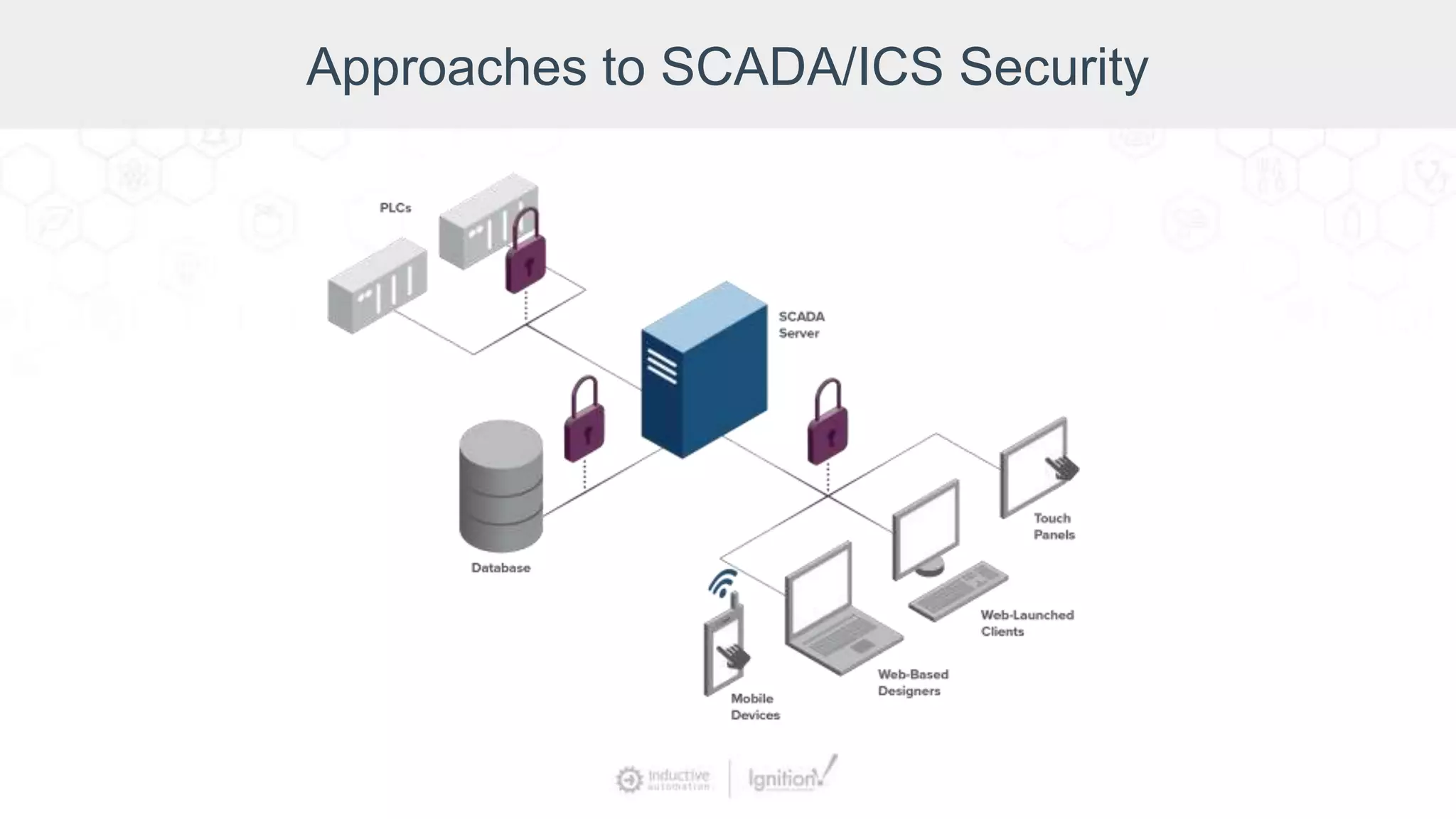
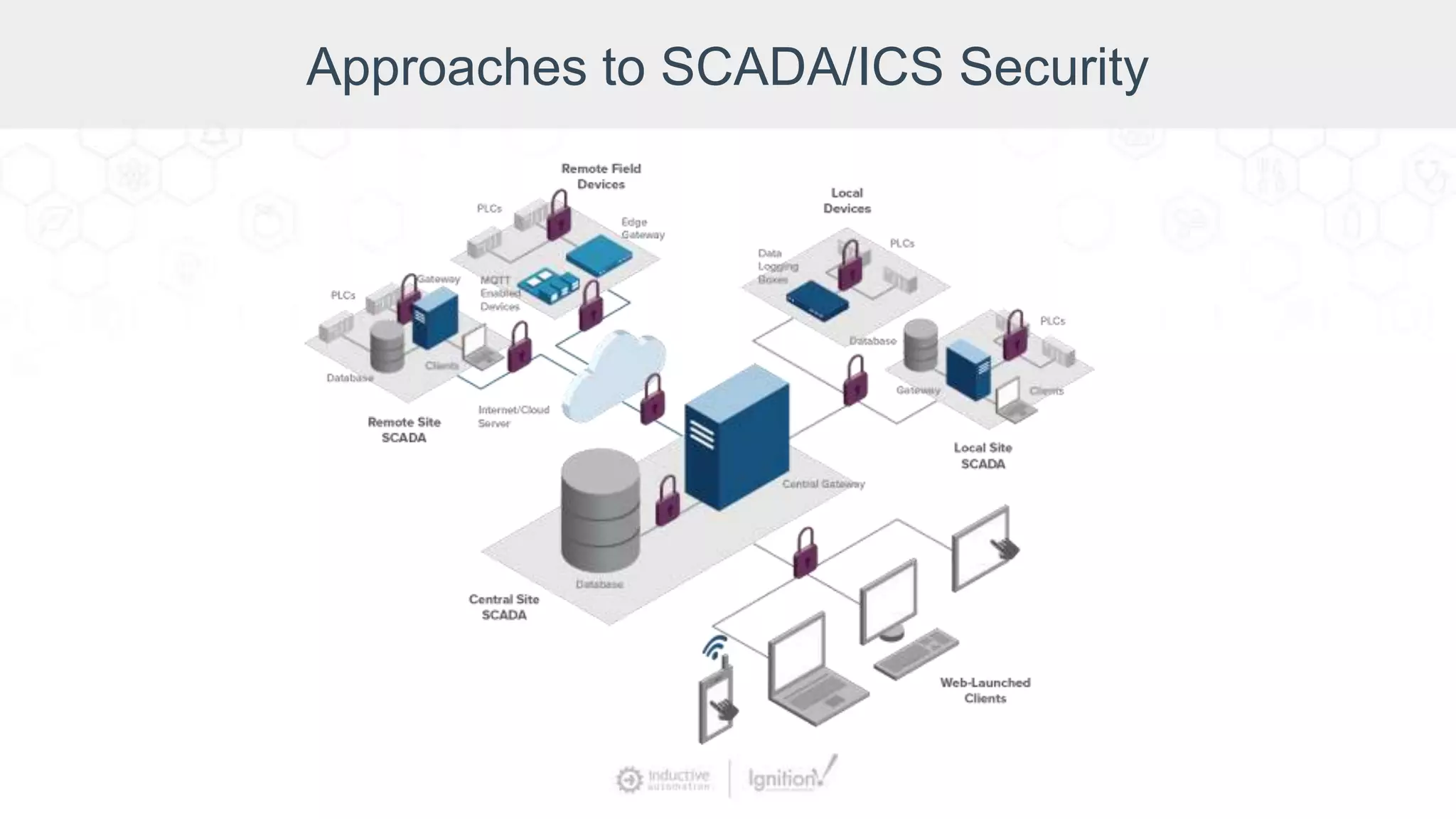
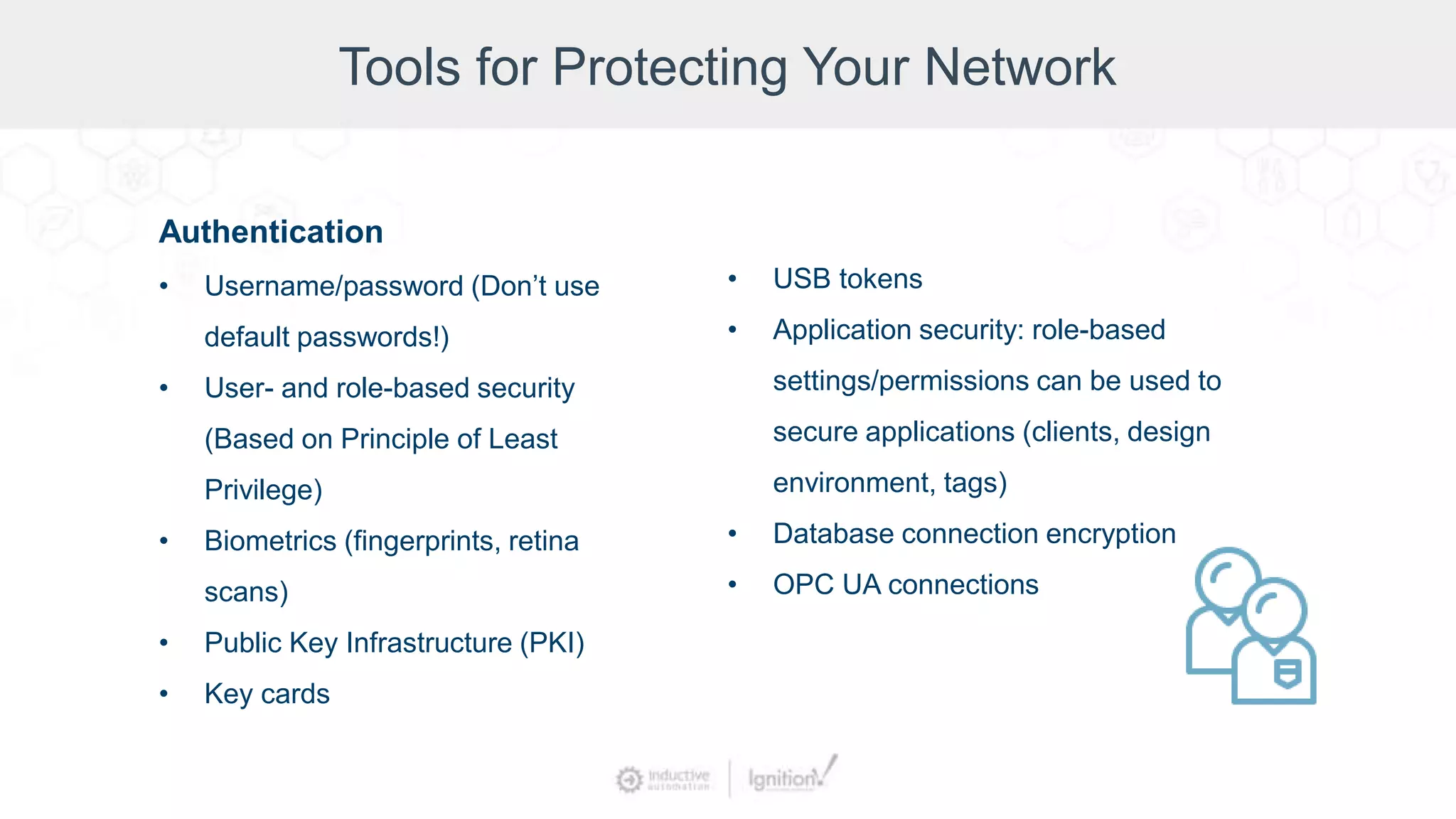
