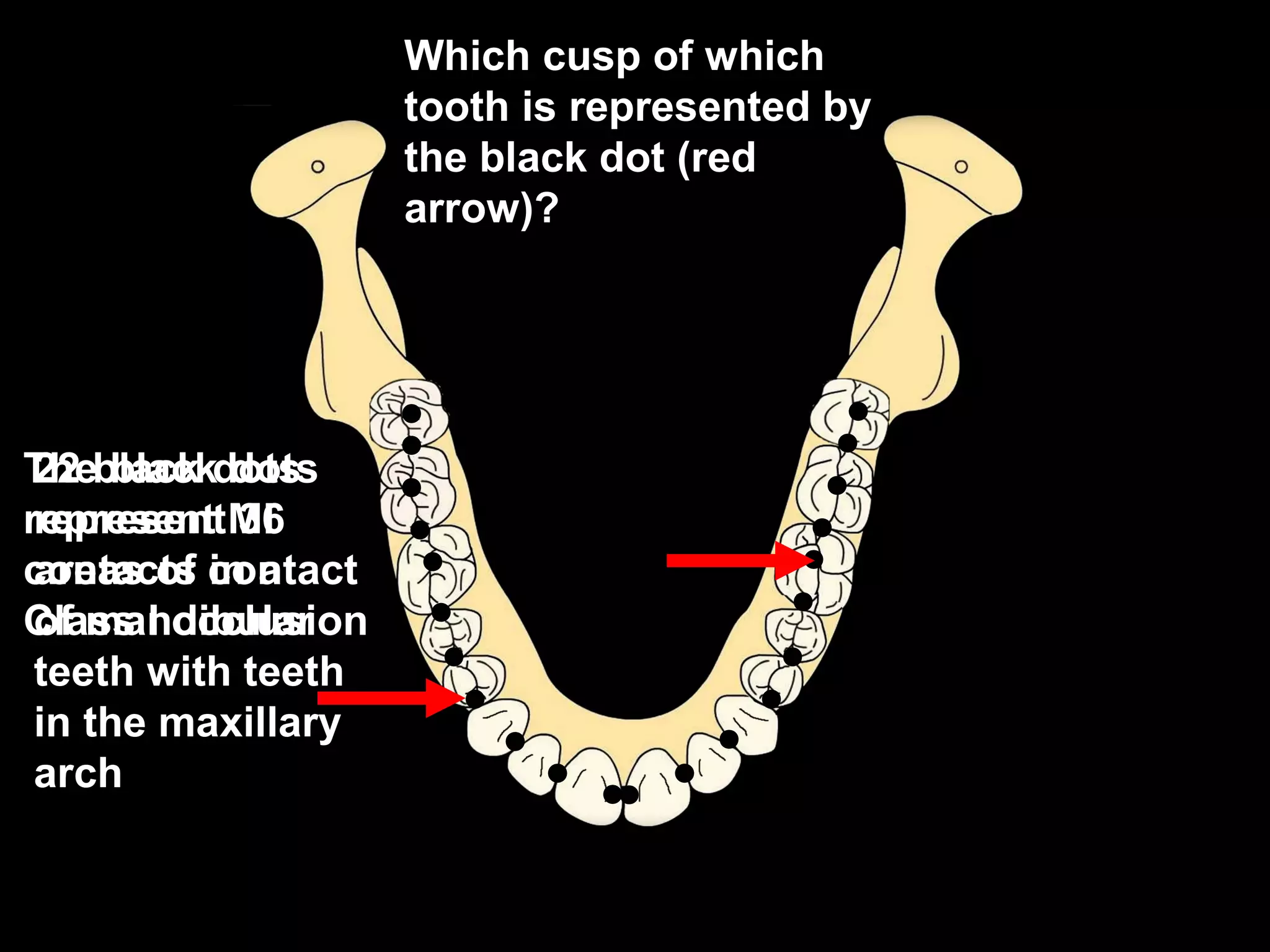
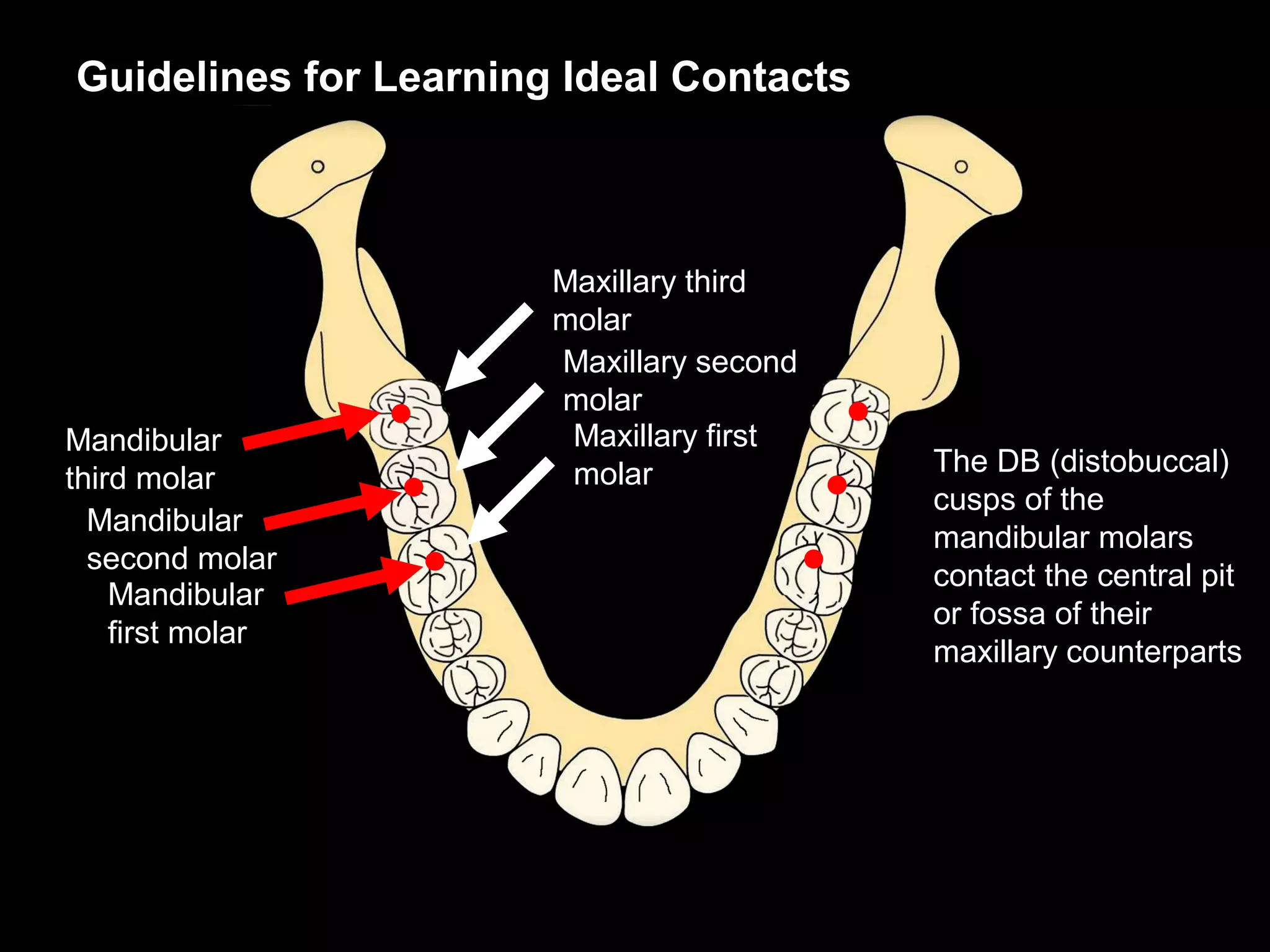
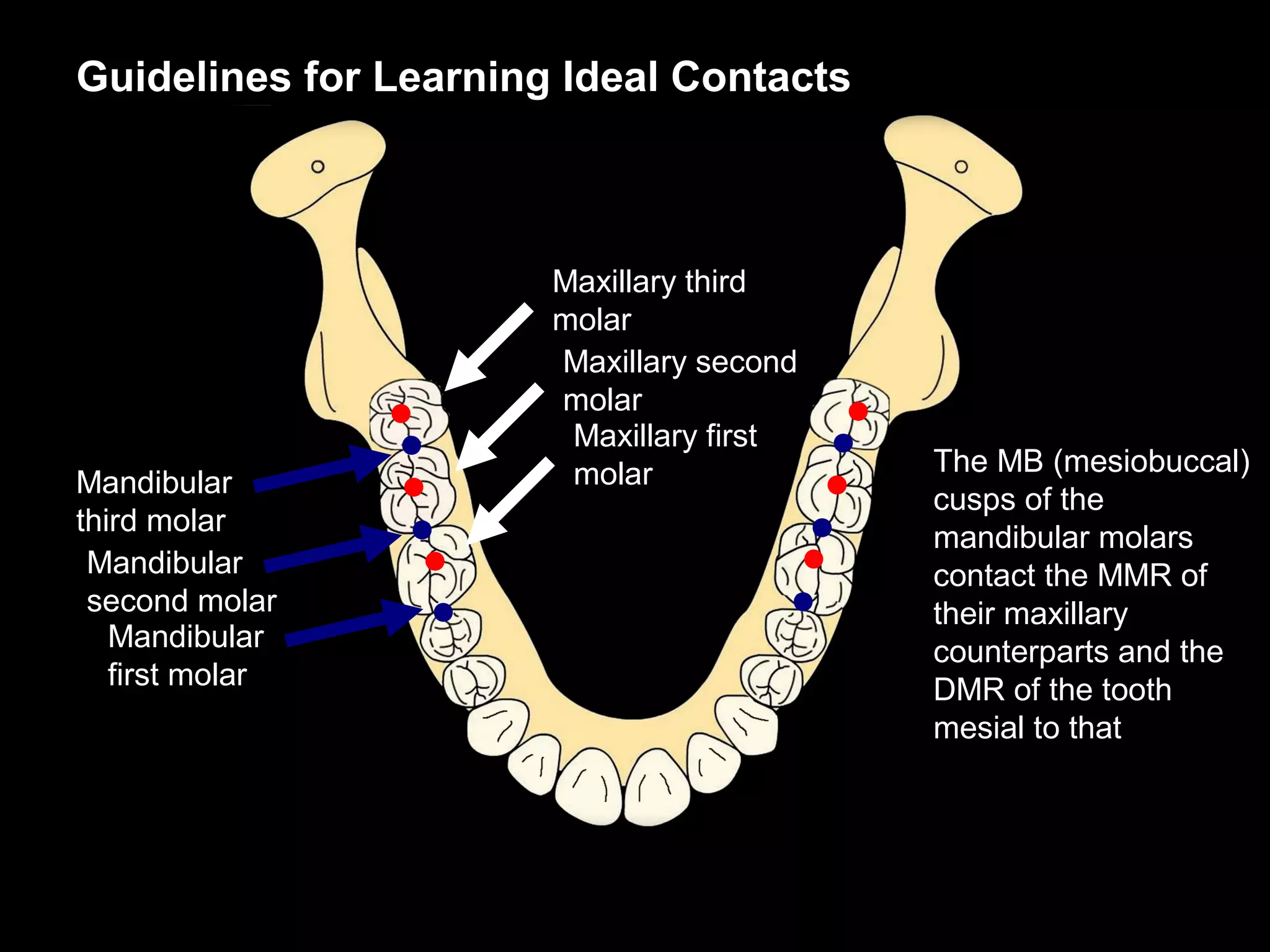
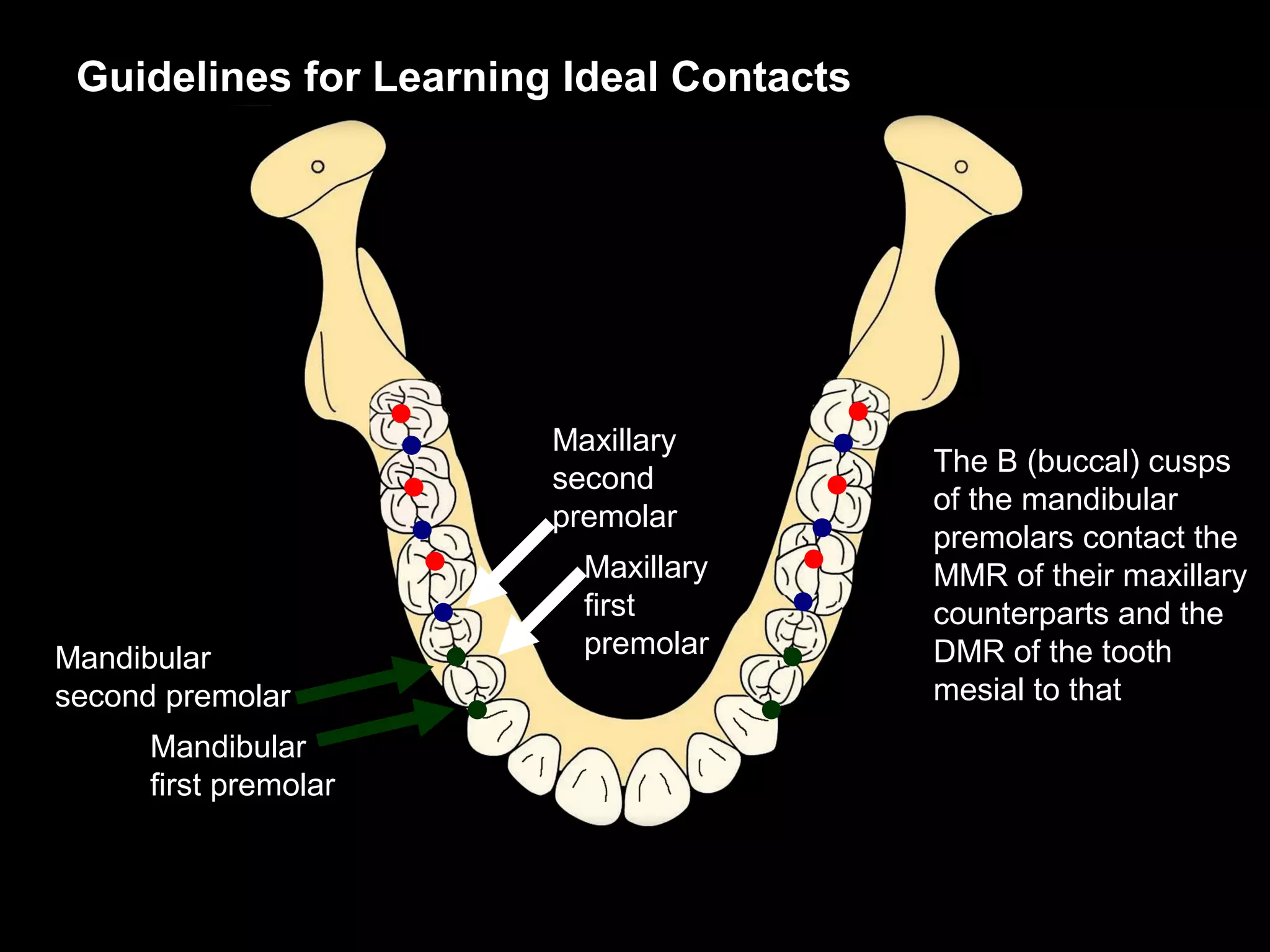
