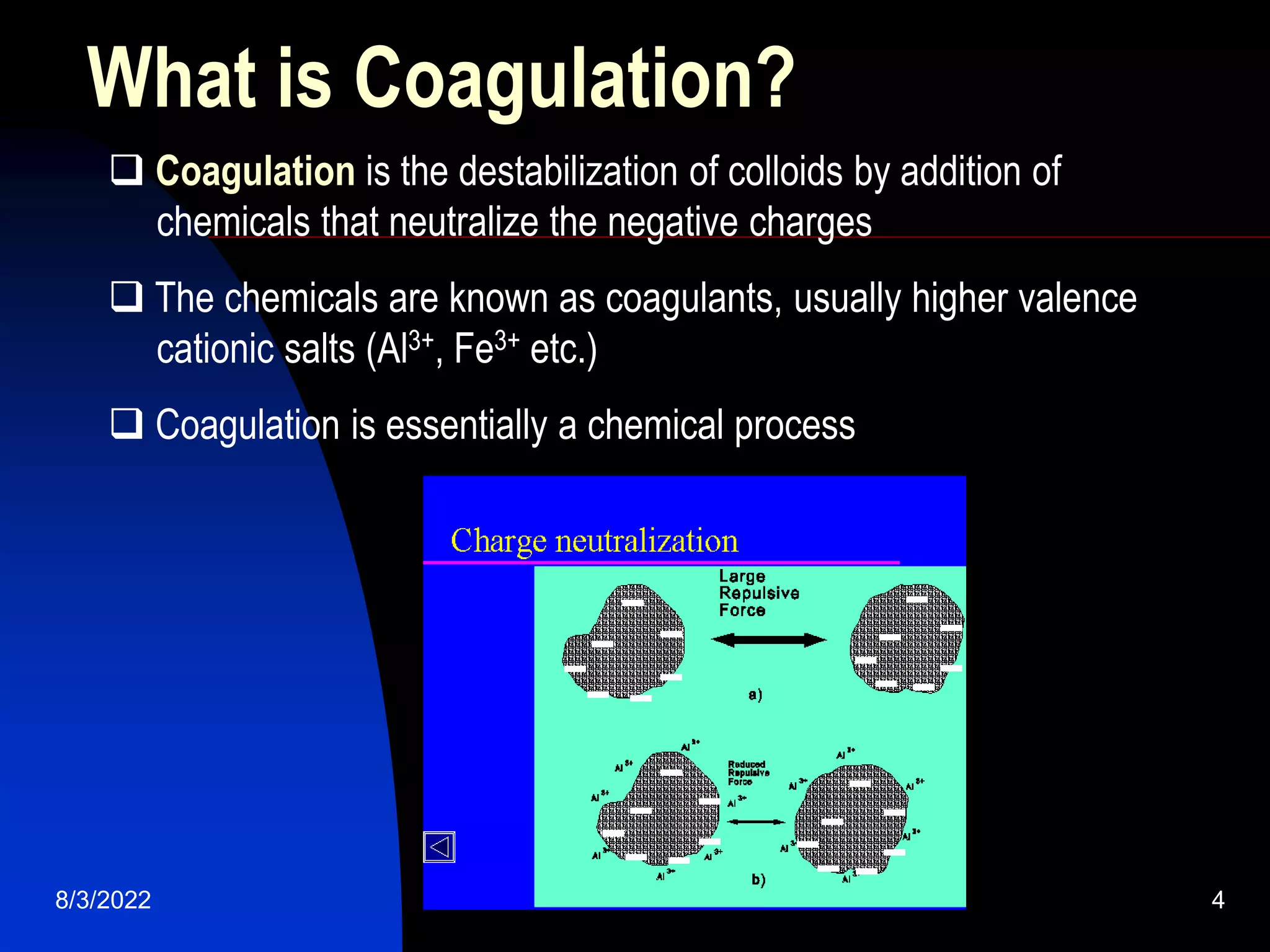
