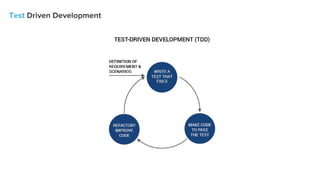
Testing is important for project quality and reliability. Unit tests check individual code units for correct functionality, are fast and independent. Behavior-driven development (BDD) applies business needs through scenarios defined in Gherkin. Test doubles replace code to independently test objects like dummies, fakes, stubs and mocks. Integration tests check connections between components while acceptance tests check overall project behavior from the user perspective, ensuring expected functionality but are slower and require more maintenance.