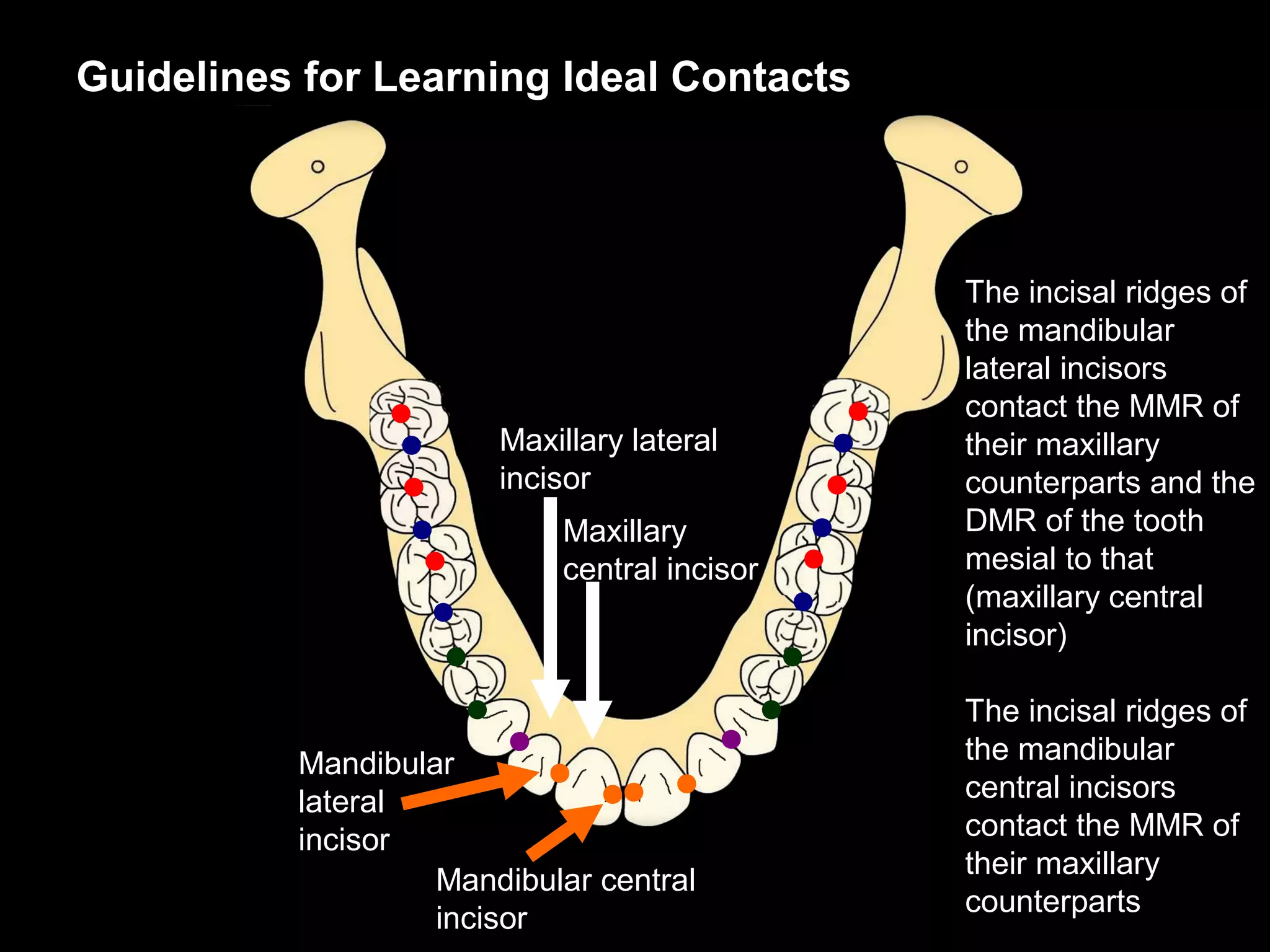
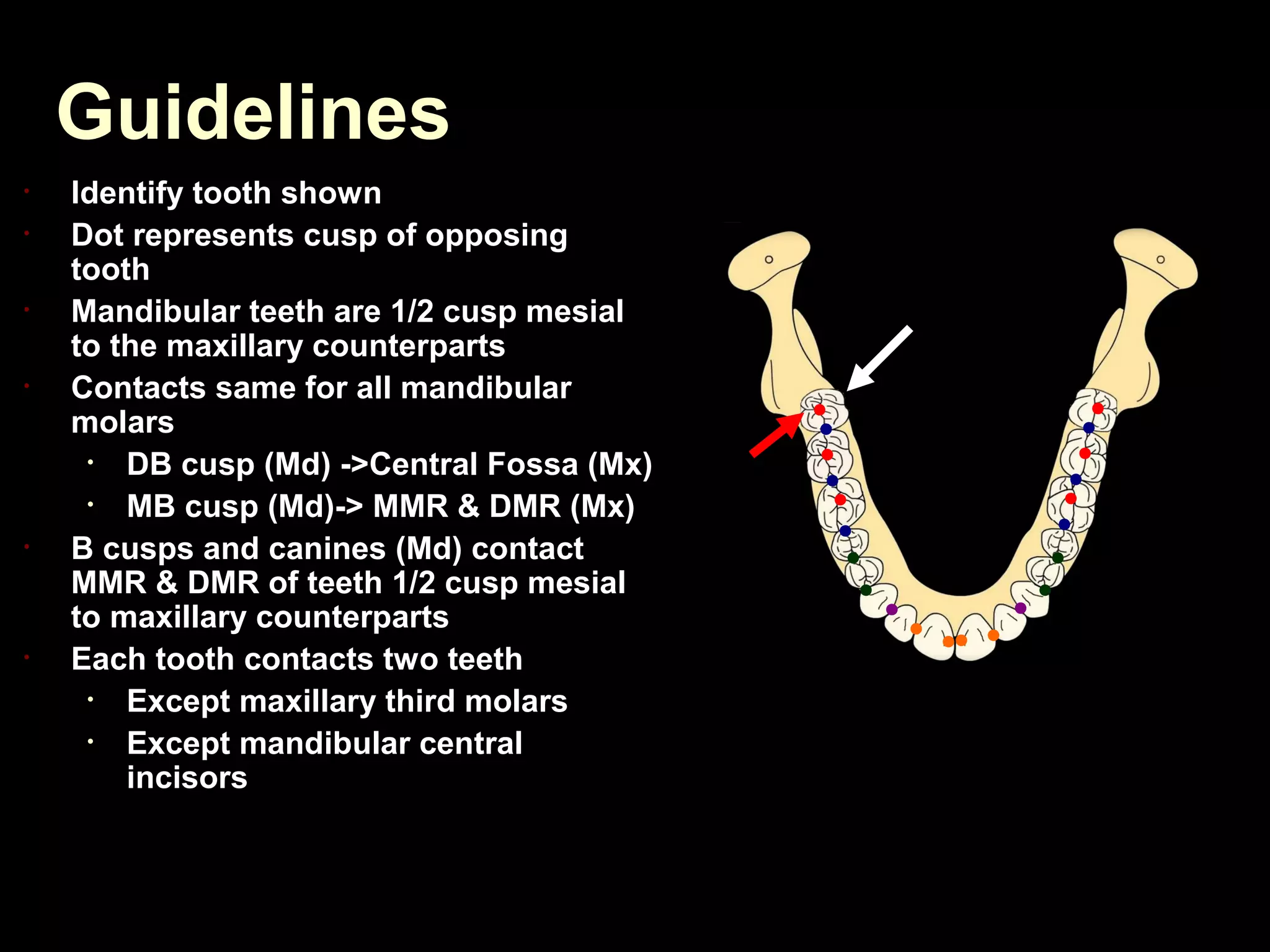
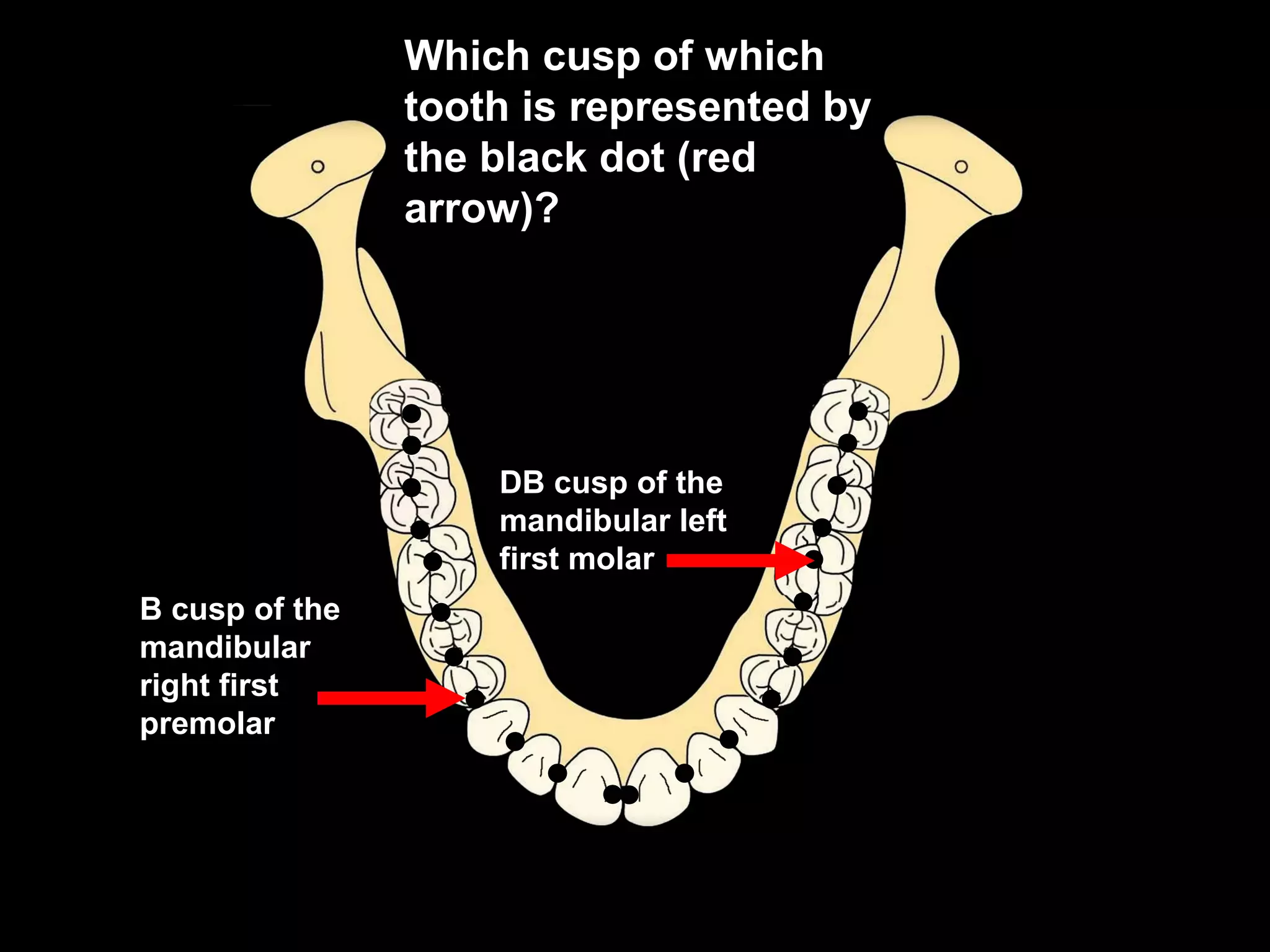
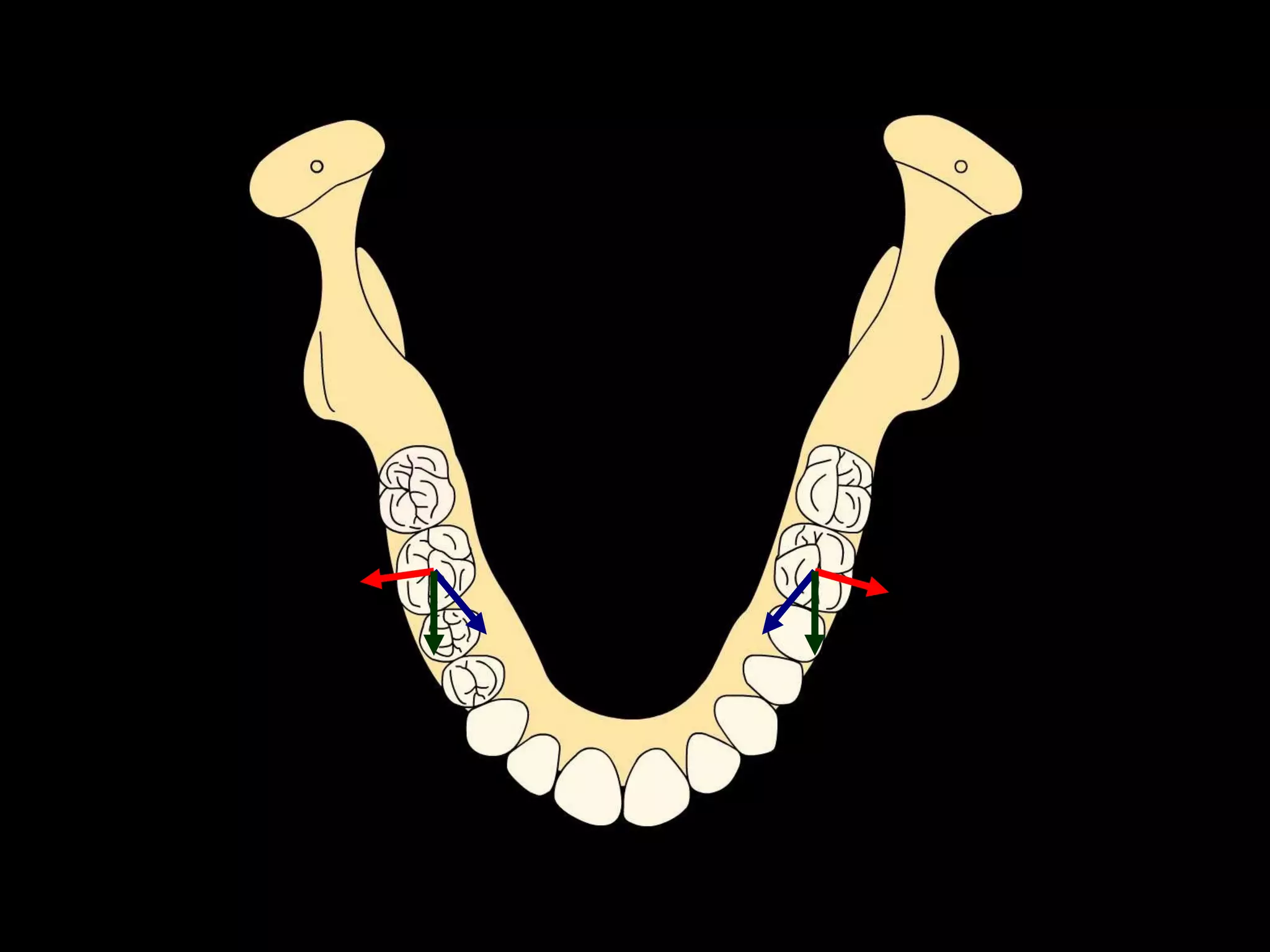
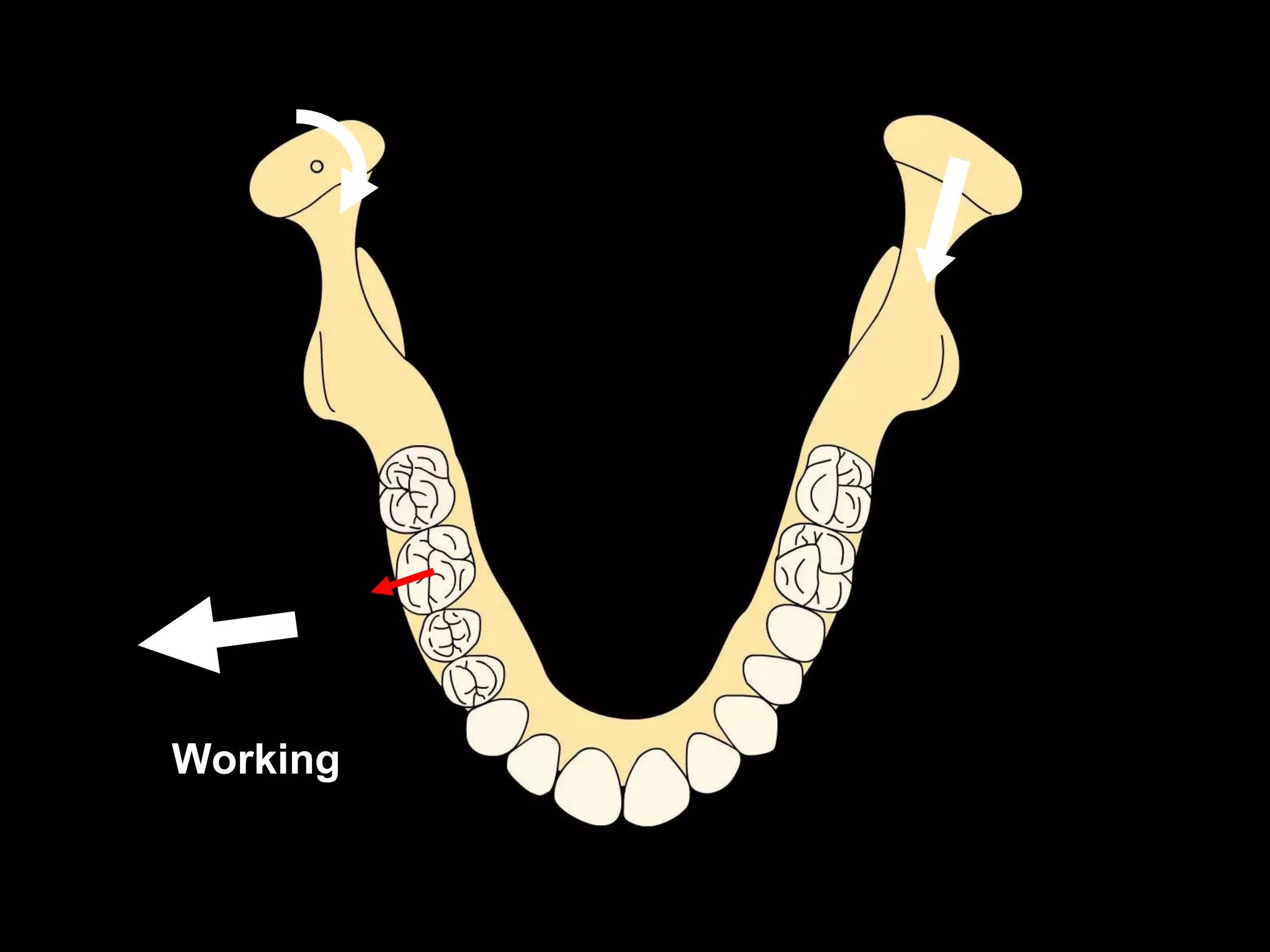