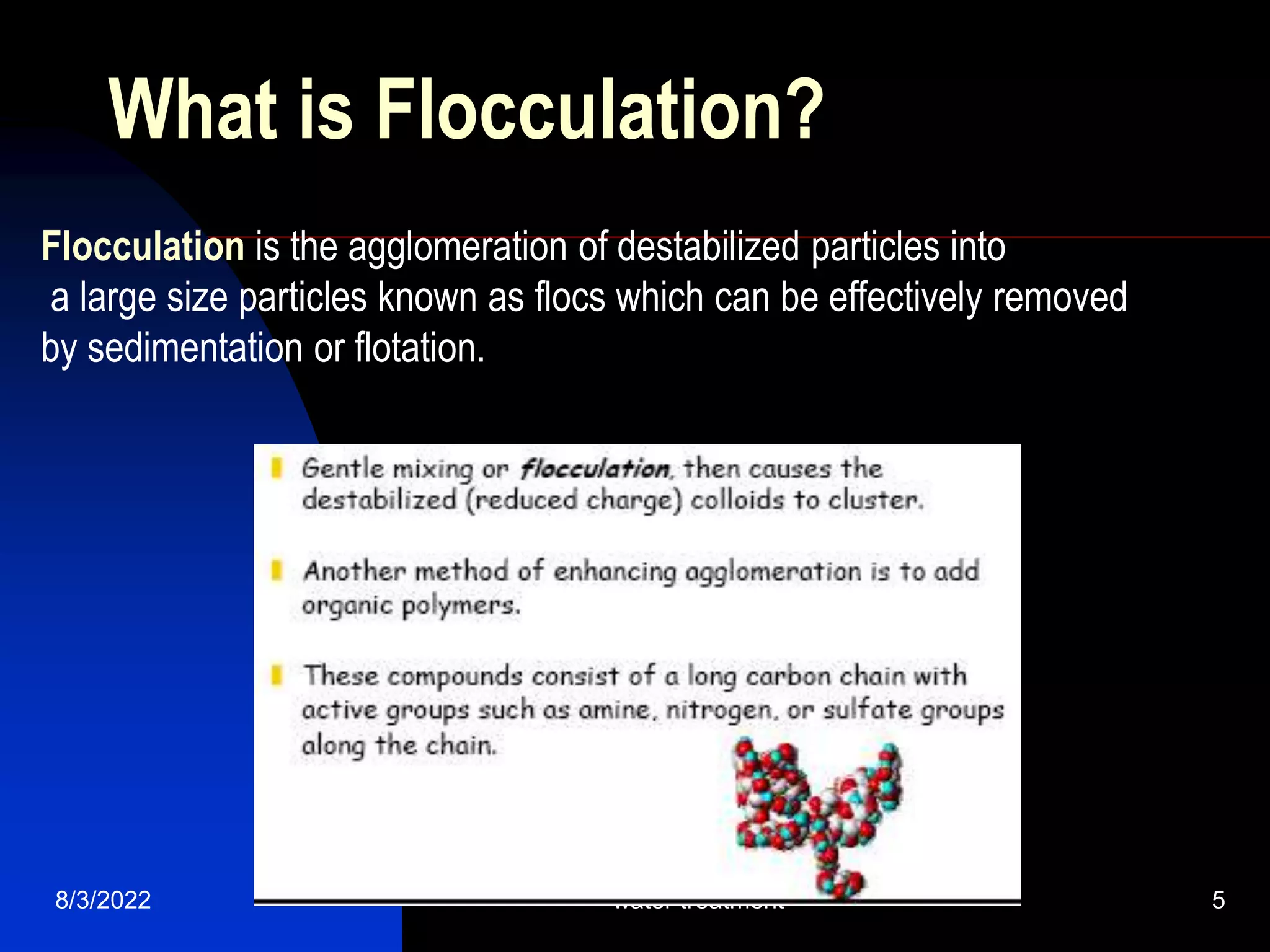
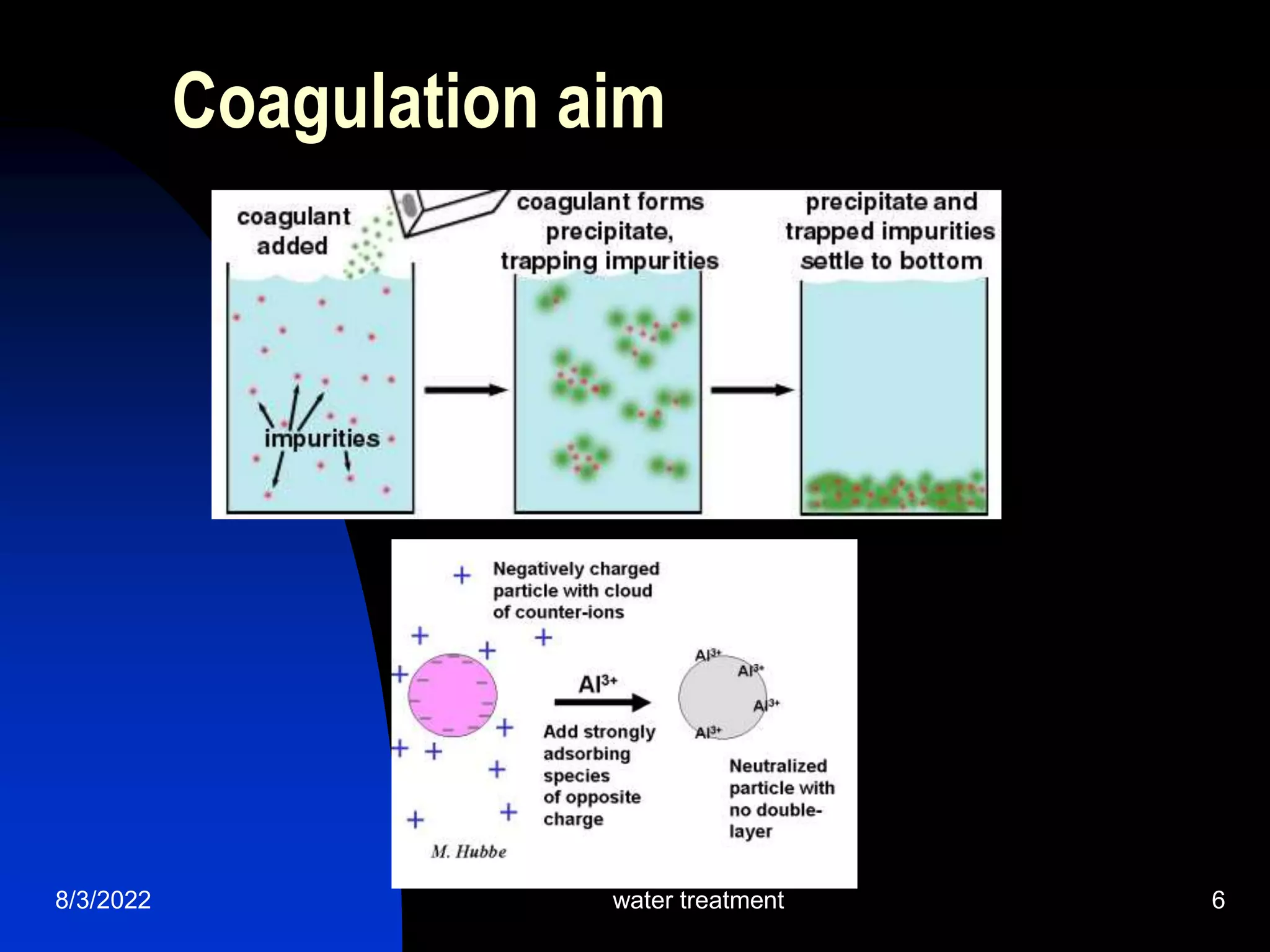