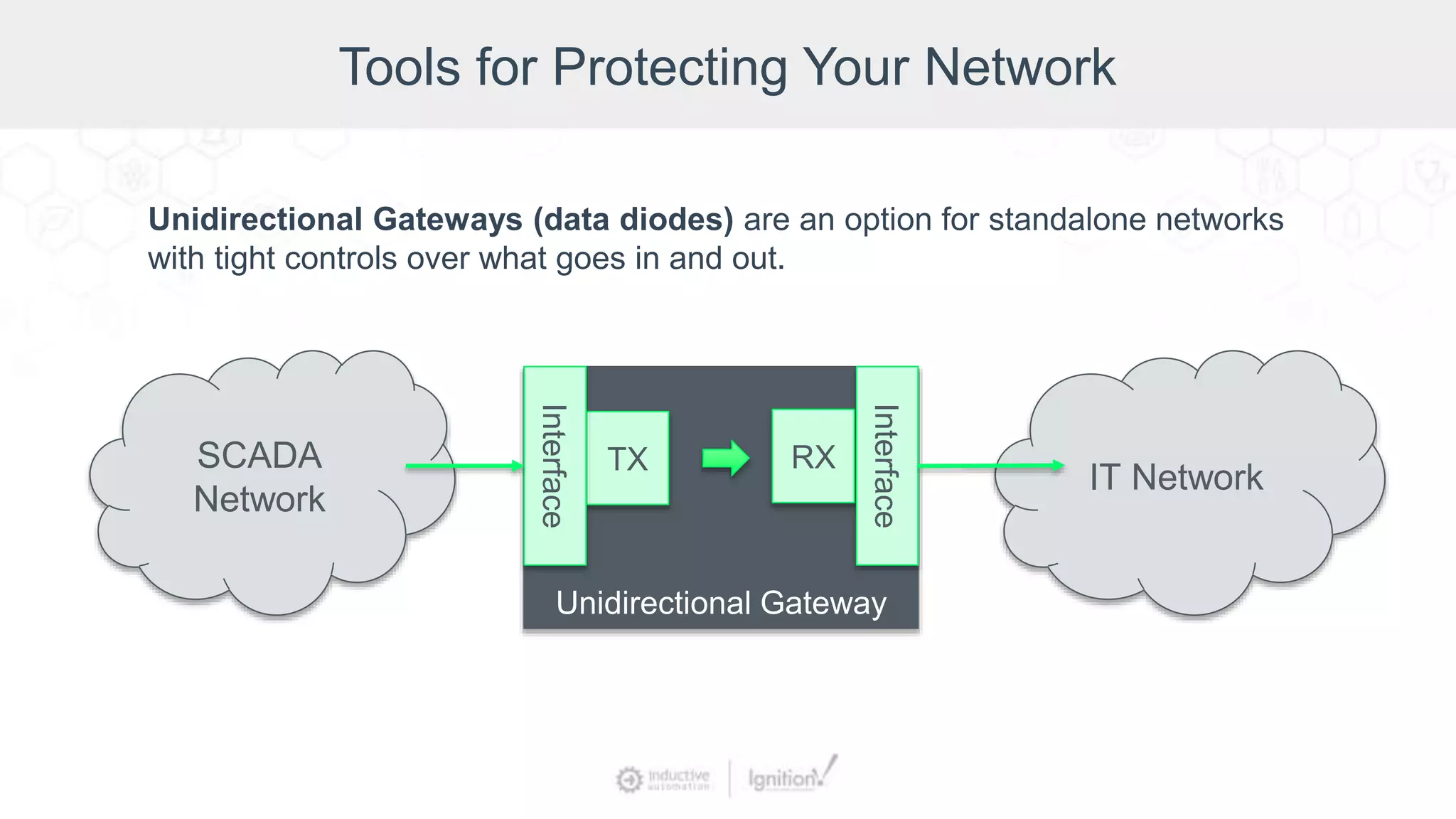
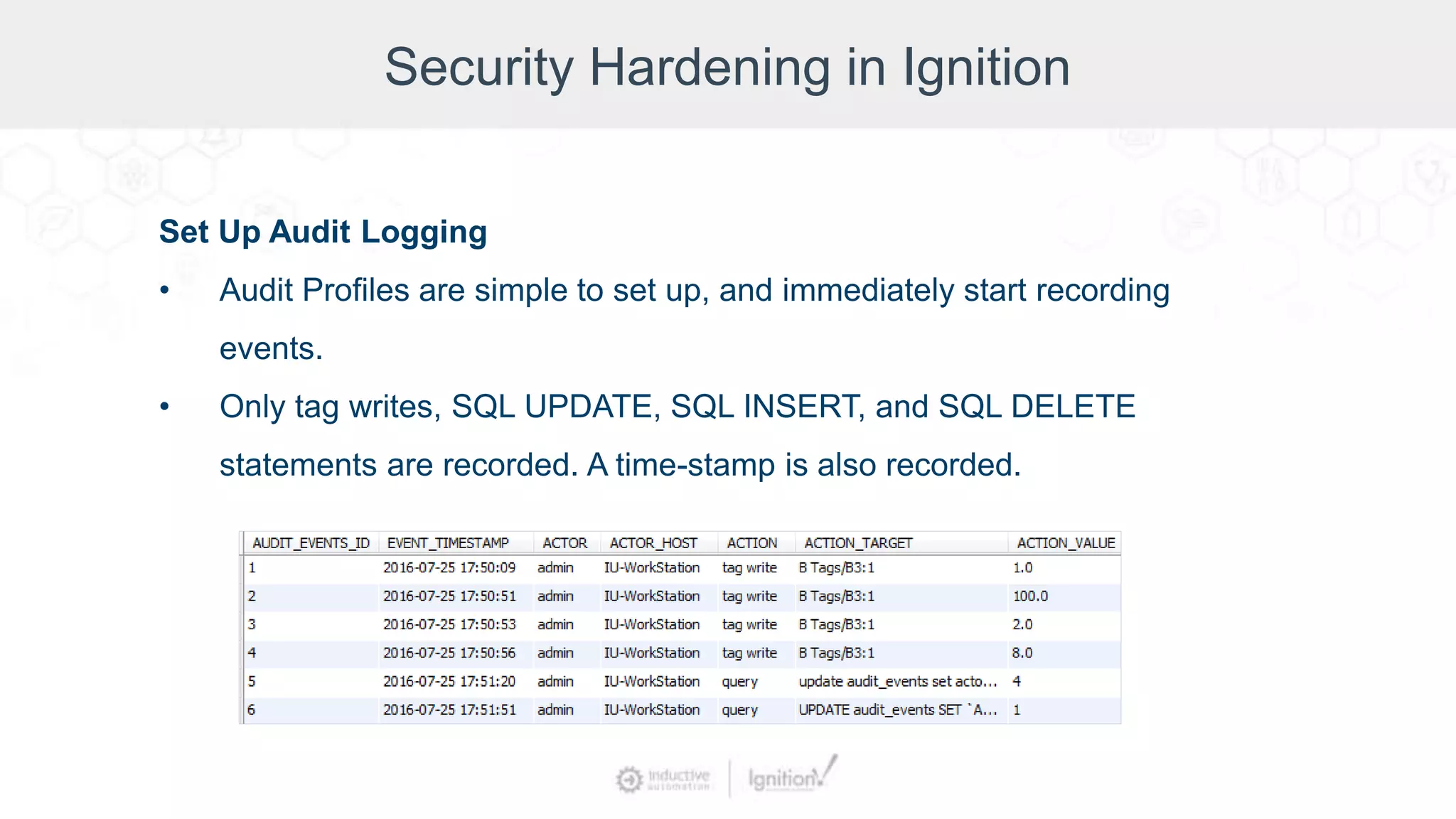