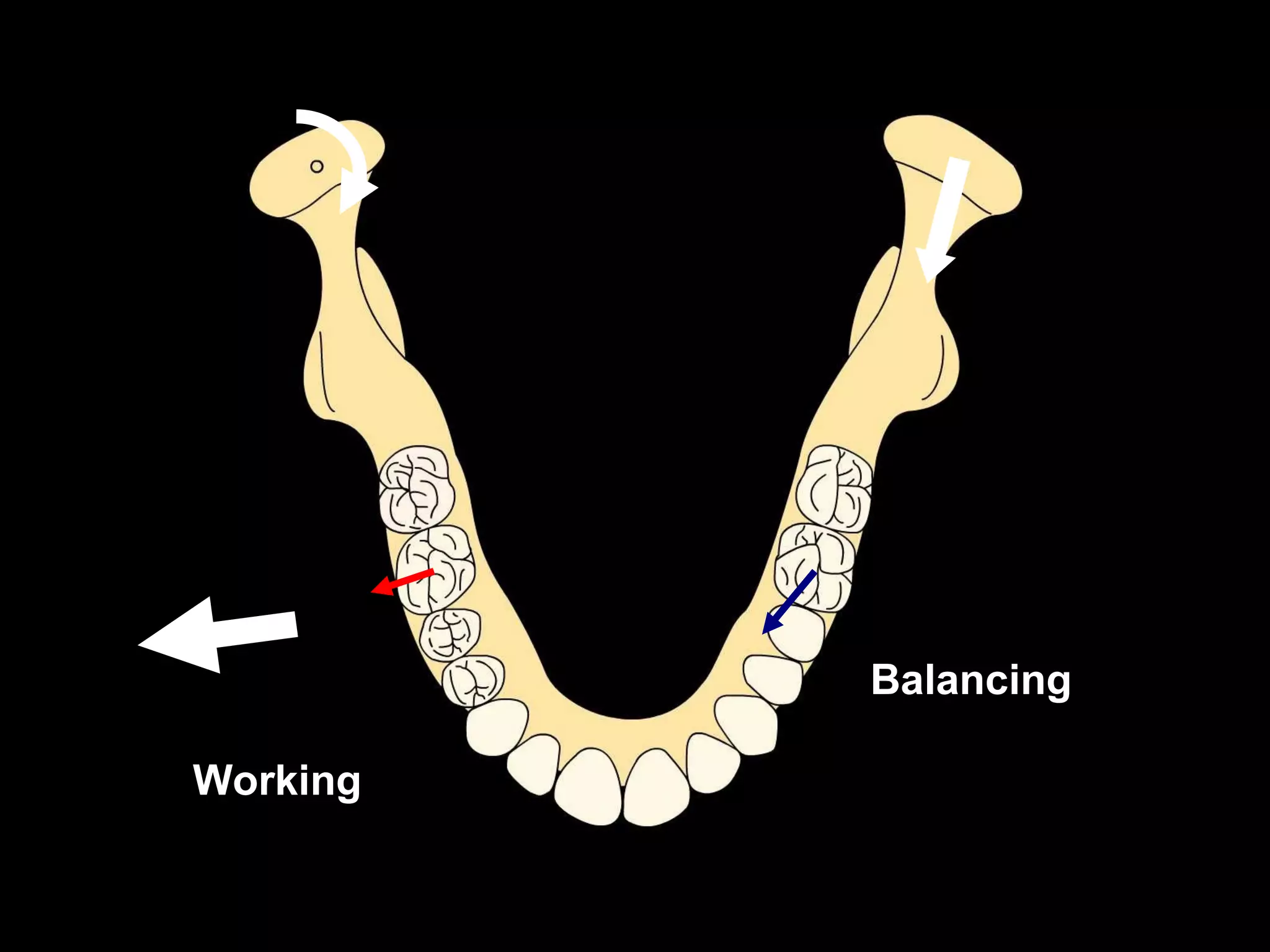
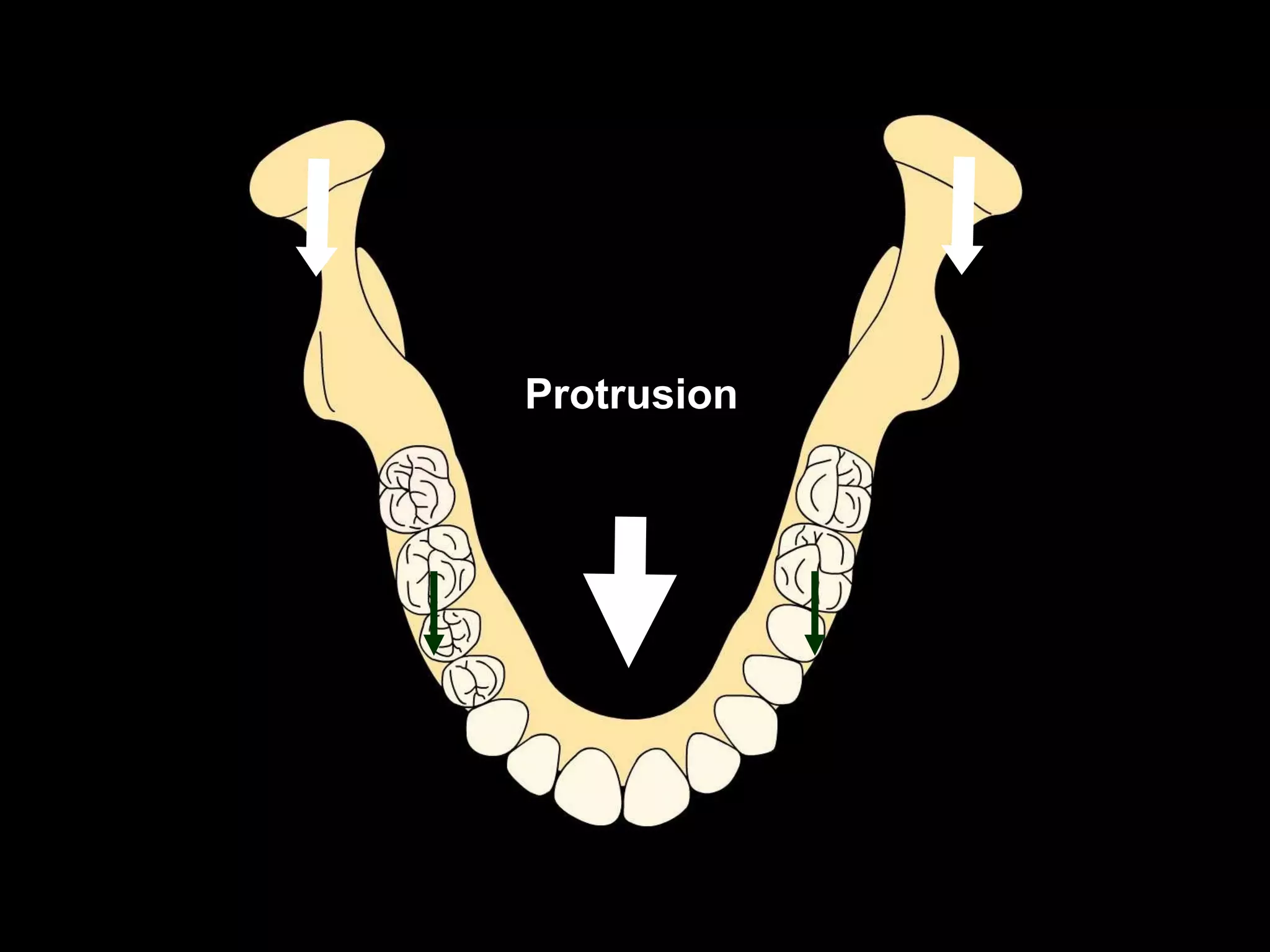
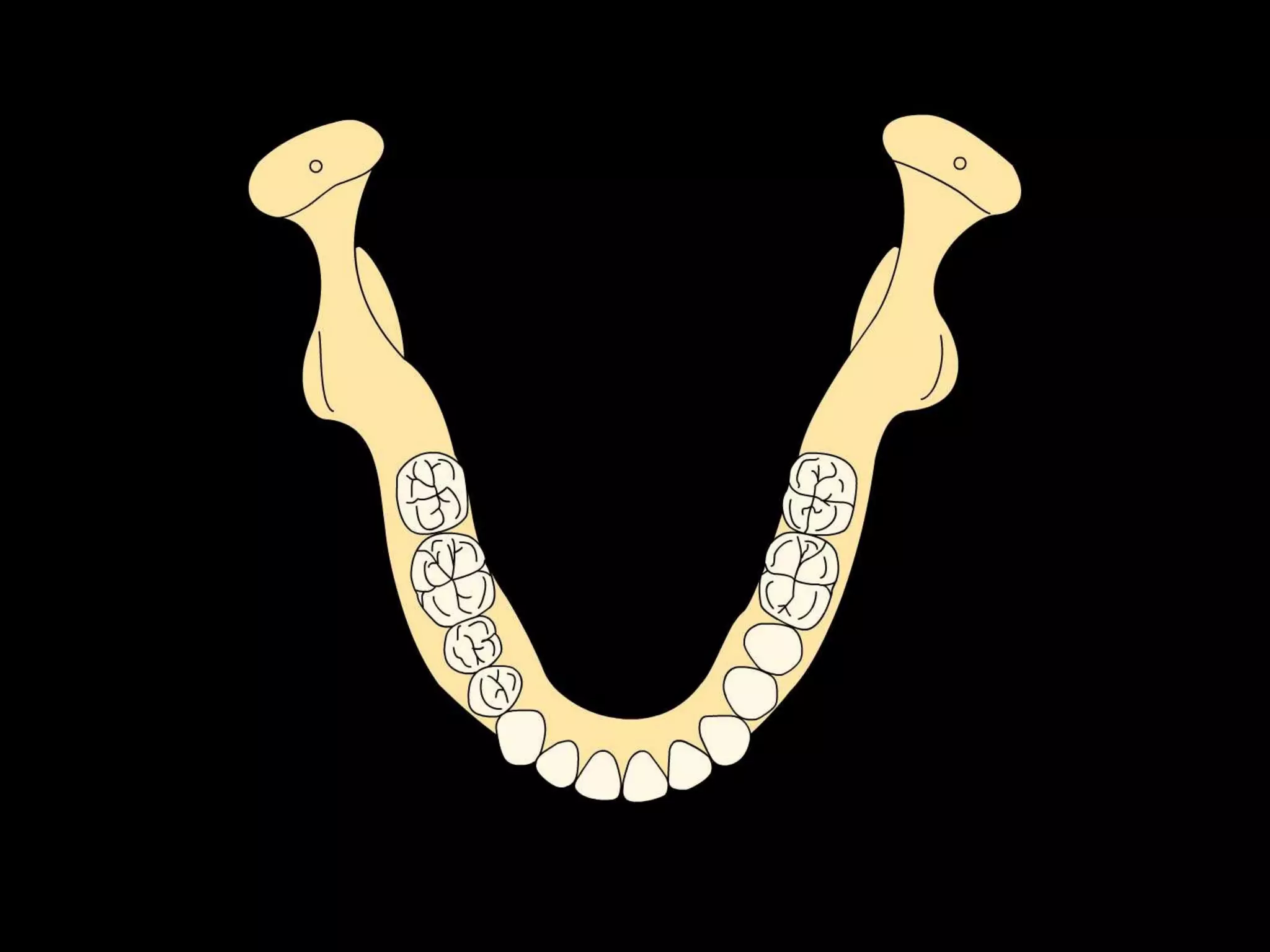
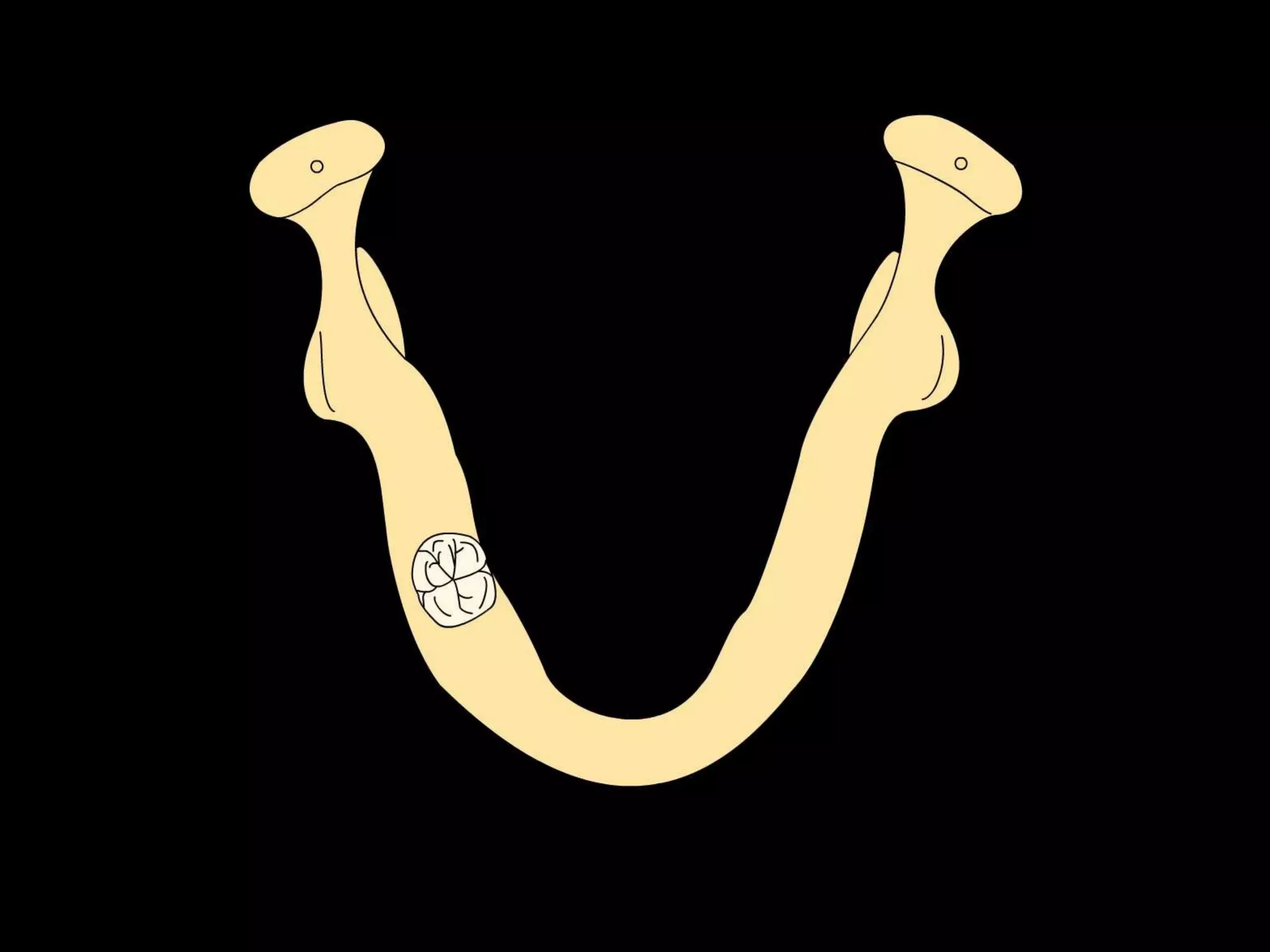