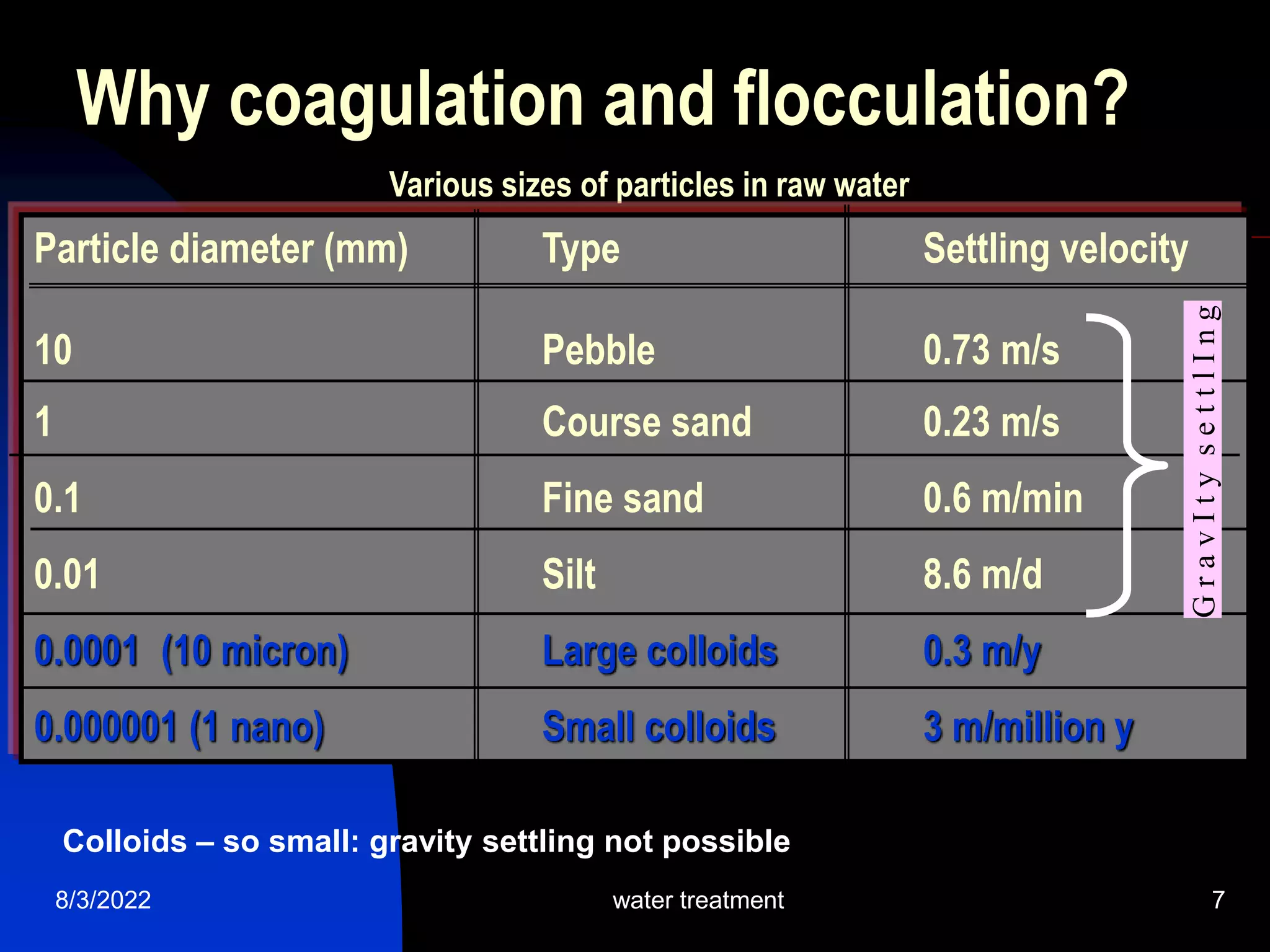
