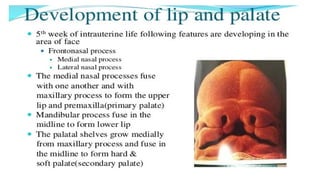
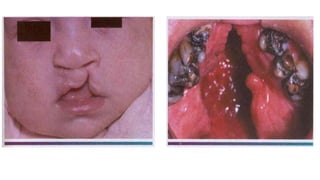
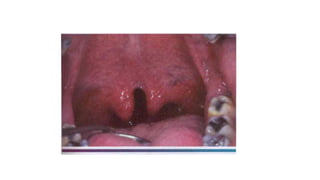
The document details various developmental disturbances affecting the lip and palate, including conditions such as Van der Woude’s syndrome and cleft lip/palate malformations, their etiology, clinical features, and associated treatments. It also discusses lesser-known conditions like cheilitis glandularis and cheilitis granulomatosa, highlighting their symptoms, differential diagnoses, and treatment options. The information presented emphasizes the genetic factors, developmental disruptions, and the importance of surgical interventions in these congenital conditions.