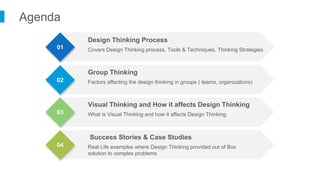
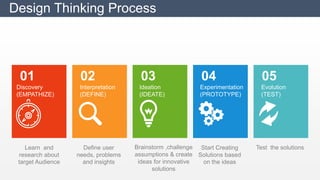
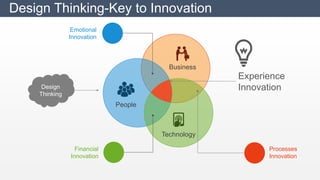
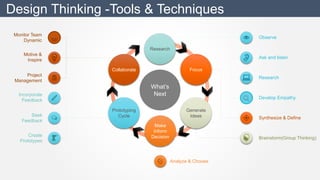
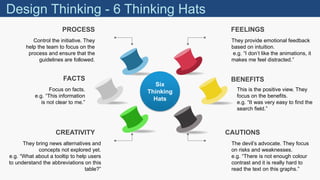
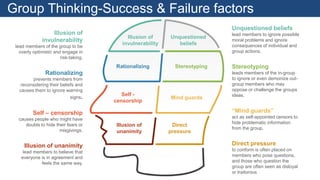
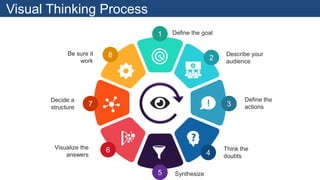
The document discusses design thinking as an iterative process aimed at understanding user needs and redefining problems for innovative solutions. It covers the design thinking process, tools and techniques, factors affecting group dynamics, and visual thinking's role in enhancing design outcomes. Additionally, it includes success stories that illustrate how design thinking has driven significant growth for various enterprises.