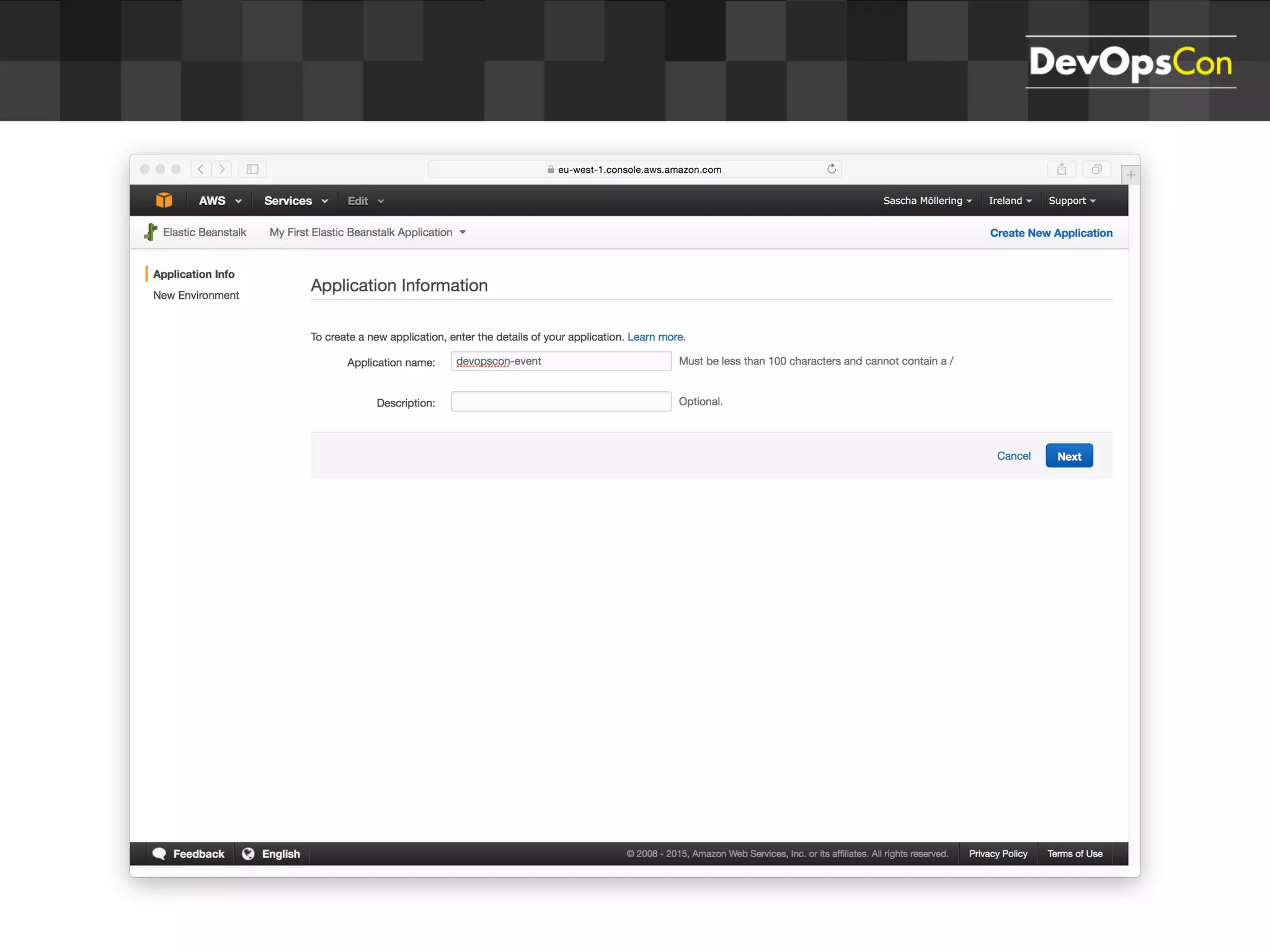
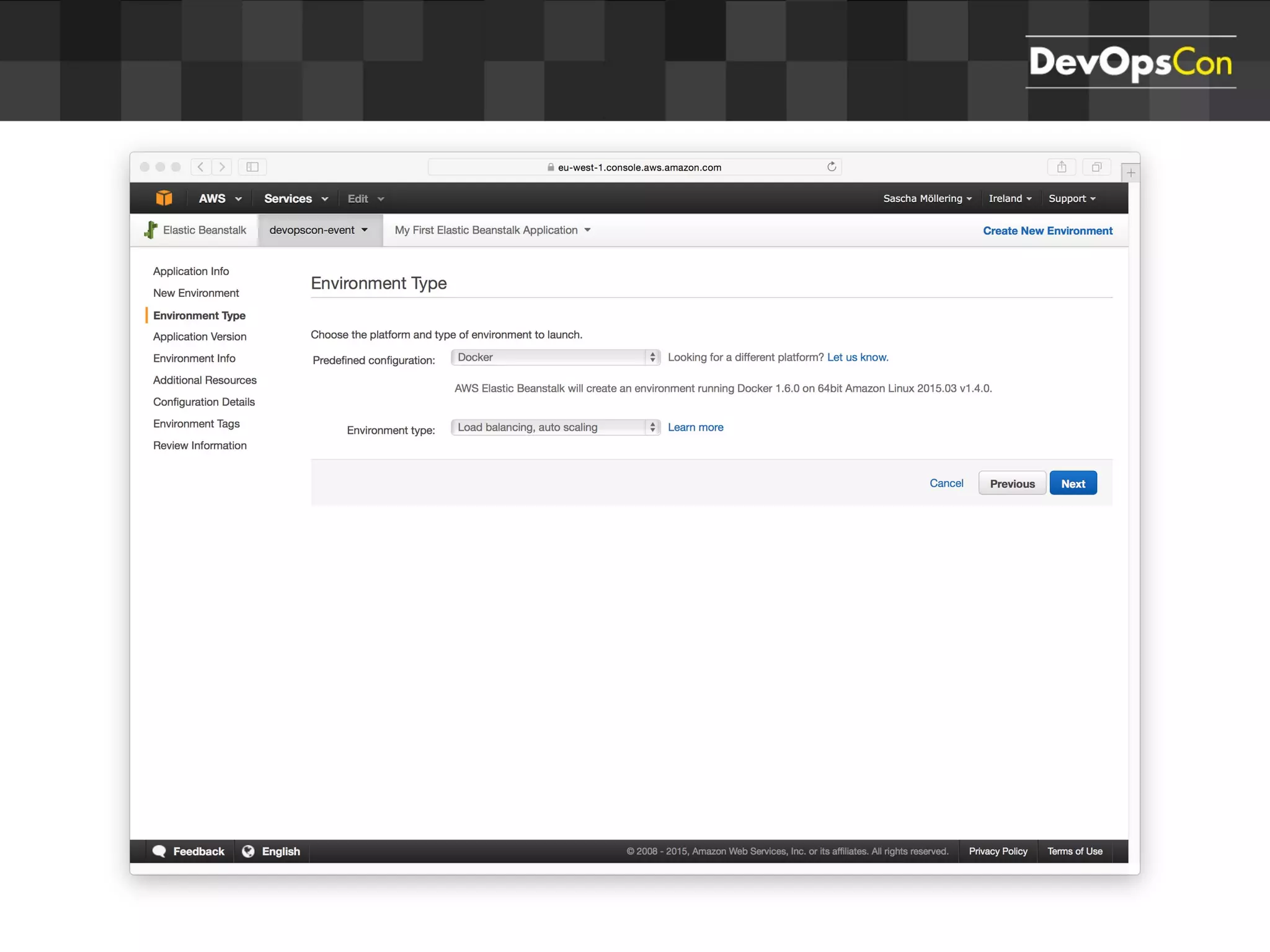
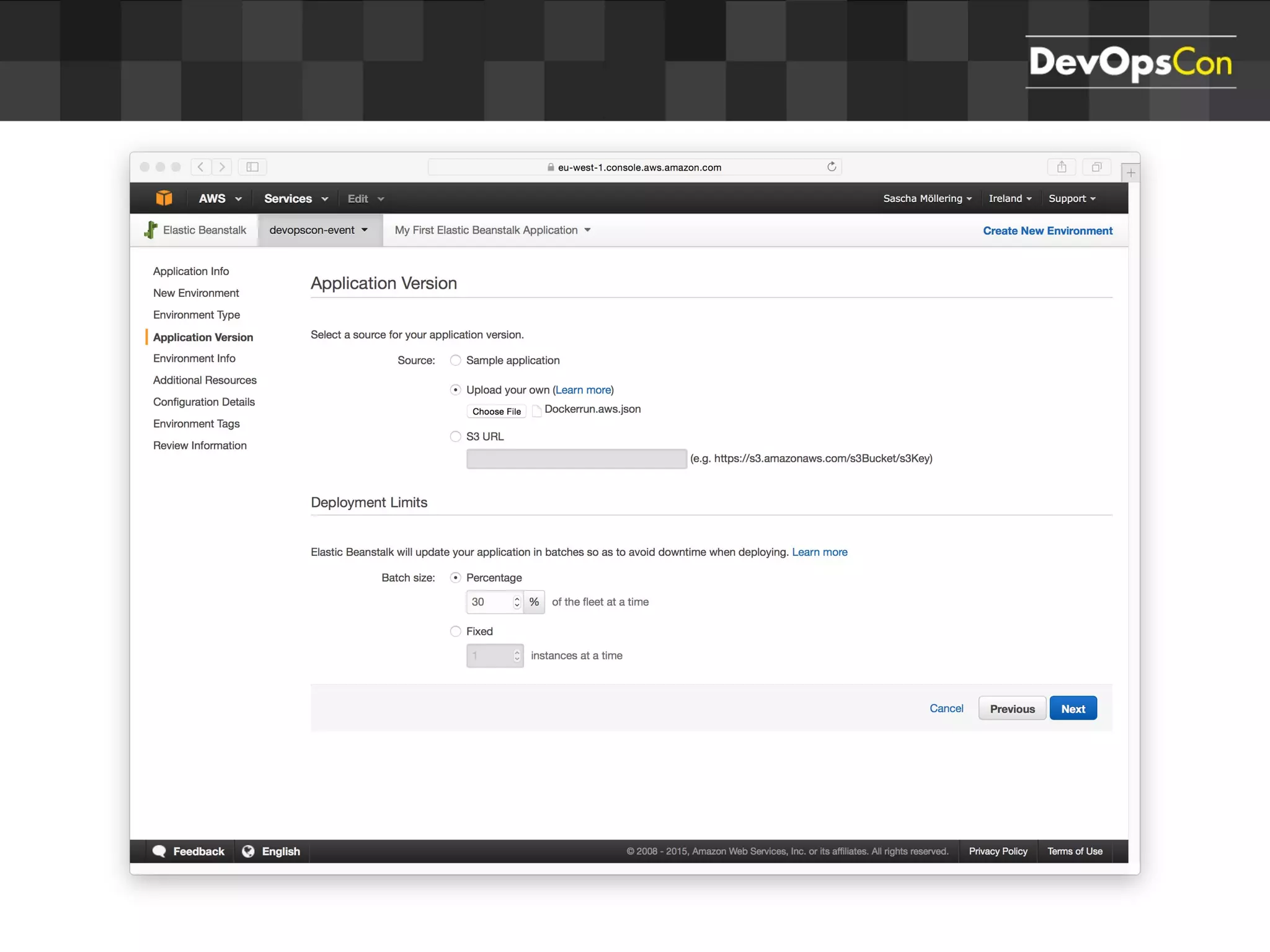
