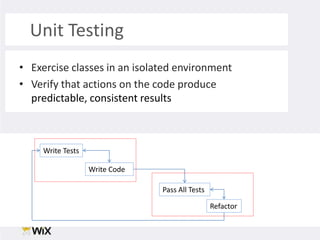
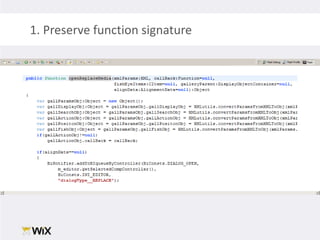
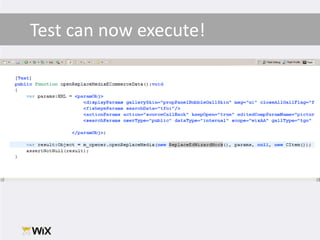
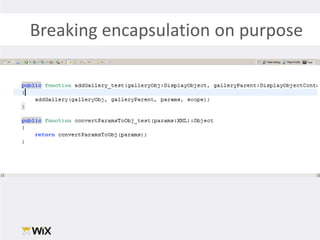
1. The document discusses techniques for testing legacy production code that was not originally written with testability in mind. This includes unit testing, which allows verifying code works as expected in isolation, and writing tests before making changes to help preserve existing behavior.
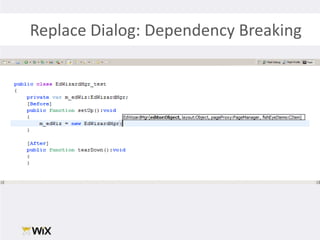
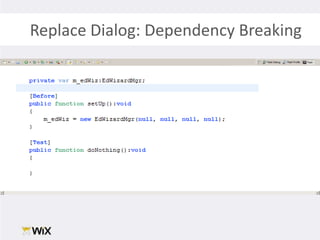
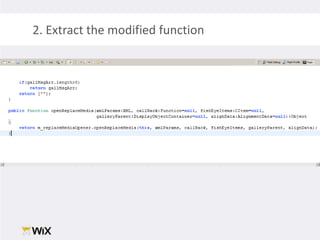
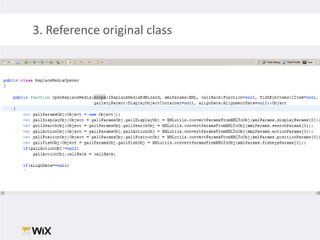
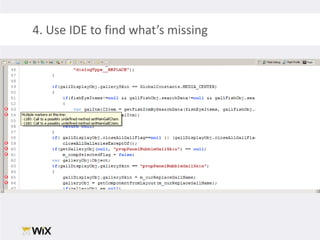
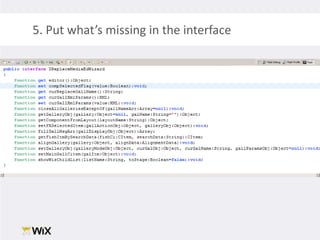
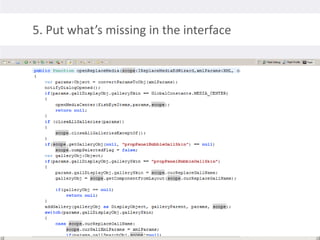
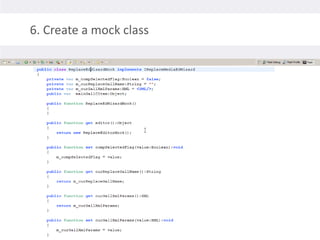
2. Testing legacy code can be challenging as the code may have dependencies that are hard to isolate for testing purposes. Techniques to address this include extracting functions to new classes, replacing static dependencies with interfaces, and overriding classes to inject test dependencies.
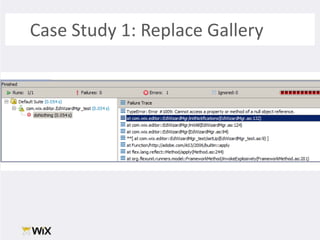
3. While testing legacy code requires more initial work, it provides long-term benefits like reducing defects, empowering refactoring, and creating a safety net for future changes. The document provides a case study and