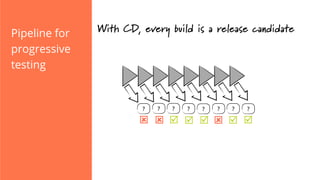
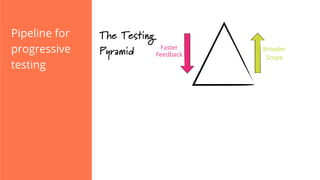
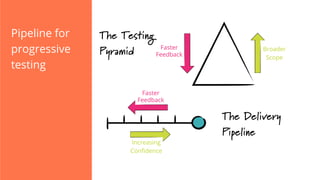
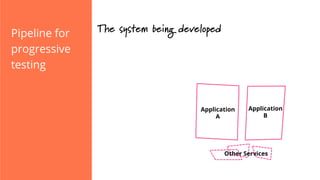
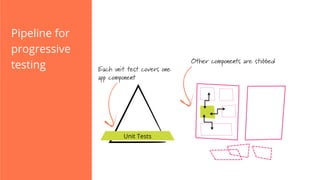
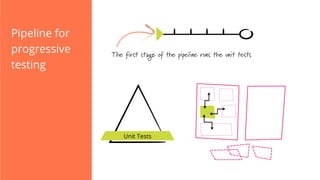
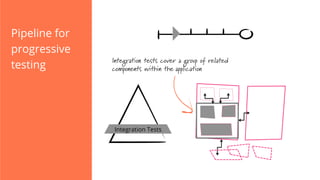
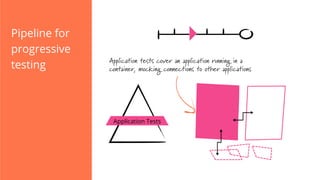
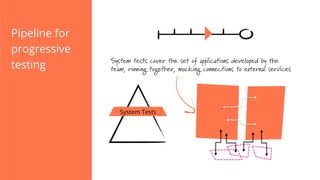
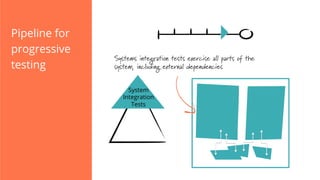
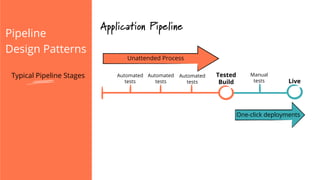
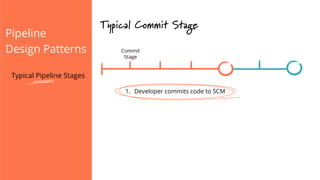
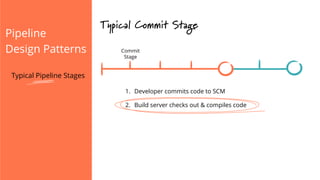
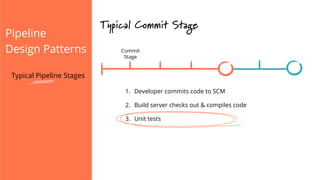
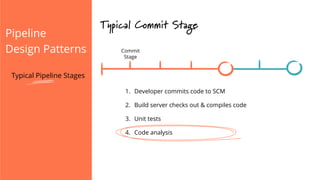
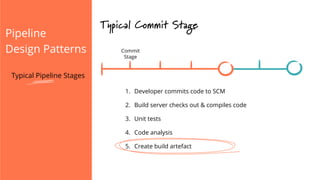
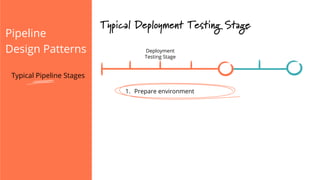
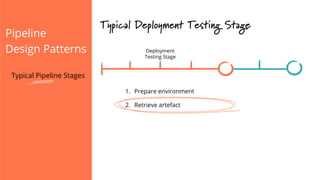
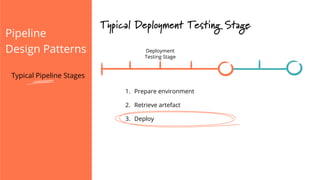
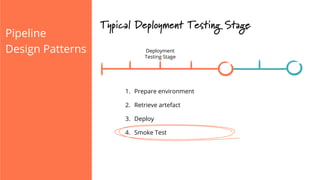
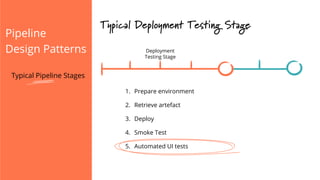
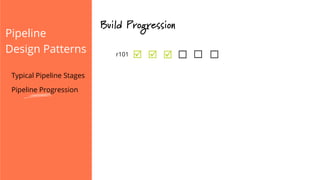
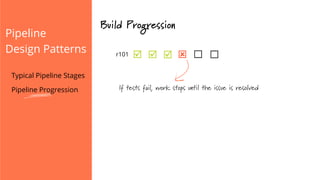
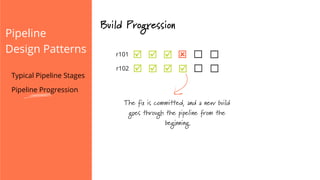
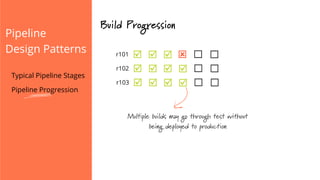
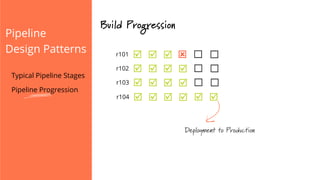
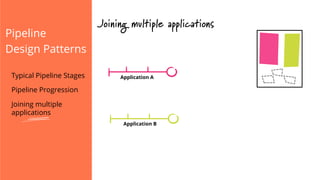
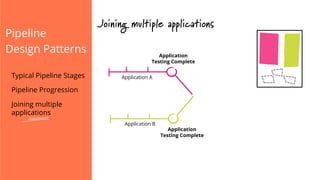
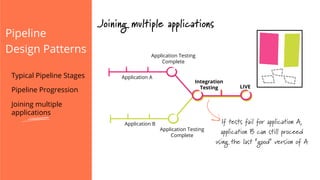
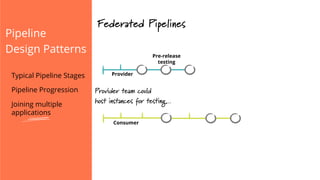
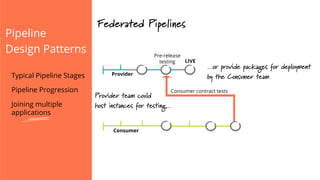
The document discusses the implementation of continuous delivery (CD) through a structured pipeline approach that emphasizes progressive testing at multiple stages, including unit tests, integration tests, and system tests. It outlines best practices for pipeline design, such as keeping everything in source control and deploying consistently, while also addressing the coordination of multiple applications within a single pipeline. The content culminates in a call to action for utilizing tools to facilitate efficient continuous delivery processes.