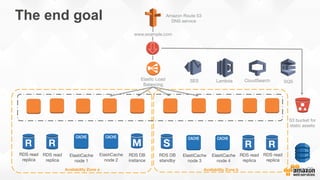
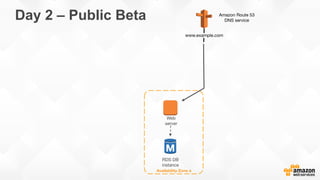
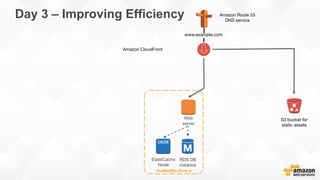
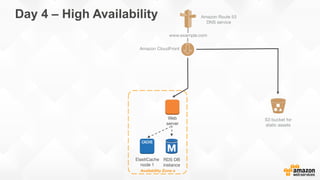
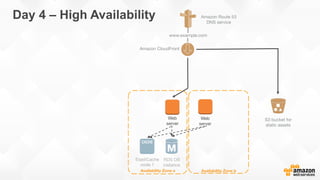
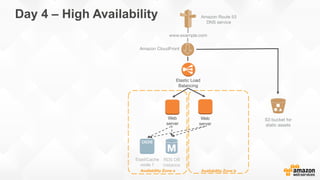
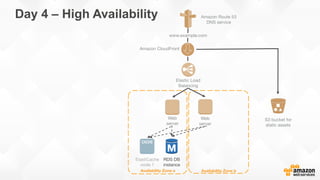
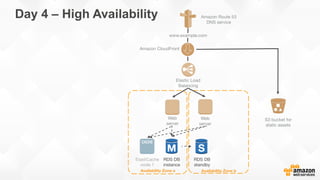
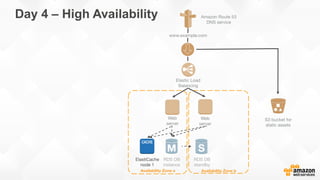
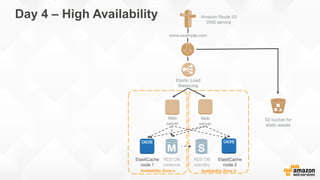
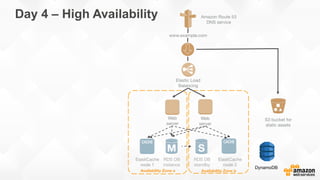
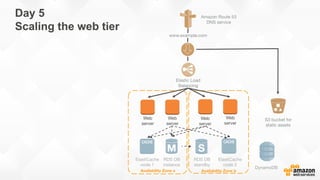
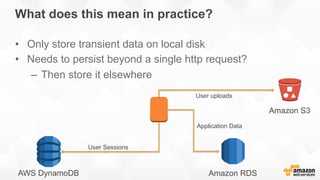
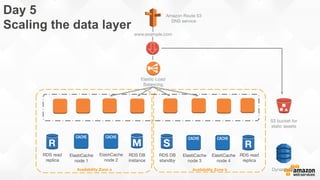
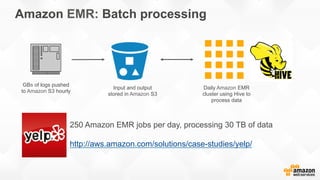
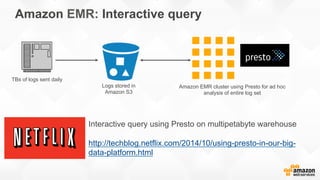
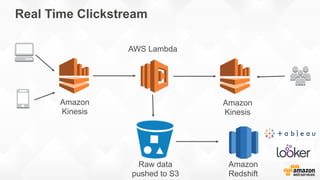
The document outlines strategies for building a scalable technology platform for startups, emphasizing the importance of avoiding over-engineering and utilizing a stateless architecture. Key components include using Amazon services like RDS, DynamoDB, and Elastic Load Balancing to support growth without performance degradation. It also highlights the necessity of simplifying operations with deployment tools and maintaining control over infrastructure while ensuring high availability and efficient resource management.