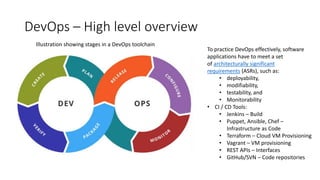
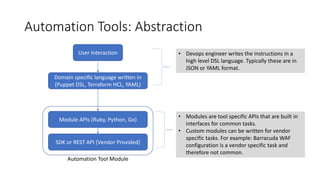
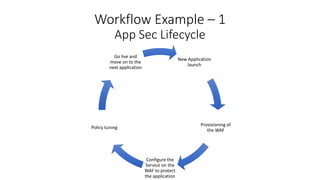
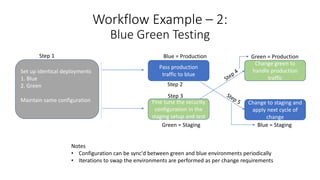
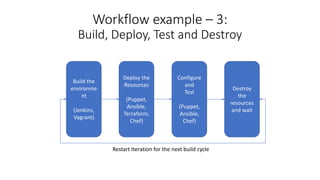
DevOps and DevSecOps tools and workflows were discussed. Key tools include Jenkins, Puppet/Ansible/Chef, and Terraform. DevSecOps incorporates security testing. Automation tools use domain-specific languages and modules to abstract common tasks. Example workflows covered blue-green deployment testing, building/deploying/testing environments then destroying them, and managing application security through a WAF using its REST API.