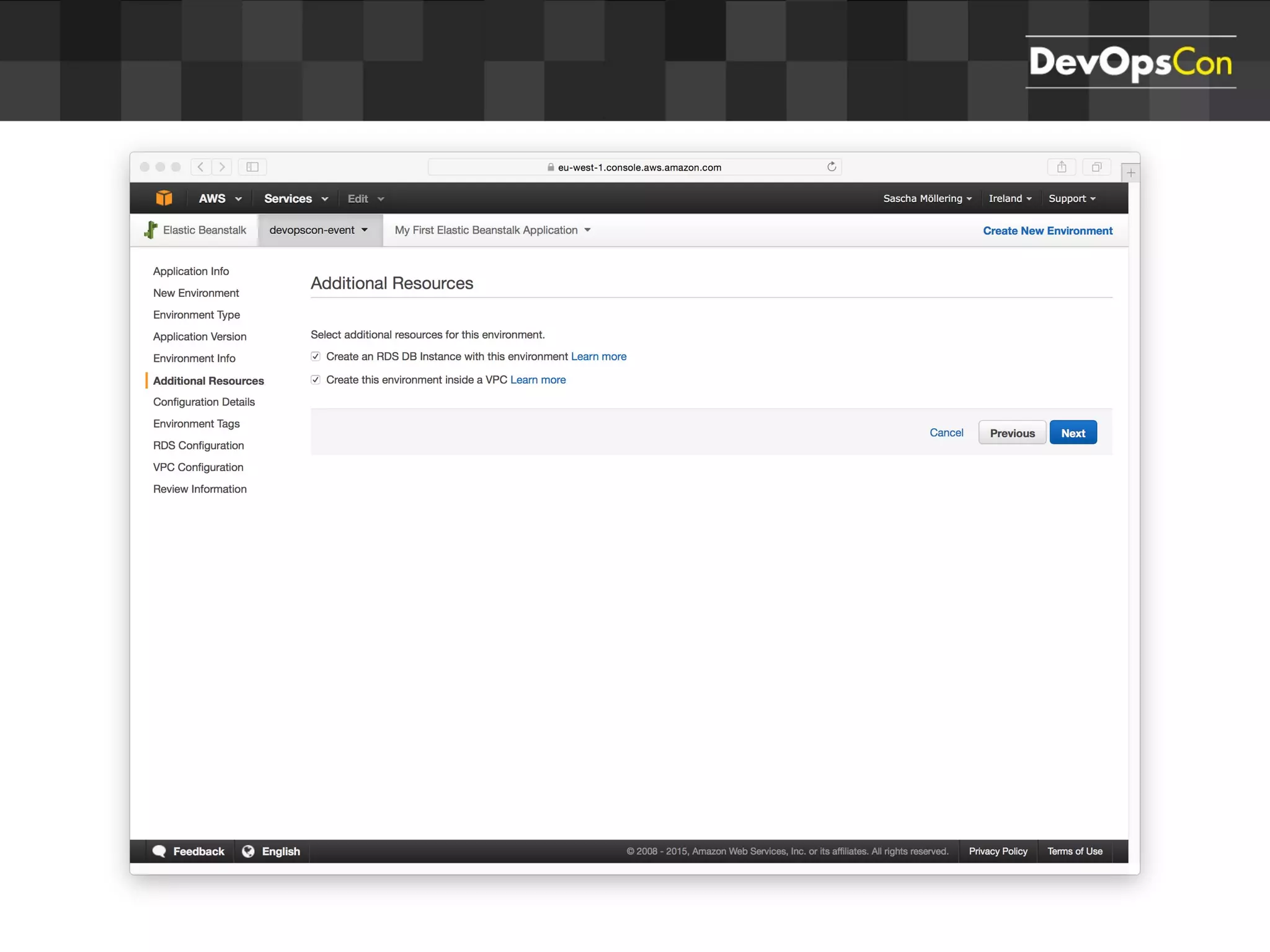
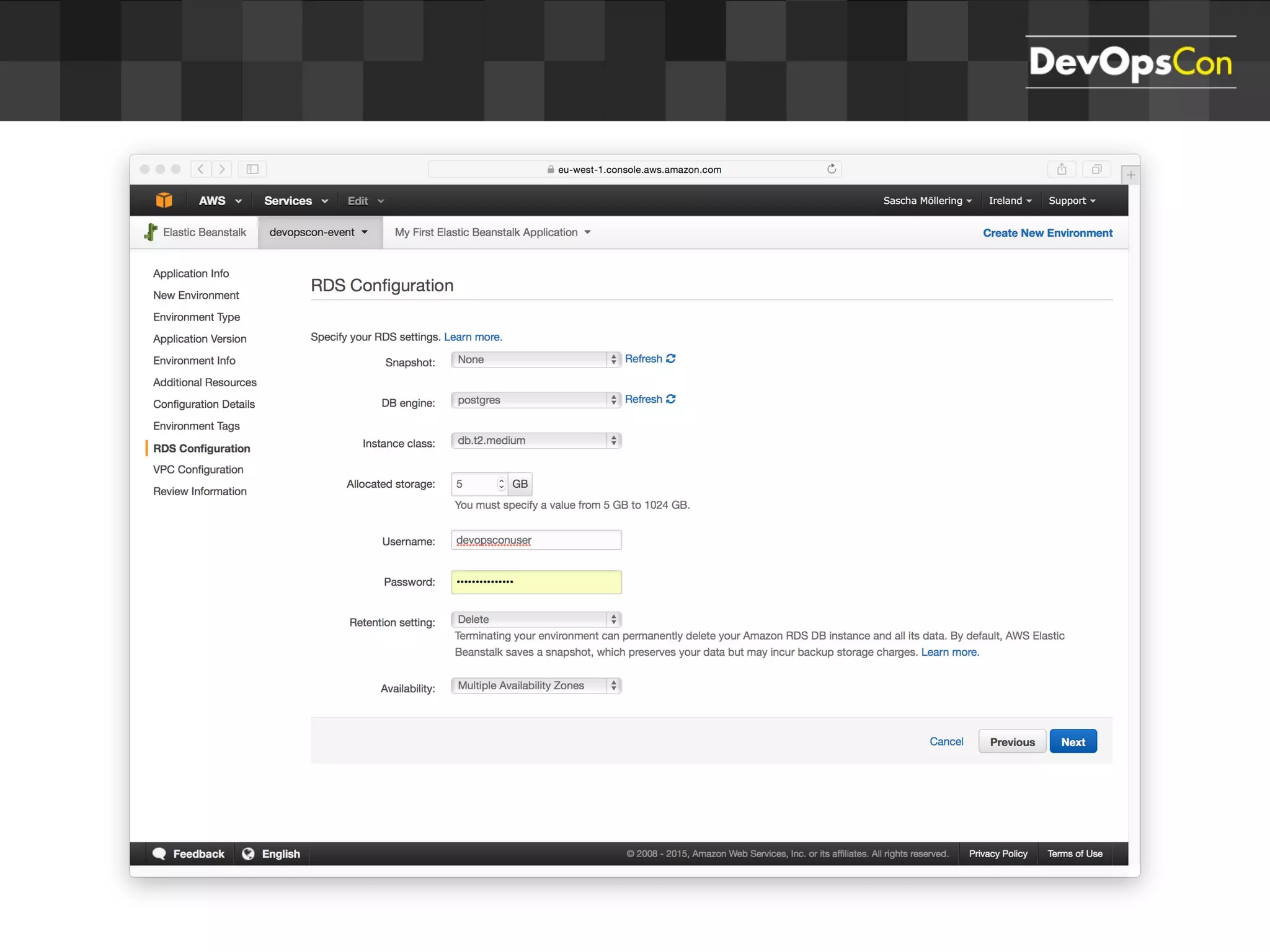
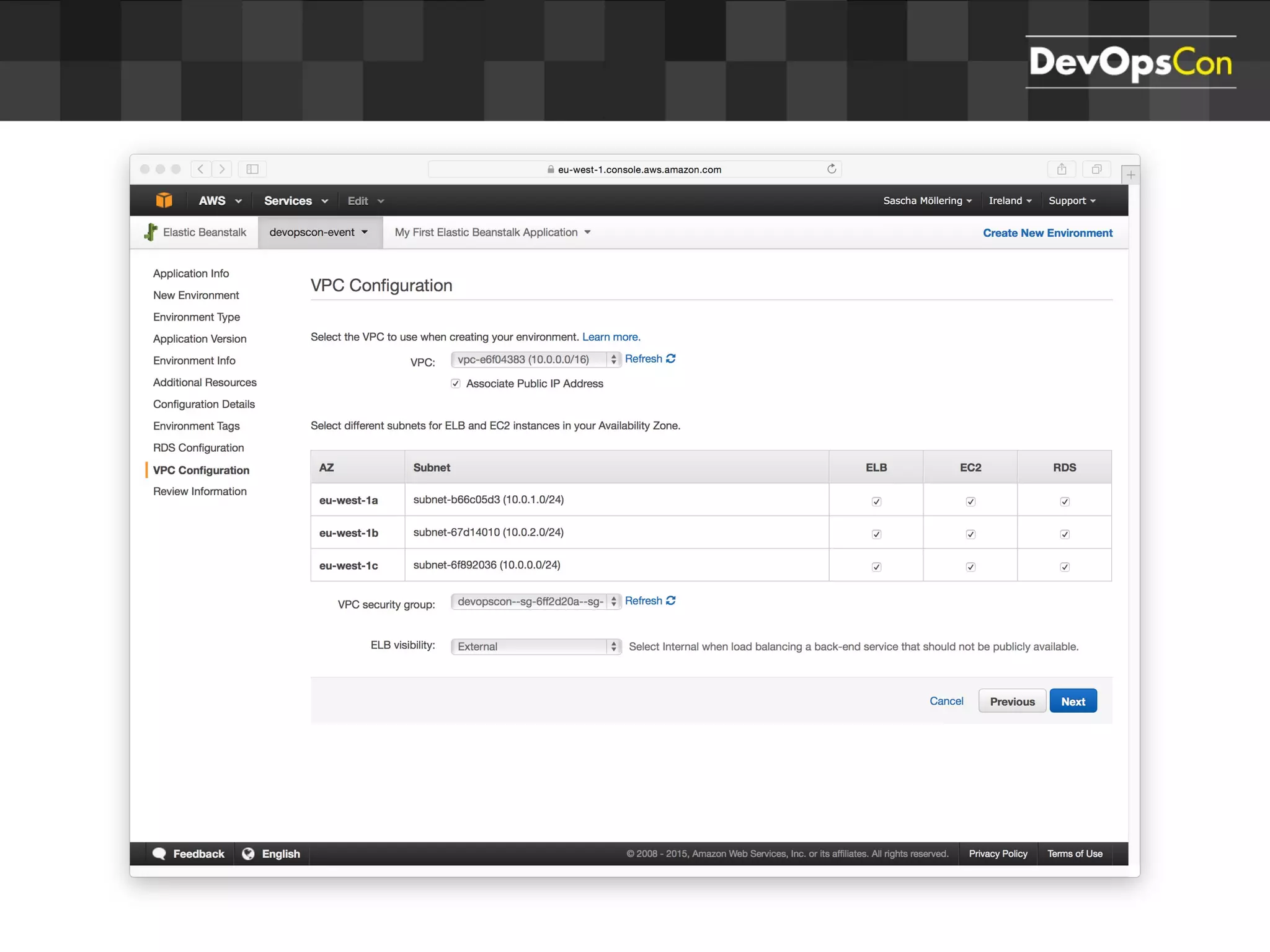