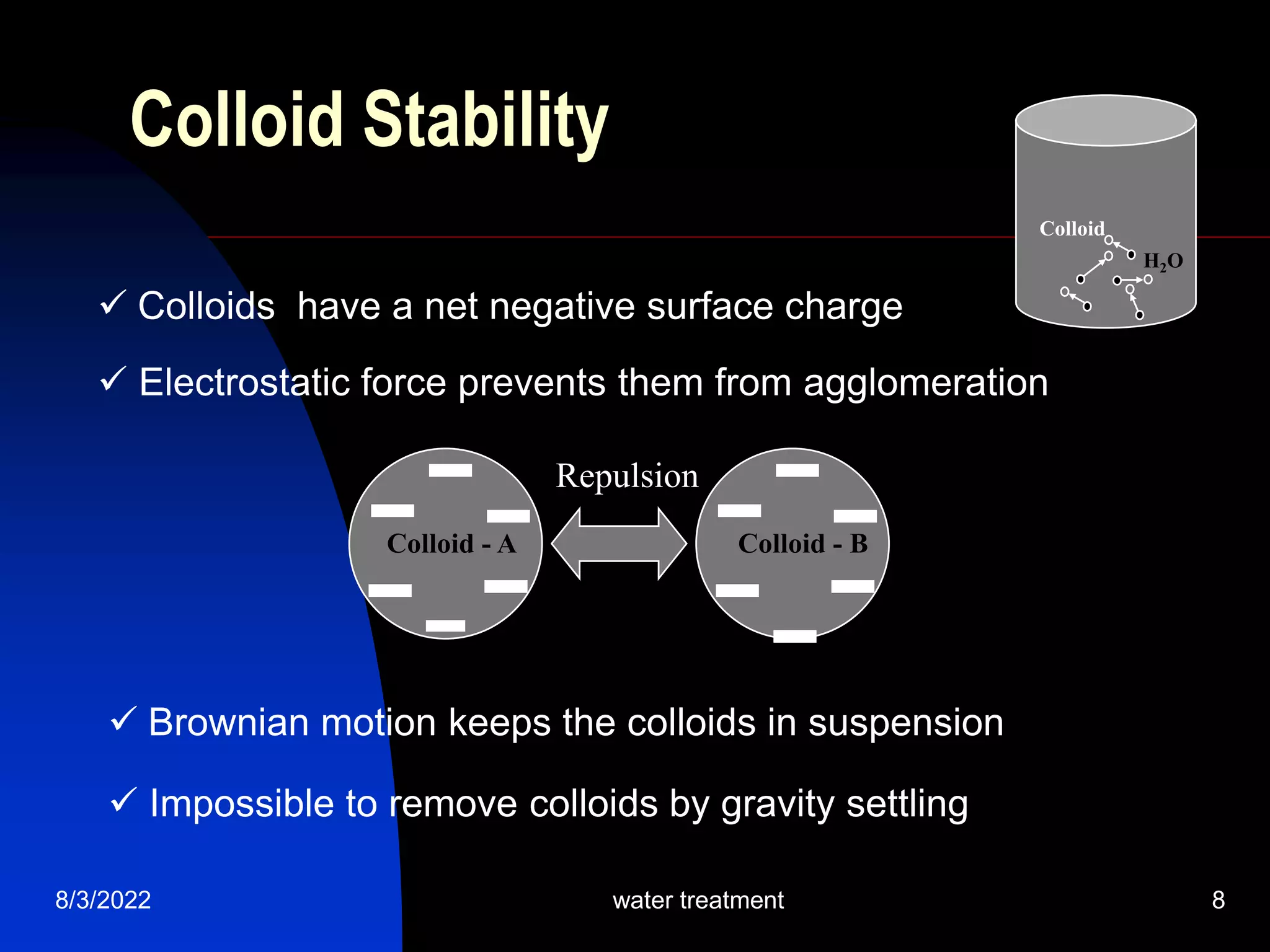
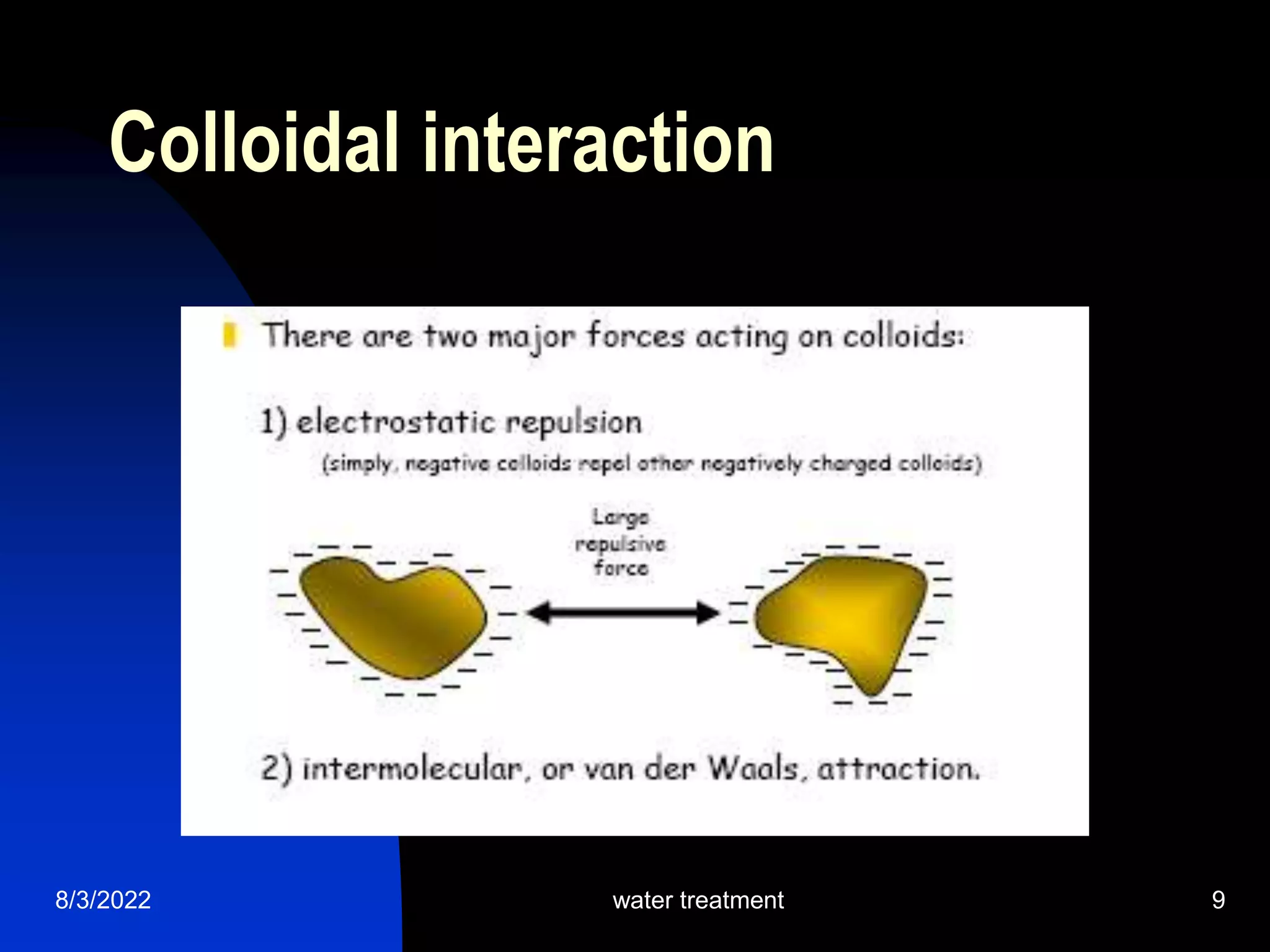
