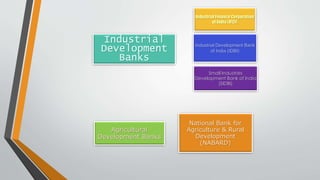
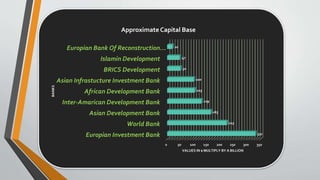
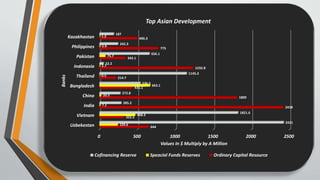
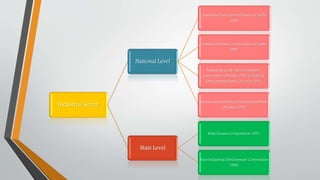
Development banking in India began post-World War II to finance the reconstruction of industries and buildings, addressing the country's backward economy at independence. Key institutions such as the Industrial Financial Corporation of India and the Industrial Development Bank of India were established to promote industrial and agricultural development. The primary objectives of development banking include fostering small and large-scale industries, enhancing foreign trade, supporting entrepreneurs, and promoting economic activities in underdeveloped regions.