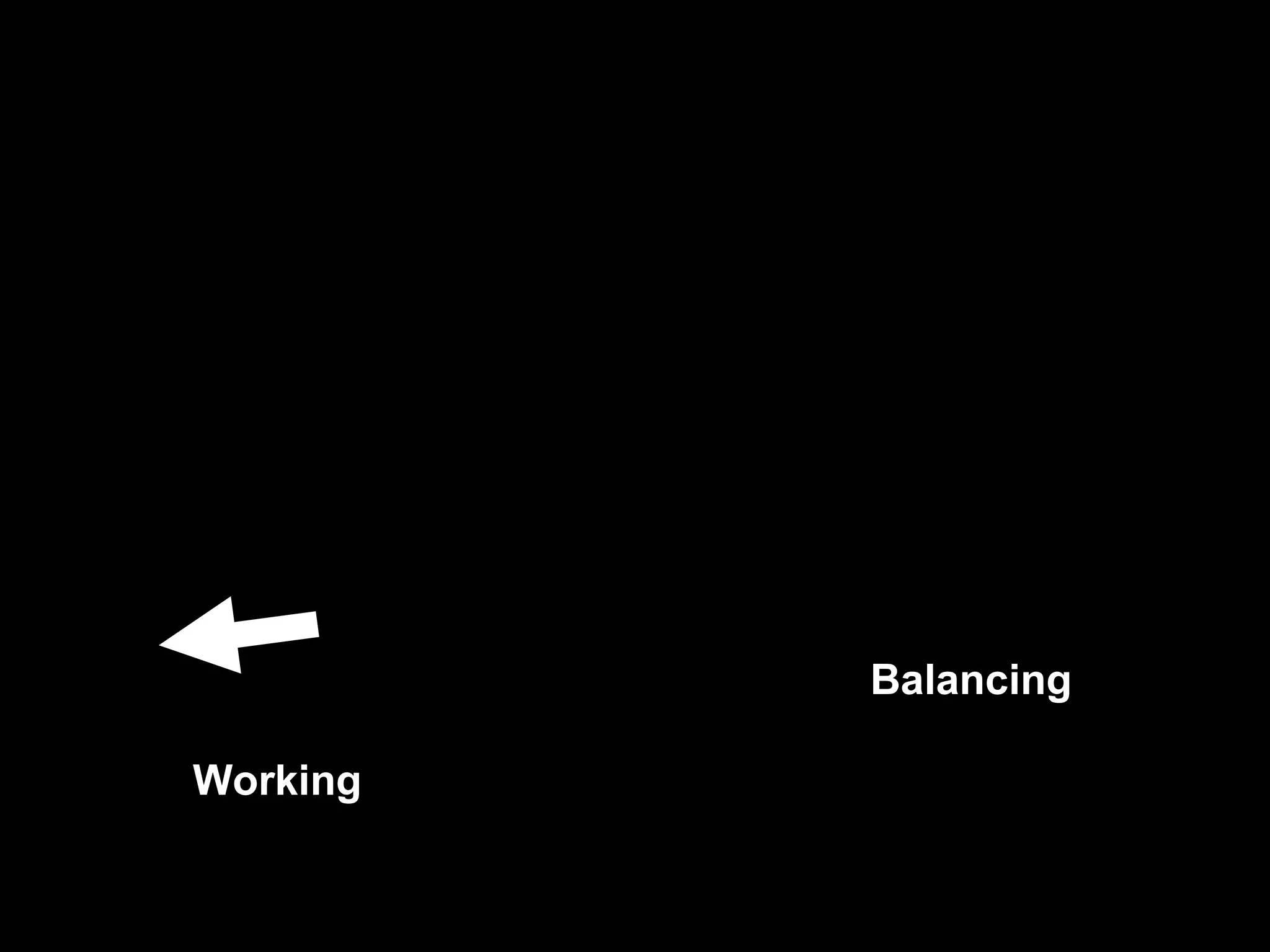
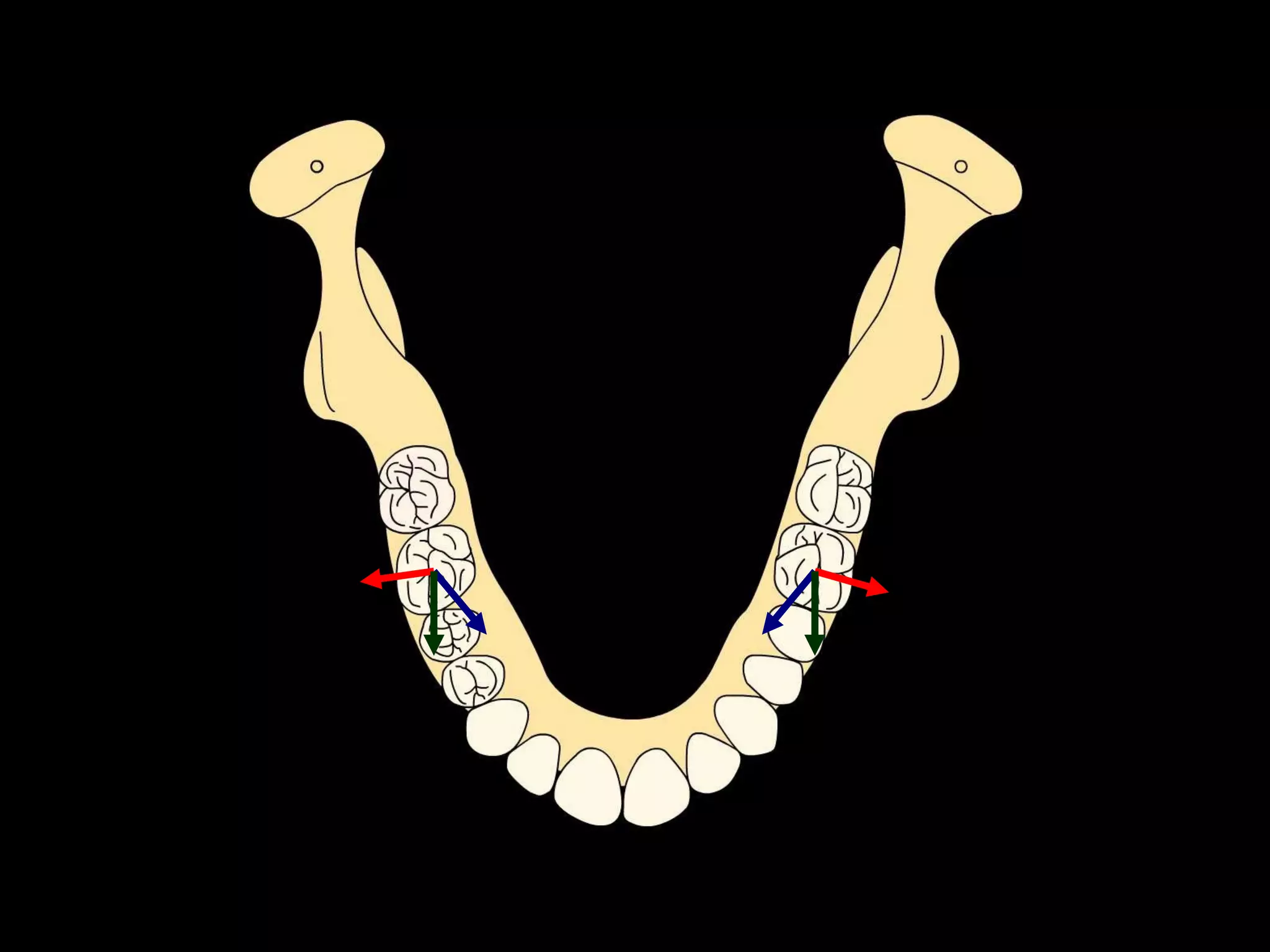
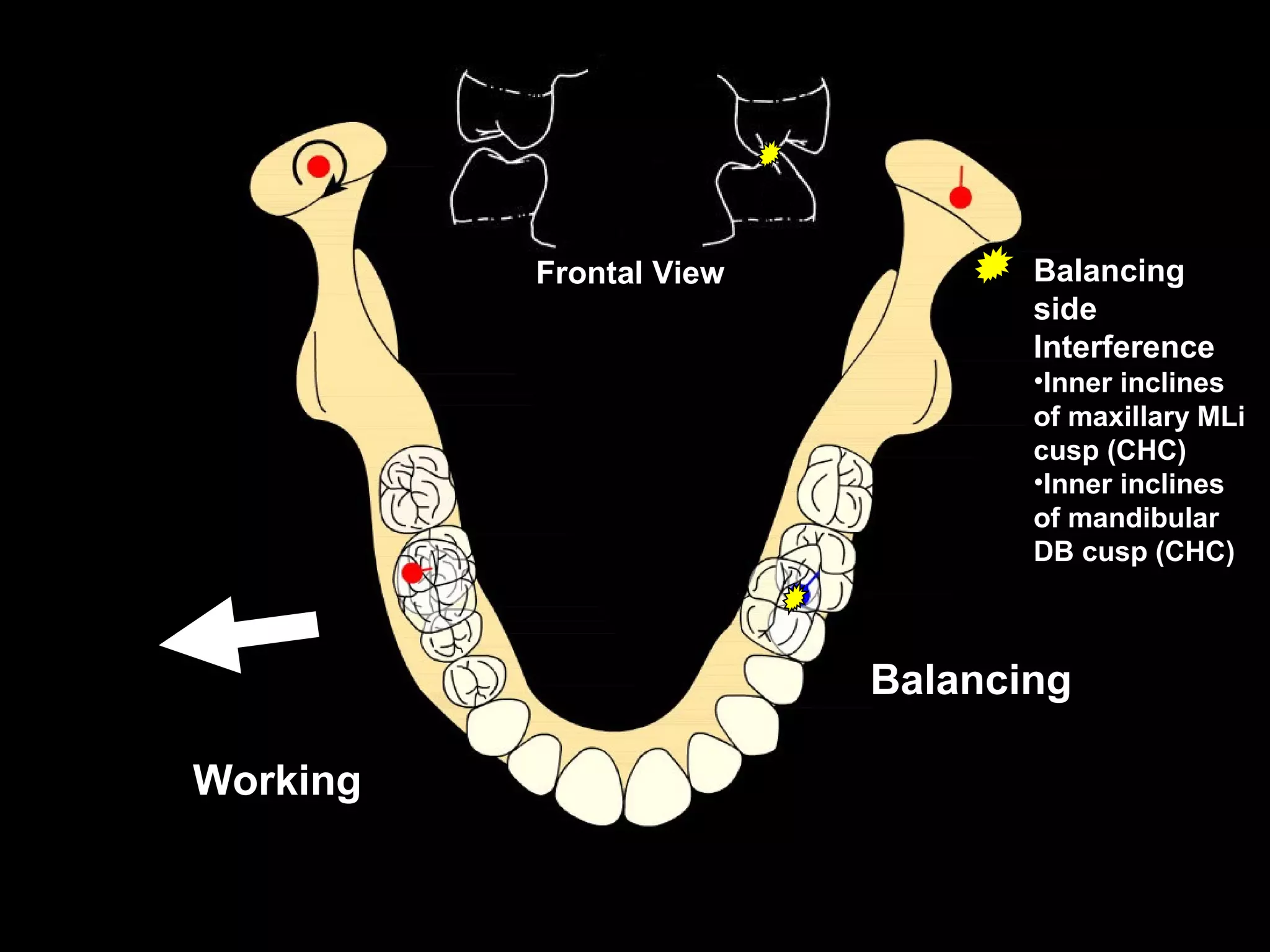
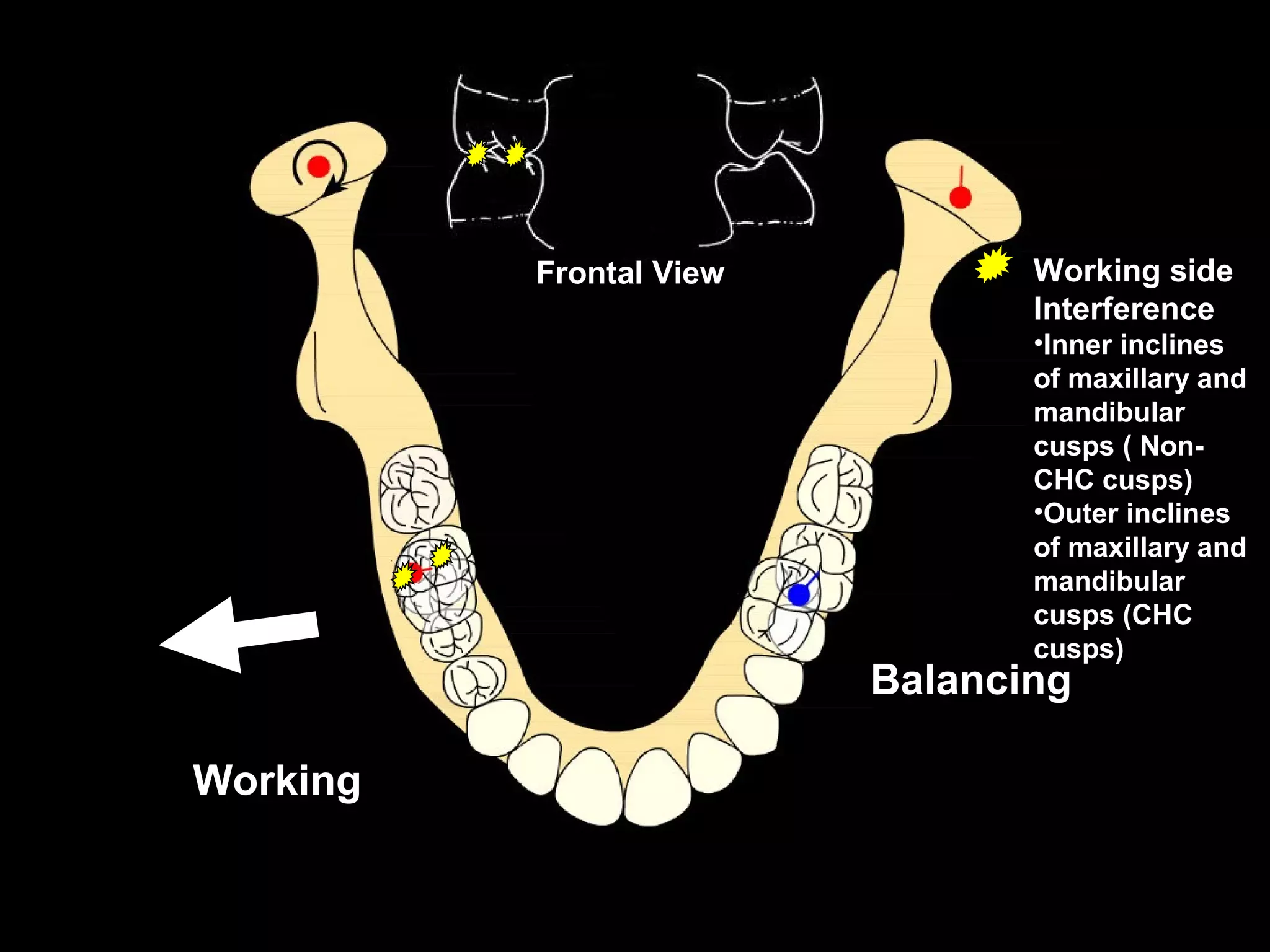
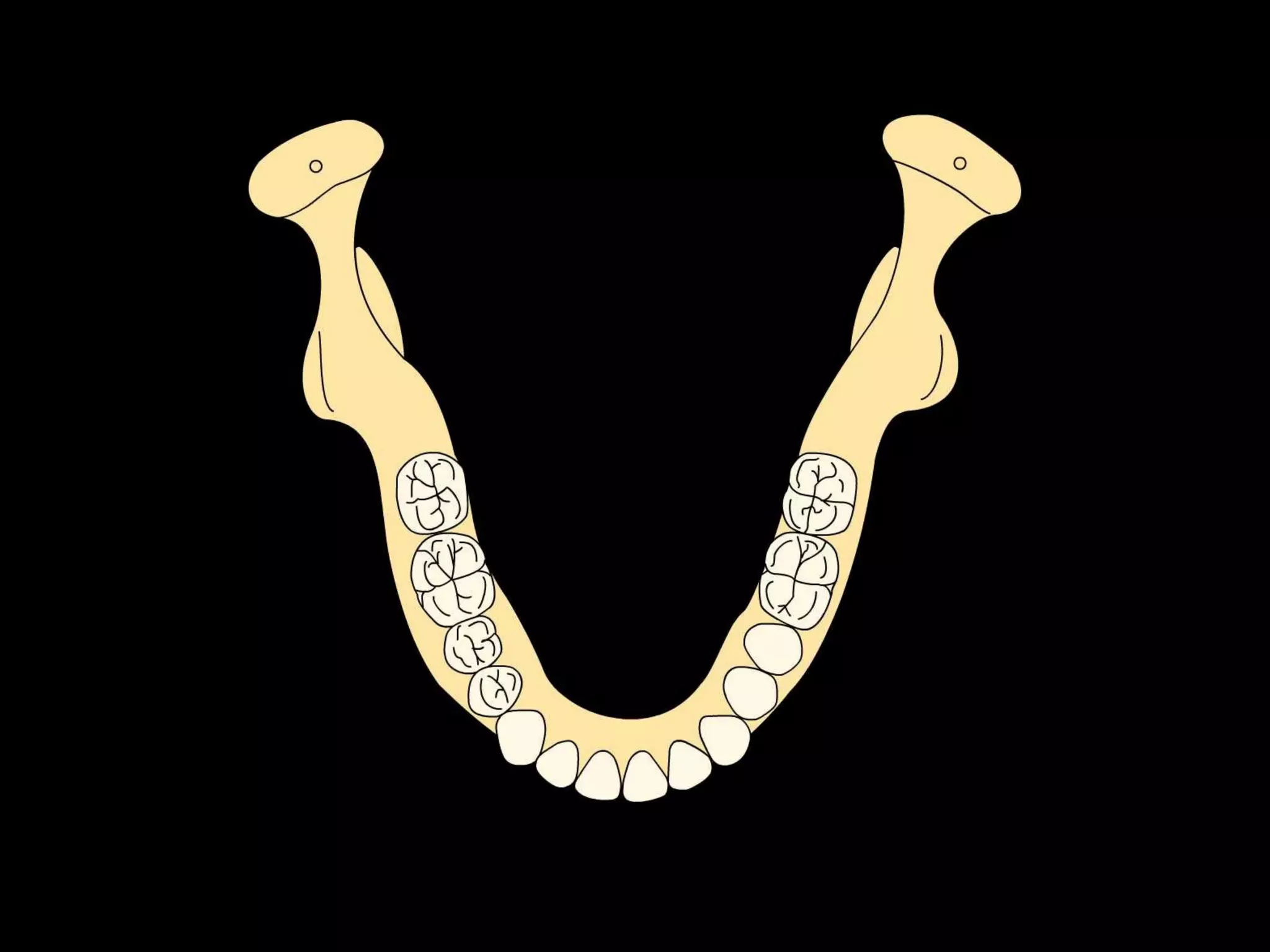