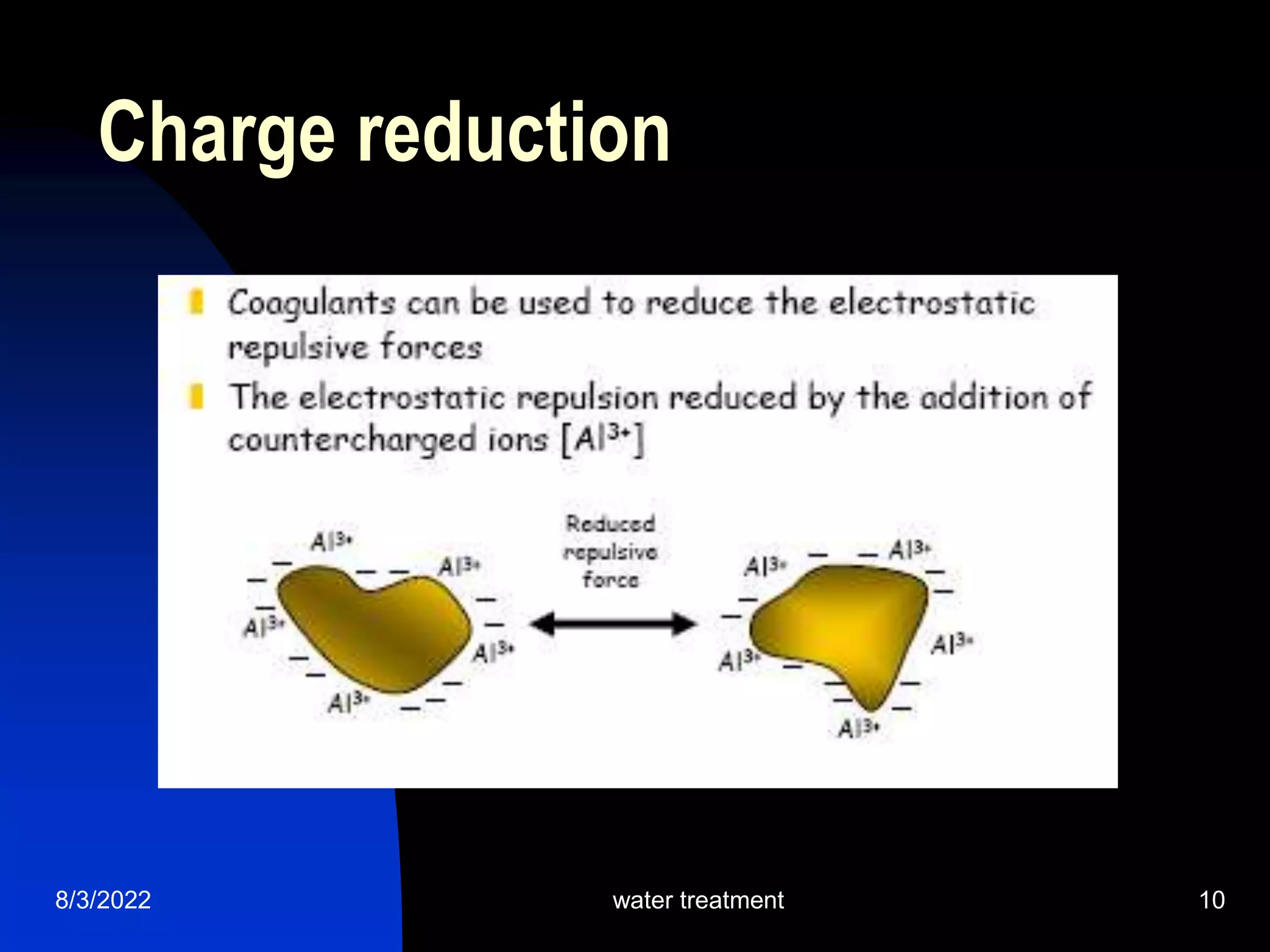