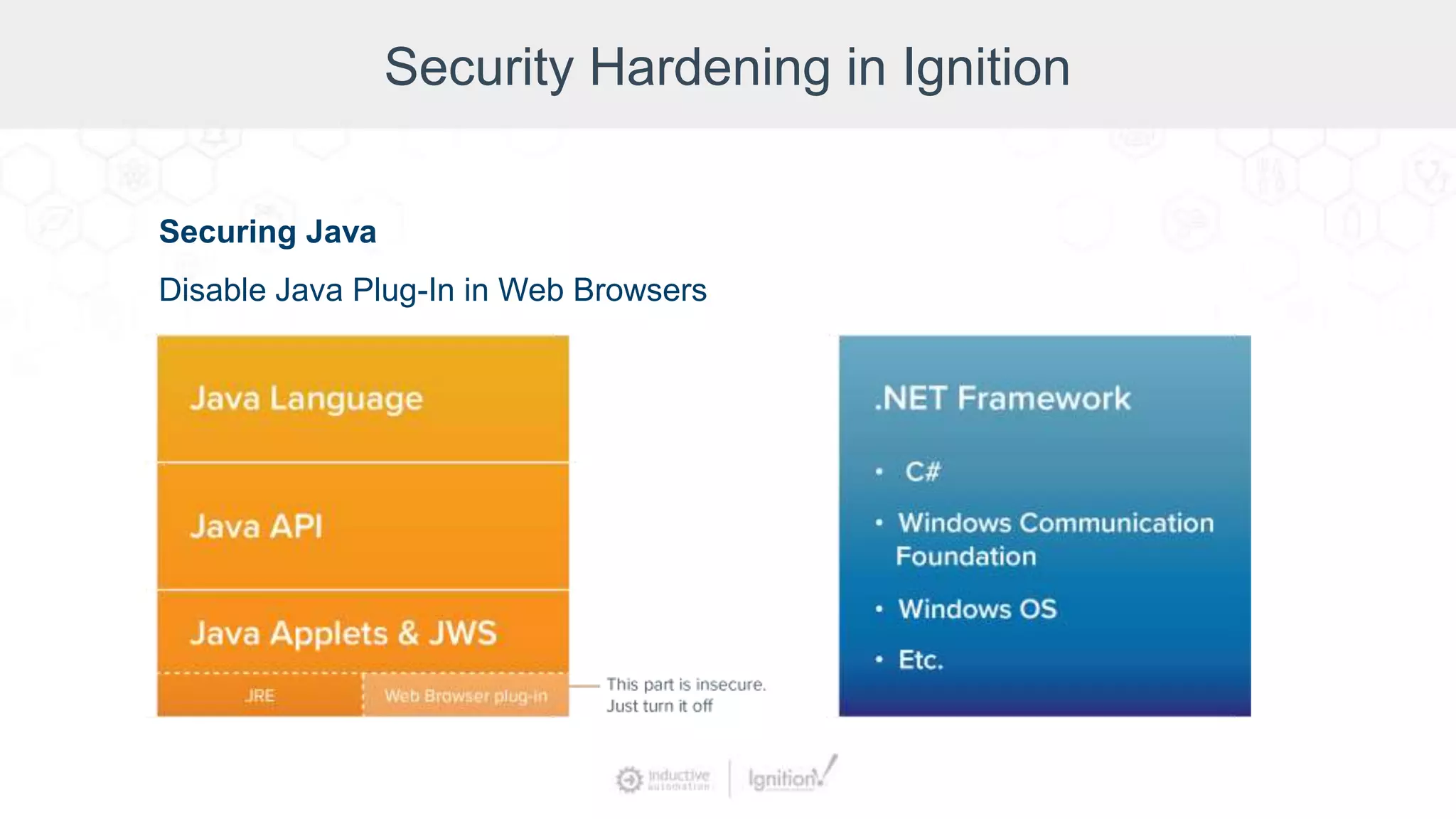
The webinar, led by Inductive Automation experts, provides an overview of SCADA/ICS security, highlighting essential strategies and tools for protecting networks and devices. It emphasizes the importance of prevention and outlines basic security laws while discussing various types of attacks and vulnerabilities. The presentation also covers security hardening practices specific to the Ignition platform.