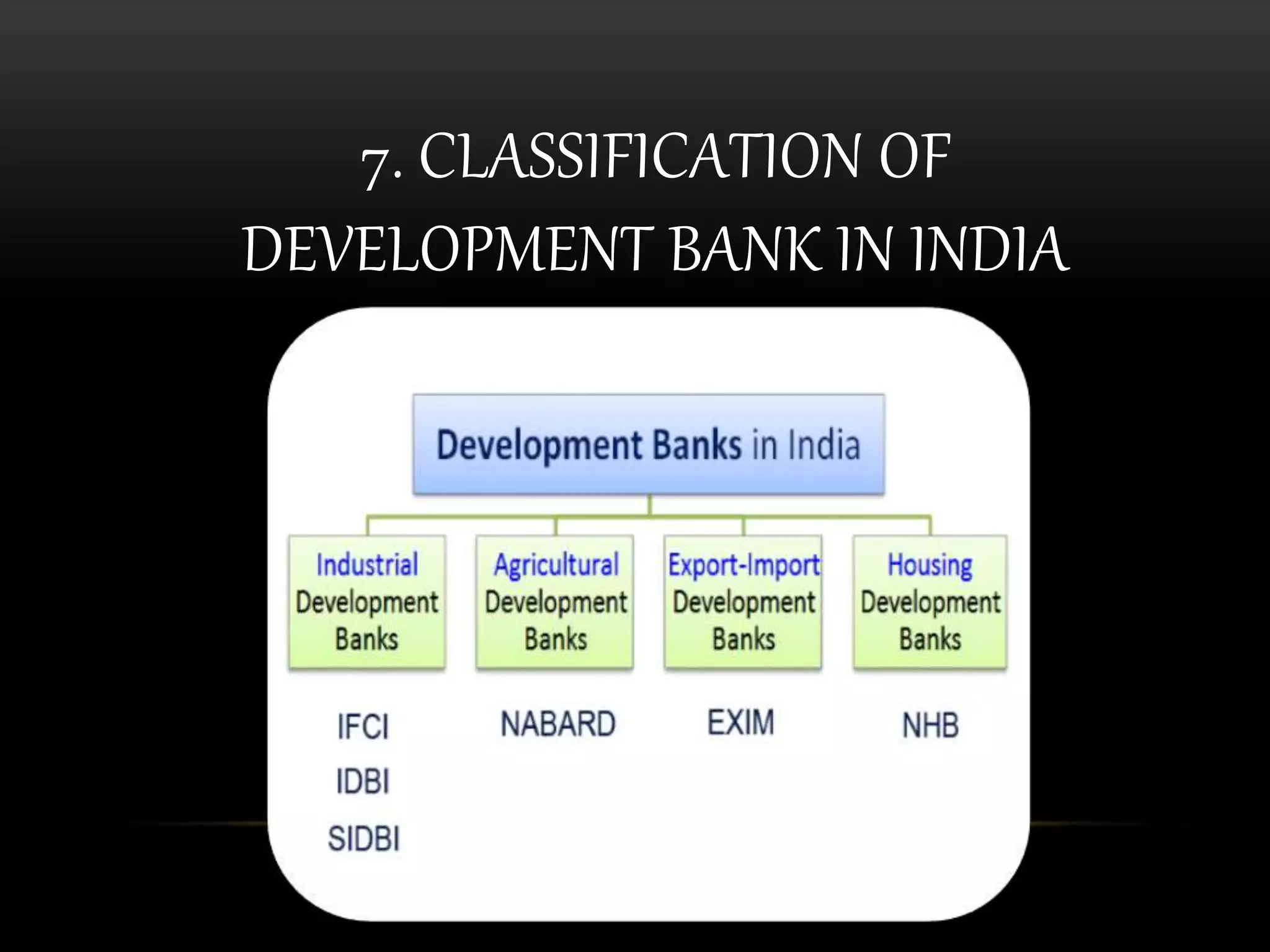
This document provides an overview of development banks in India. It defines development banks as specialized financial institutions that provide medium and long-term financing to sectors like agriculture, industry, and infrastructure. It then classifies and describes several major development banks in India, including the Industrial Development Bank of India, National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development, Small Industries Development Bank of India, and Export-Import Bank of India, and outlines their key functions in promoting sectors like small businesses, housing, agriculture, and foreign trade.