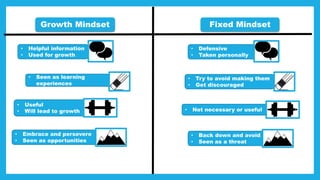
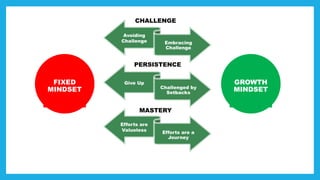
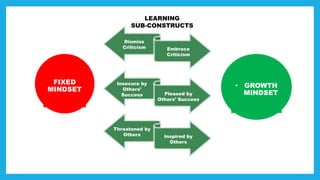
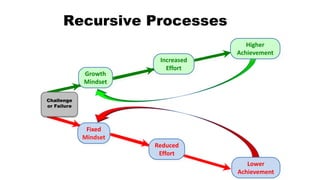
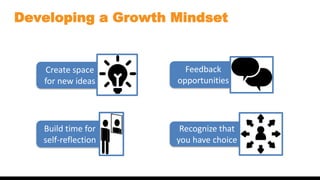
The document discusses the concept of mindset, particularly focusing on the difference between fixed and growth mindsets, and their implications on personal and professional success. It emphasizes that a growth mindset, which sees abilities as developable through effort and learning, can enhance productivity and motivation in the workplace. Additionally, it outlines strategies for developing a growth mindset, such as embracing challenges, learning from failures, and providing constructive feedback.