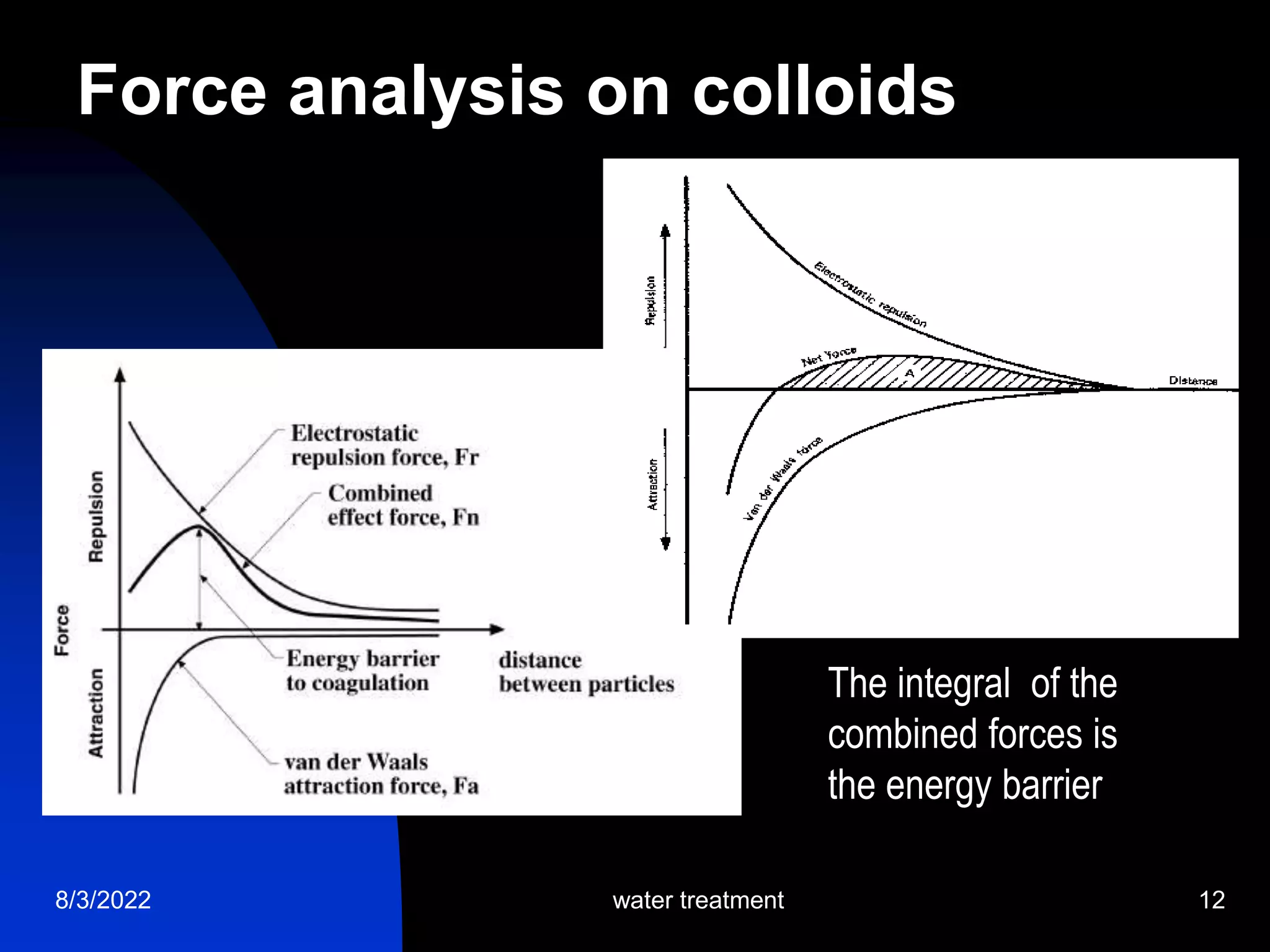