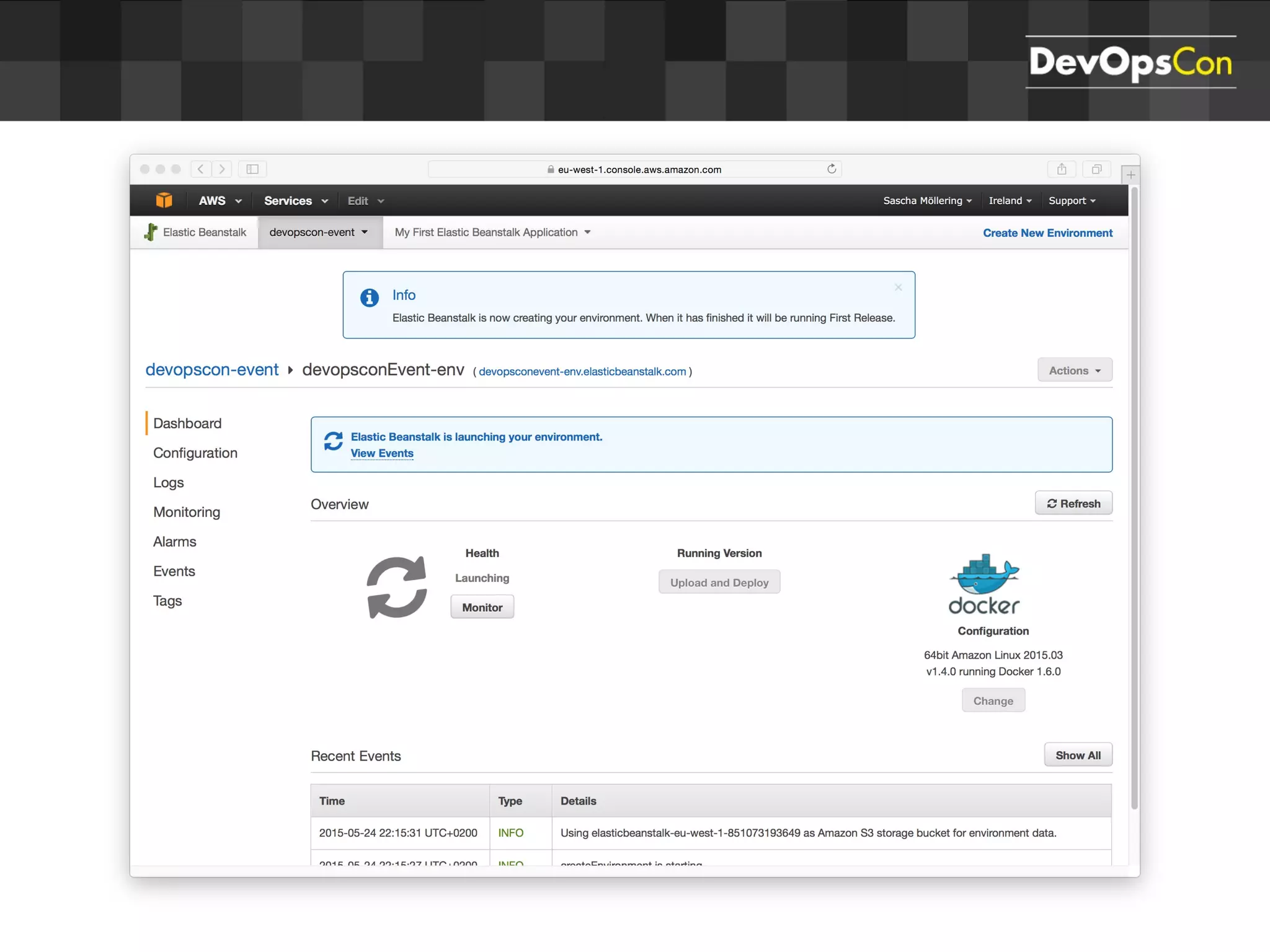
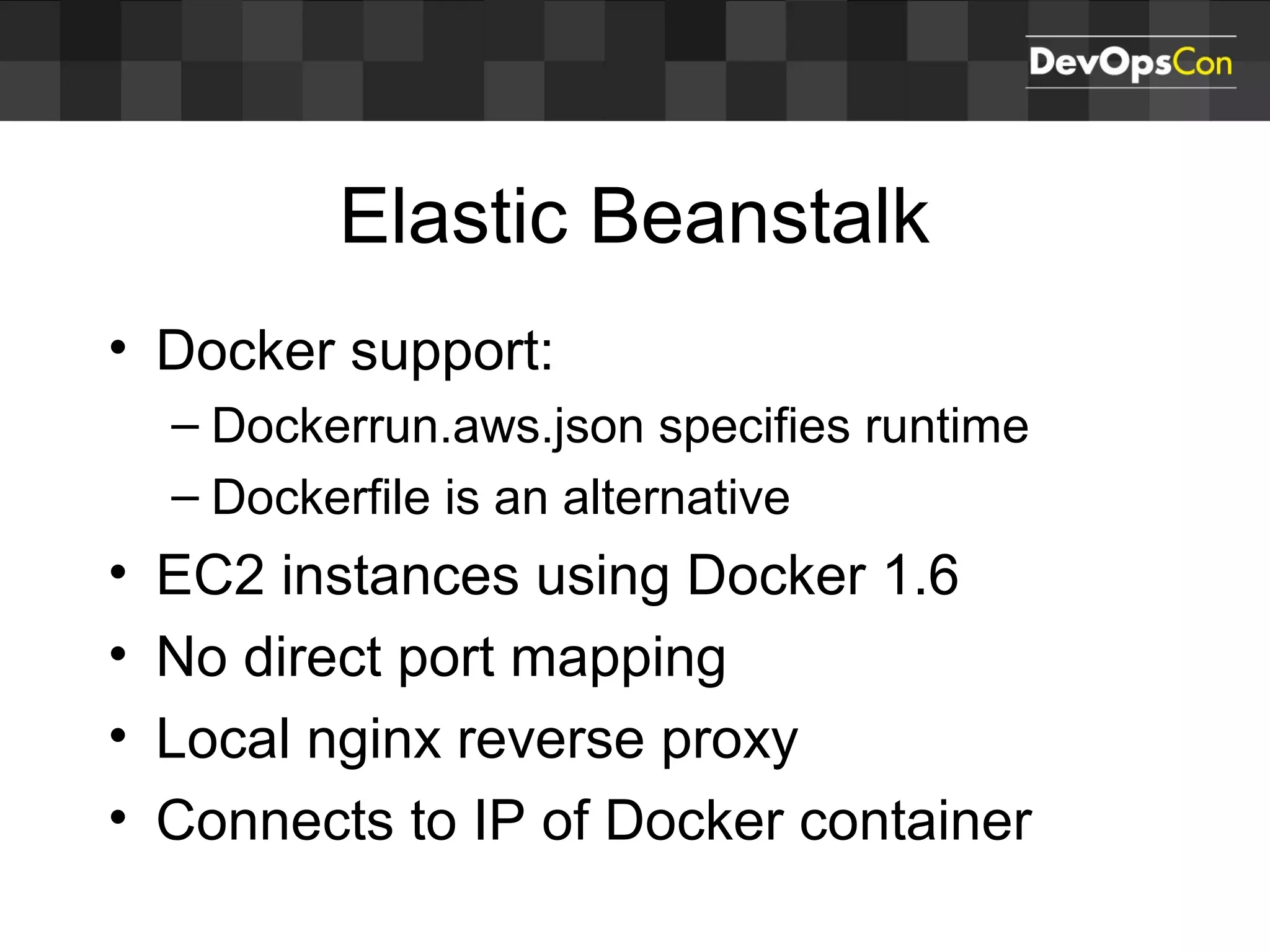
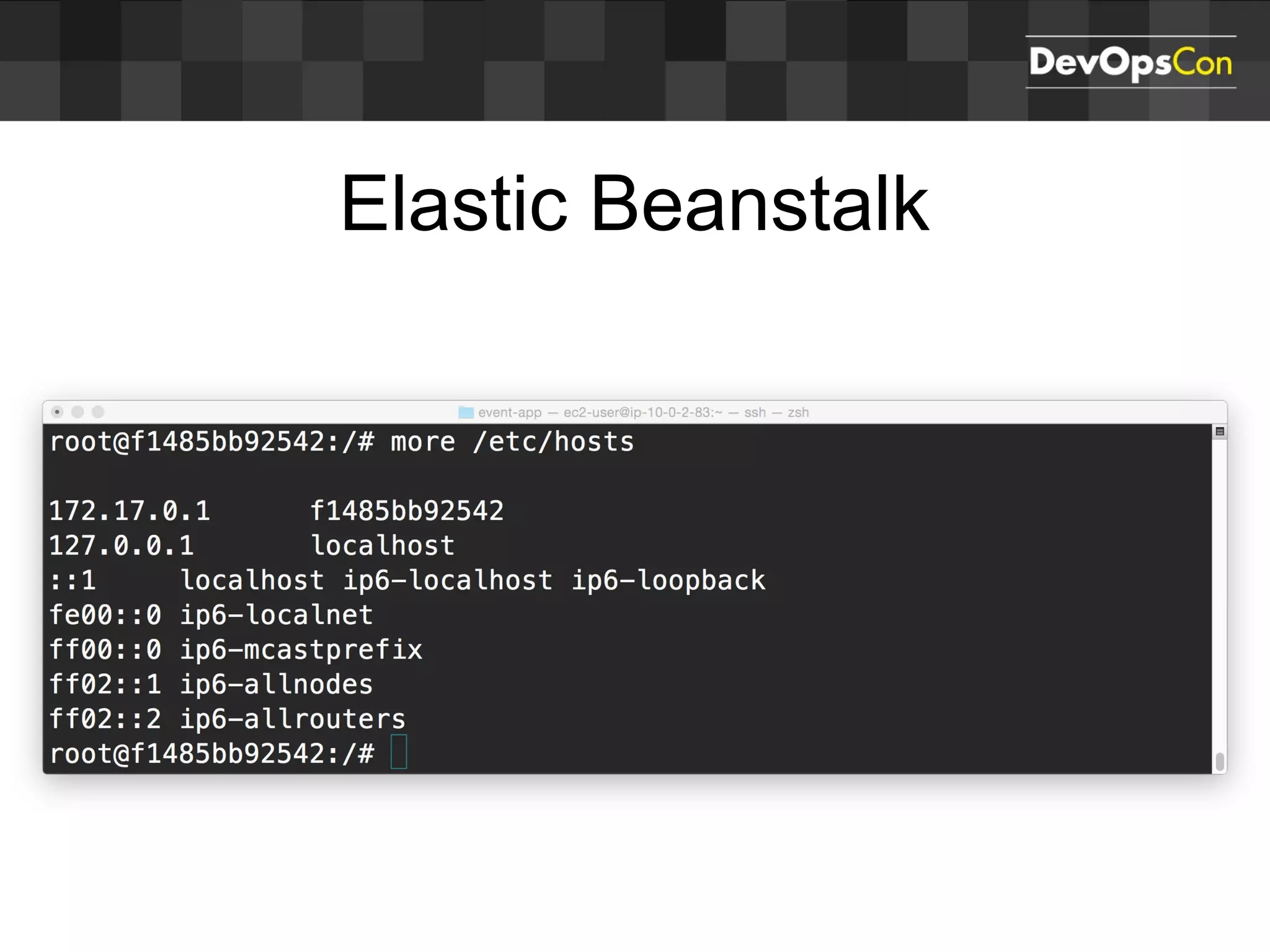
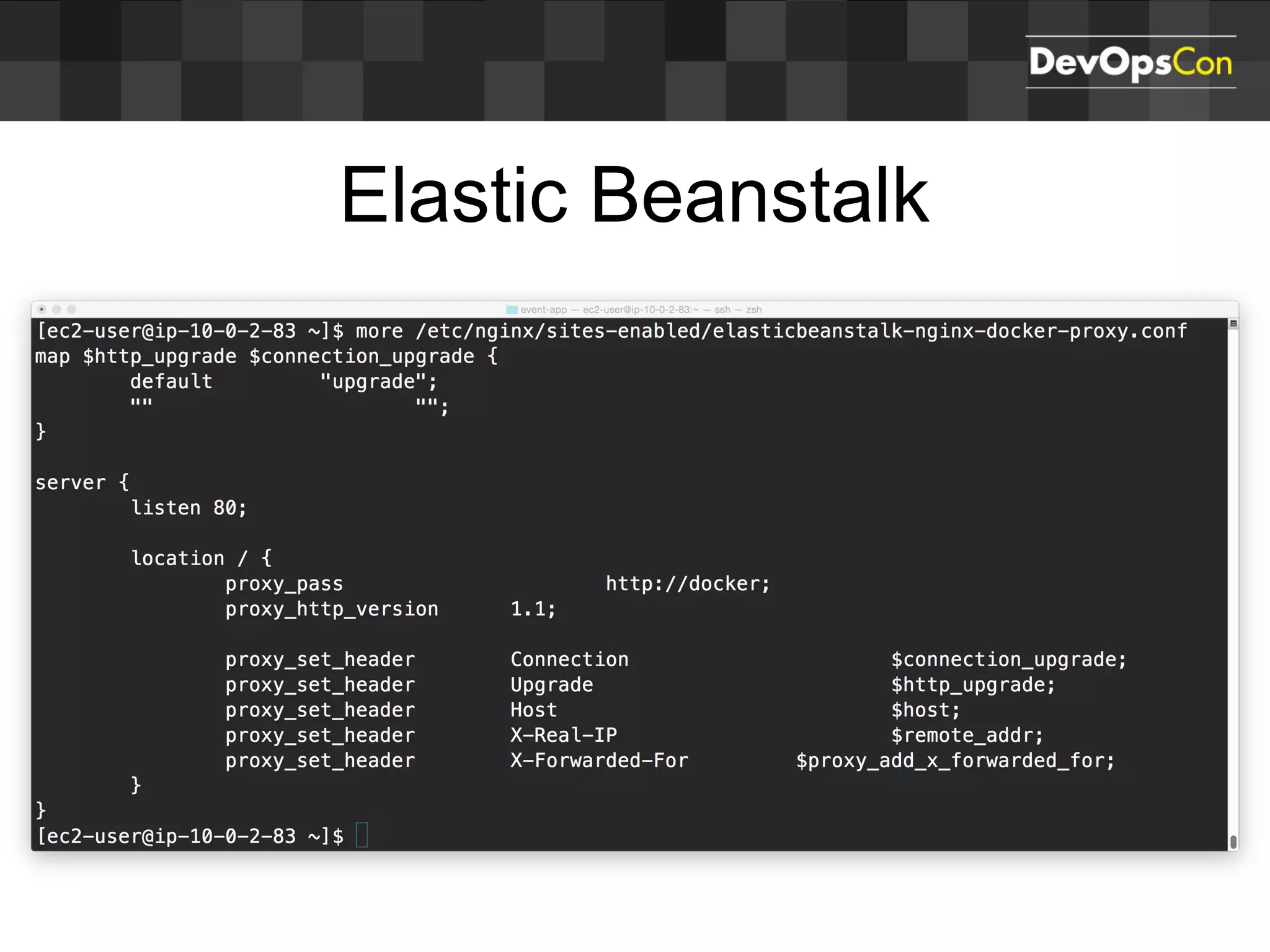
Sascha Möllering gave a presentation on deploying applications to the AWS cloud. He began with an overview of AWS services like EC2, S3, RDS and explained how to initially create a simple cloud service with one instance each for a web application and database. He then described how to improve the architecture by separating components, adding redundancy and elasticity using services like ELB, autoscaling and read replicas. Sascha demonstrated deploying a sample application built with JHipster and Docker to AWS Elastic Beanstalk, which handles running the containers and mapping environment variables for the database connection.