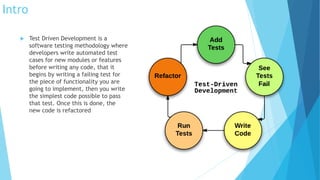
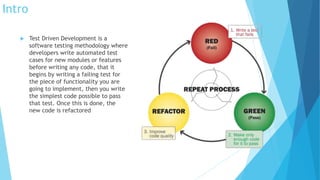
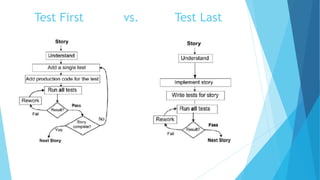
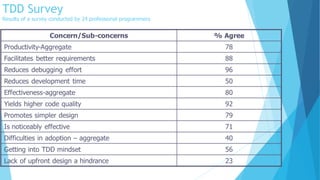
Test Driven Development (TDD) is a software testing methodology where developers write automated test cases before writing any code. It involves writing a failing test case for new functionality, then writing the minimum amount of code to pass that test, and refactoring the code. Key steps are to add a test, run all tests and see the new one fail, write code to pass the test, run tests to succeed, and refactor code while maintaining tests. Benefits include instant feedback, better code quality, and lower rework effort. Limitations include difficulty testing certain types of code like GUIs. Unit testing tests individual units of code in isolation through mocking of external dependencies.