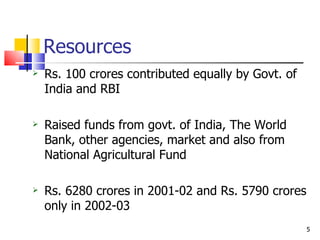
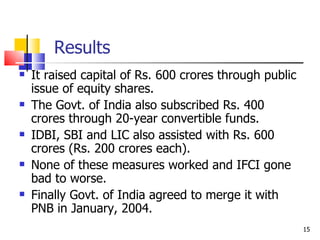
The document discusses several development banks in India:
1. NABARD was established in 1982 as the apex development bank for agriculture and rural development. It provides refinancing and long-term loans to cooperatives and rural institutions.
2. IFCI was established in 1948 to finance large-scale industries. It grants long and medium term loans but faced financial difficulties due to poor lending decisions.
3. IDBI was established in 1964 to provide long-term financing to industry. It offers various types of loans and assistance to promote industrial development.