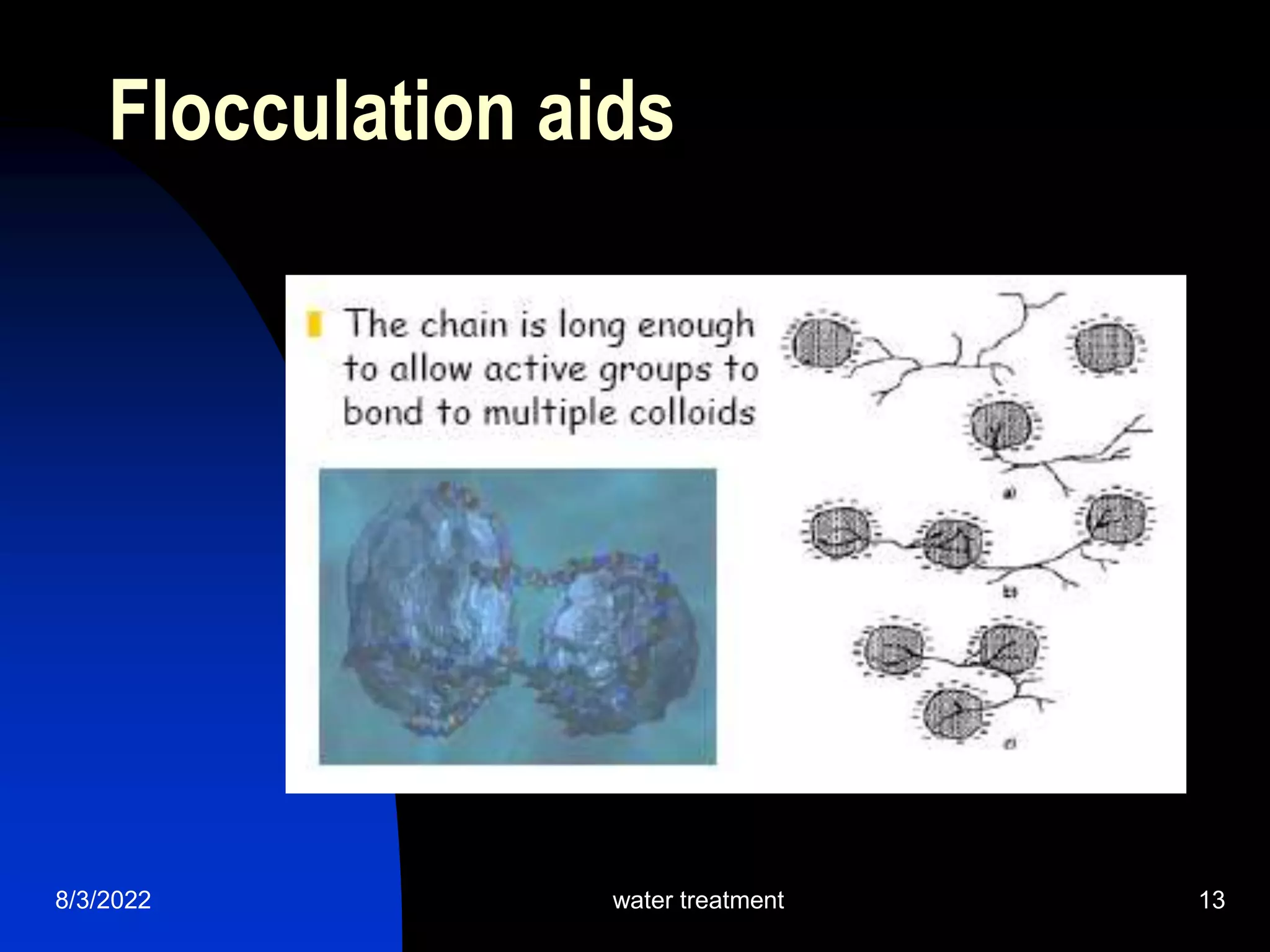
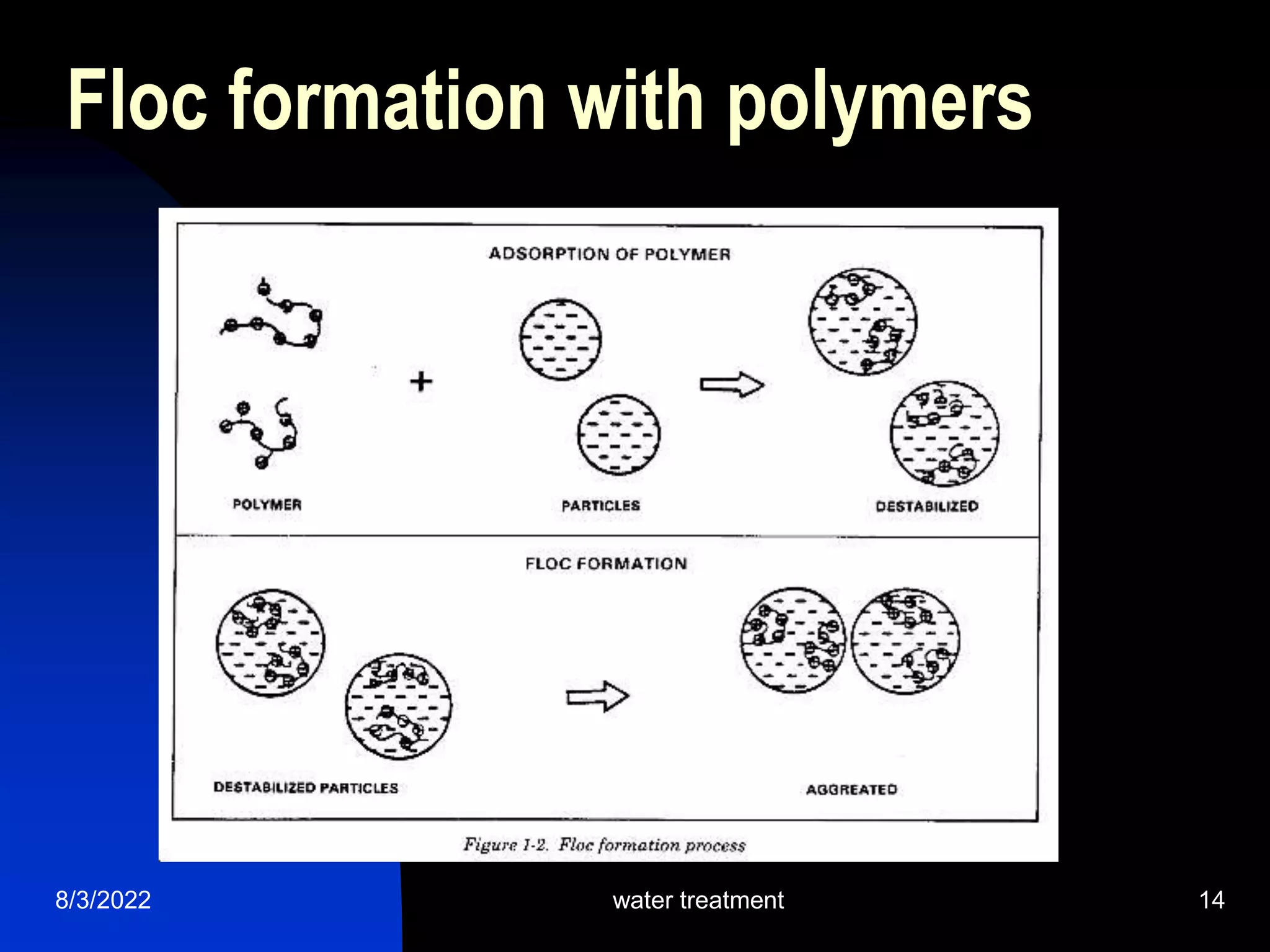
