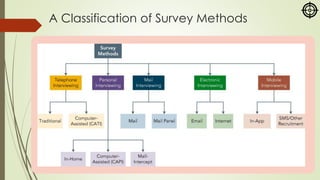
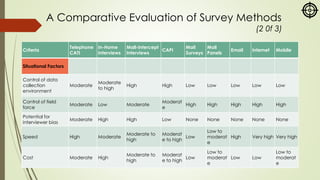
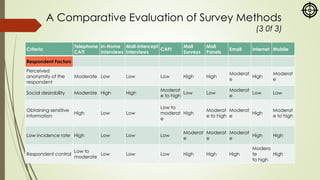
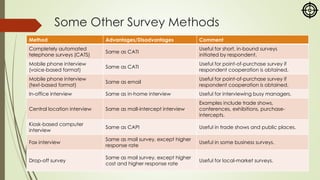
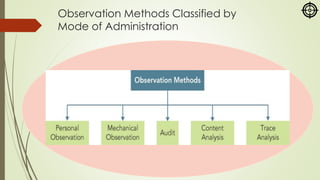
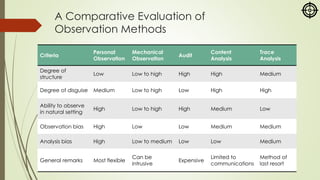
The document focuses on various marketing research methodologies, particularly survey and observation methods, detailing their advantages, disadvantages, and evaluations based on several criteria. It includes a discussion on ethnographic research and outlines ethical concerns in marketing research, such as the practices of 'sugging' and 'frugging,' as well as issues related to respondent consent and privacy. Overall, it emphasizes the importance of selecting appropriate methods to obtain reliable data while adhering to ethical standards.