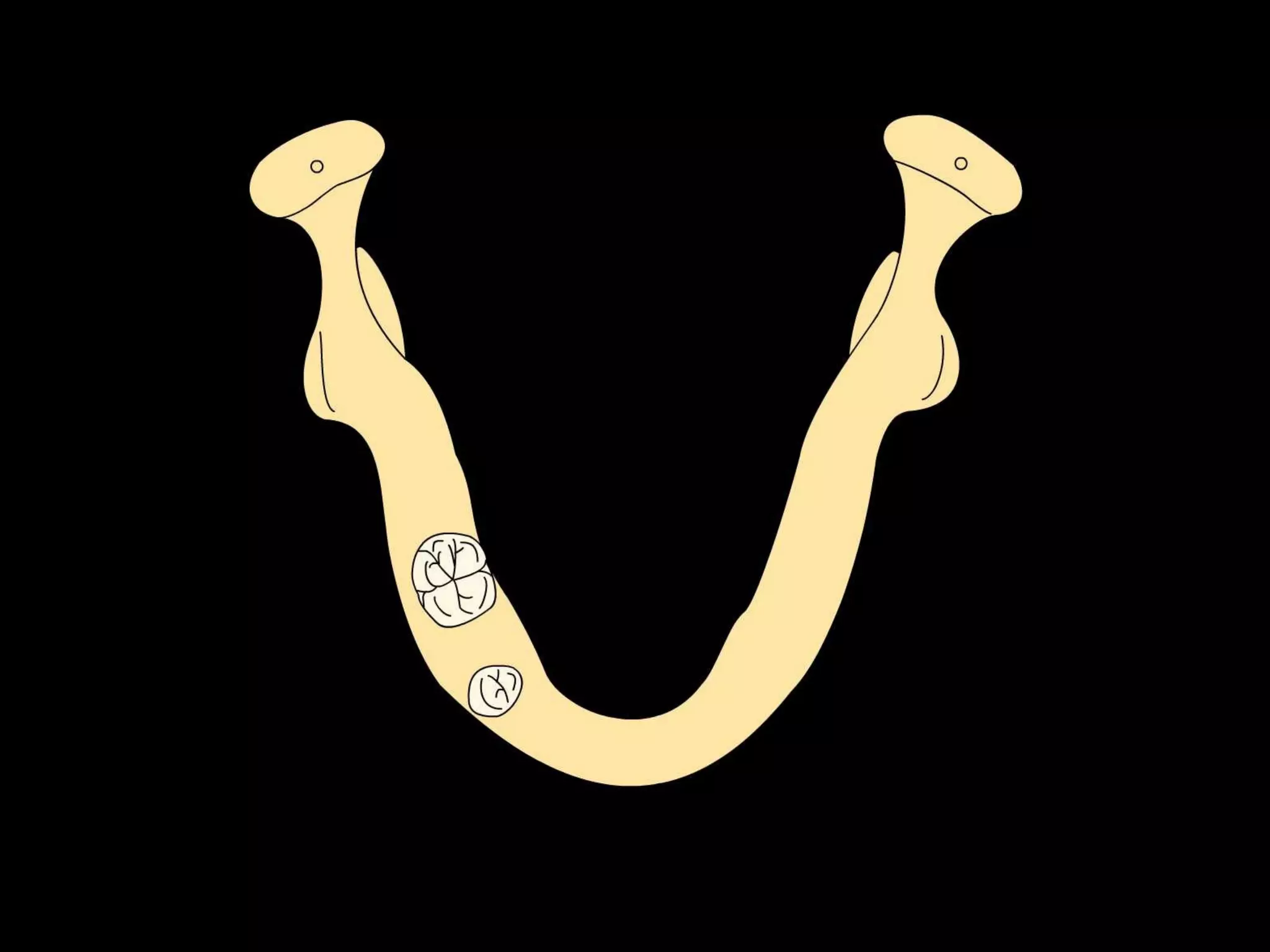
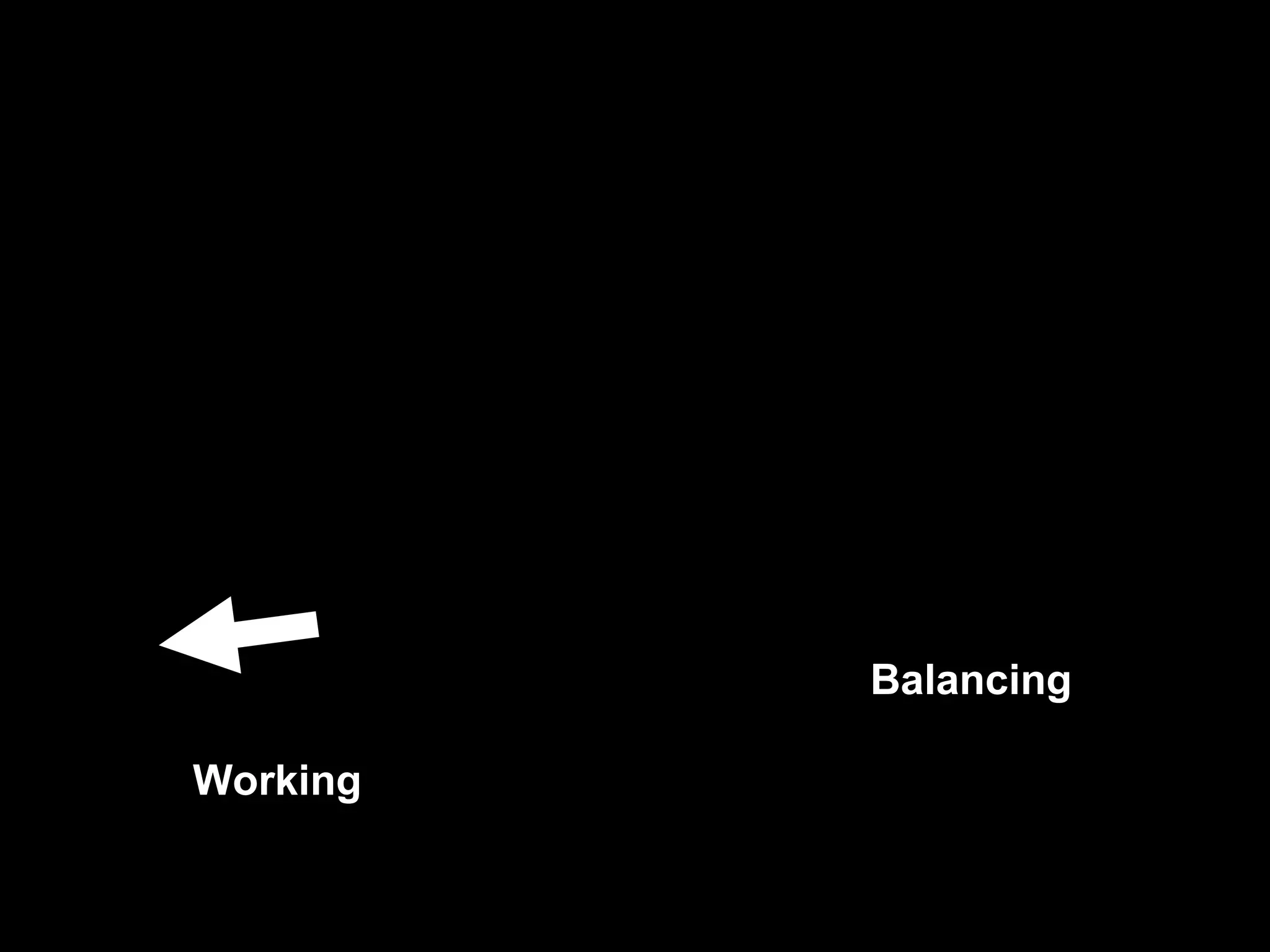
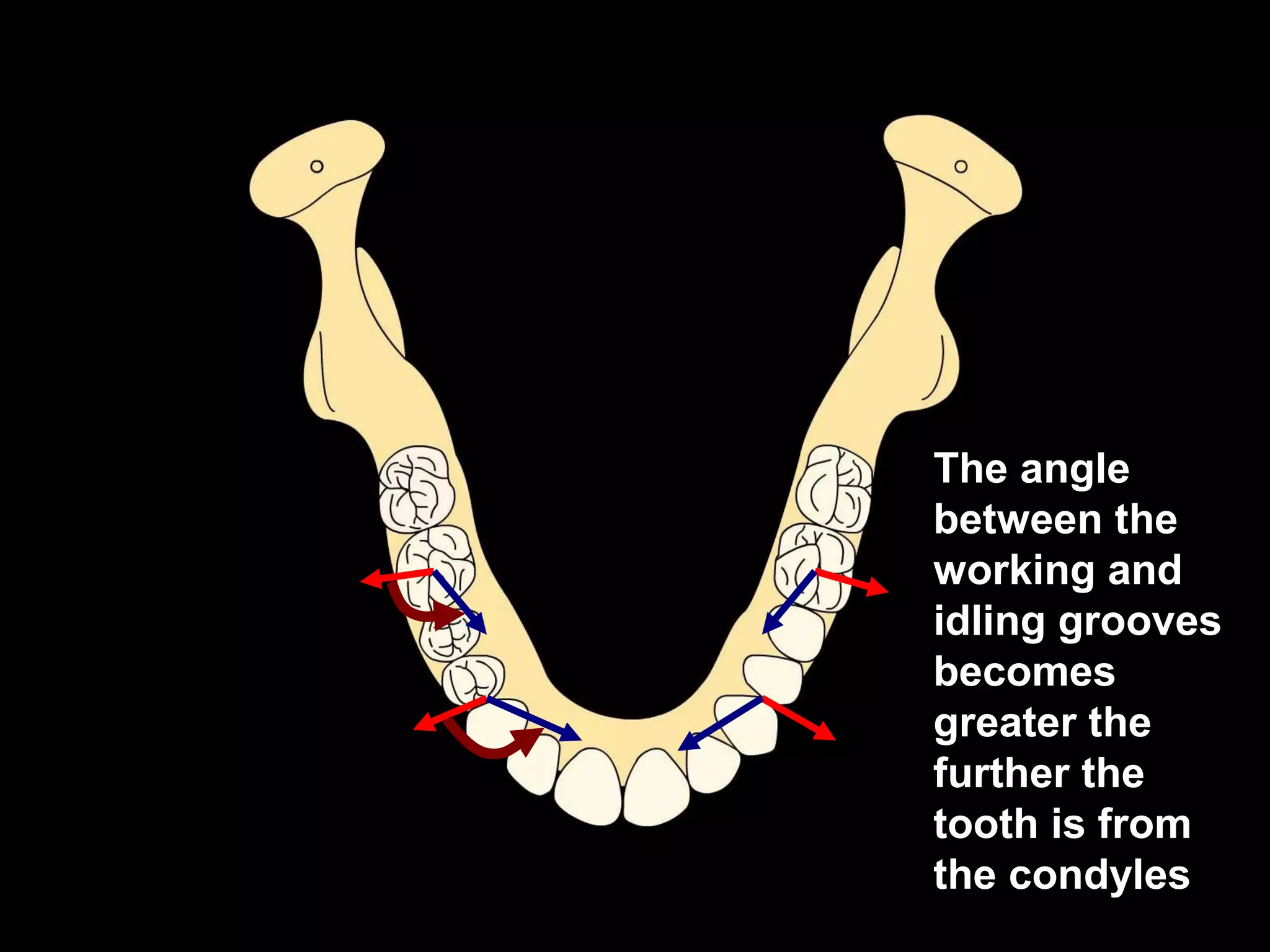
This document discusses the ideal anatomical contacts between the maxillary and mandibular teeth in a Class I occlusion. It explains that the mandibular teeth contacts are positioned one half cusp mesial to their maxillary counterparts. The specific cusp contacts between opposing teeth are described for each tooth group. Guidelines are provided for identifying the tooth and cusp represented by black dots on diagrams. Horizontal determinants of occlusion including ridge and groove direction, balancing and working side interferences, and the effect of distance from the condyles are also outlined.