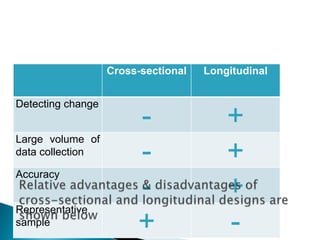
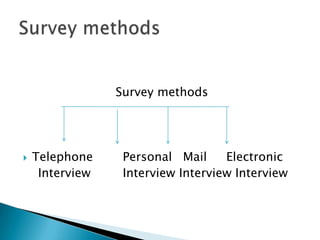
The document describes different types of research methods used in market research. It discusses cross-sectional and longitudinal research designs, as well as survey methods like telephone, personal, mail, and electronic interviews. It also describes observation methods like personal and mechanical observation, and provides examples of mechanical devices used like audiometers, people meters, and eye tracking monitors. The advantages and disadvantages of different research methods are highlighted.