Embed presentation
Downloaded 25 times

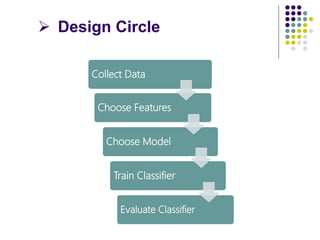
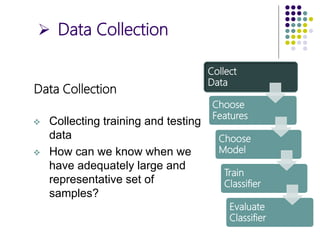
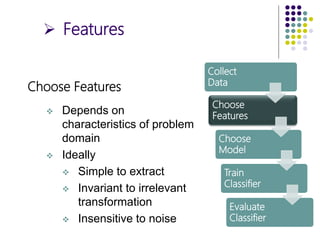
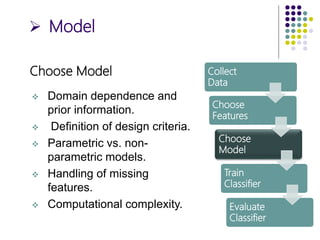
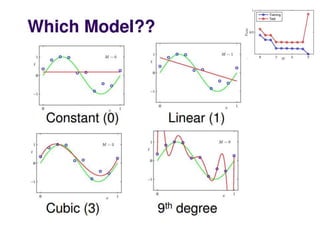
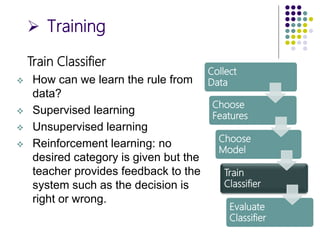
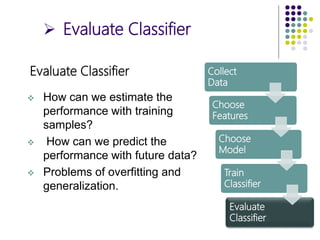


The document outlines the design cycles of pattern recognition, which involves a series of steps including data collection, feature selection, model selection, training, and evaluation. It discusses the importance of gathering a representative data set, choosing appropriate features based on the problem domain, selecting models based on various criteria, and the different learning paradigms. Additionally, it highlights evaluation methods to estimate classifier performance and addresses concerns like overfitting.









