1) A study examined using blended problem-based learning with 124 nursing students across 5 groups to develop higher-order thinking.
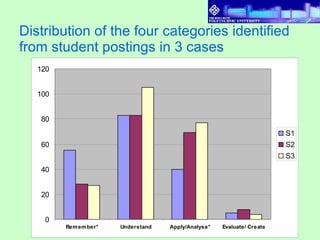
2) Students discussed 3 patient cases online by posting topics, issues, and hypotheses. Discussions were categorized according to Bloom's taxonomy.
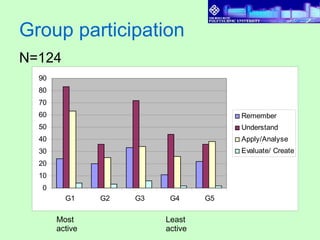
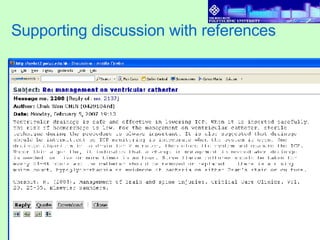
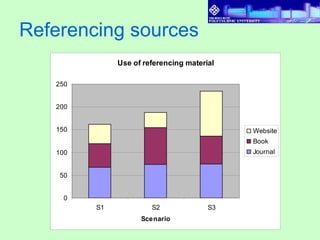
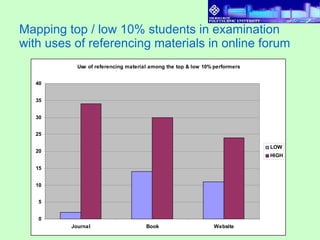
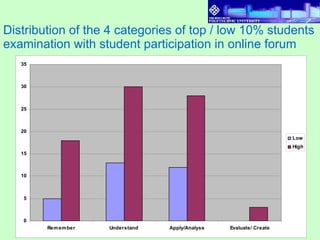
3) Results found that students had varying levels of participation. Discussions also varied between cases, with more complex categories like "apply and analyze" increasing across cases. Higher performing students referenced sources more in discussions.