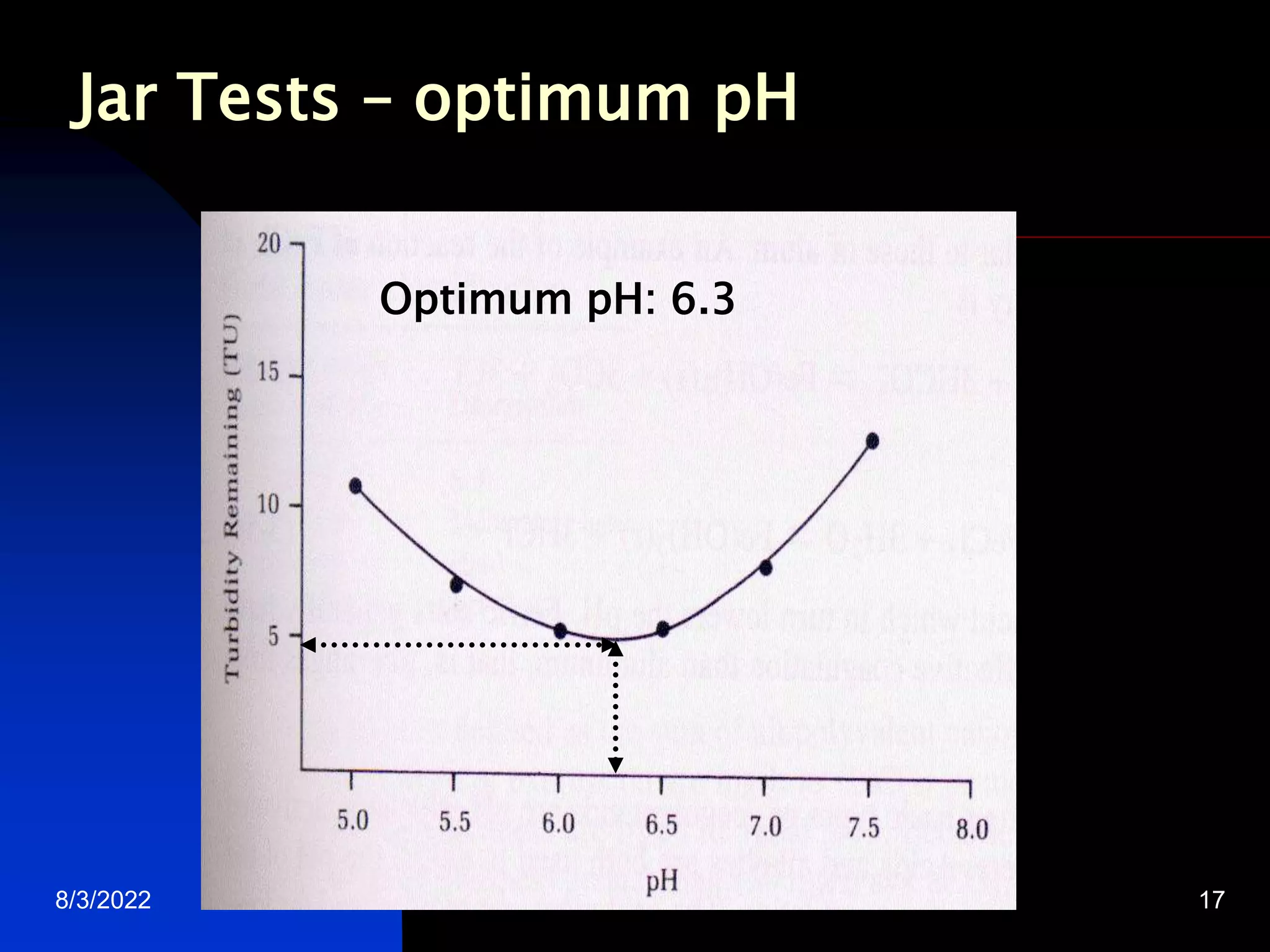
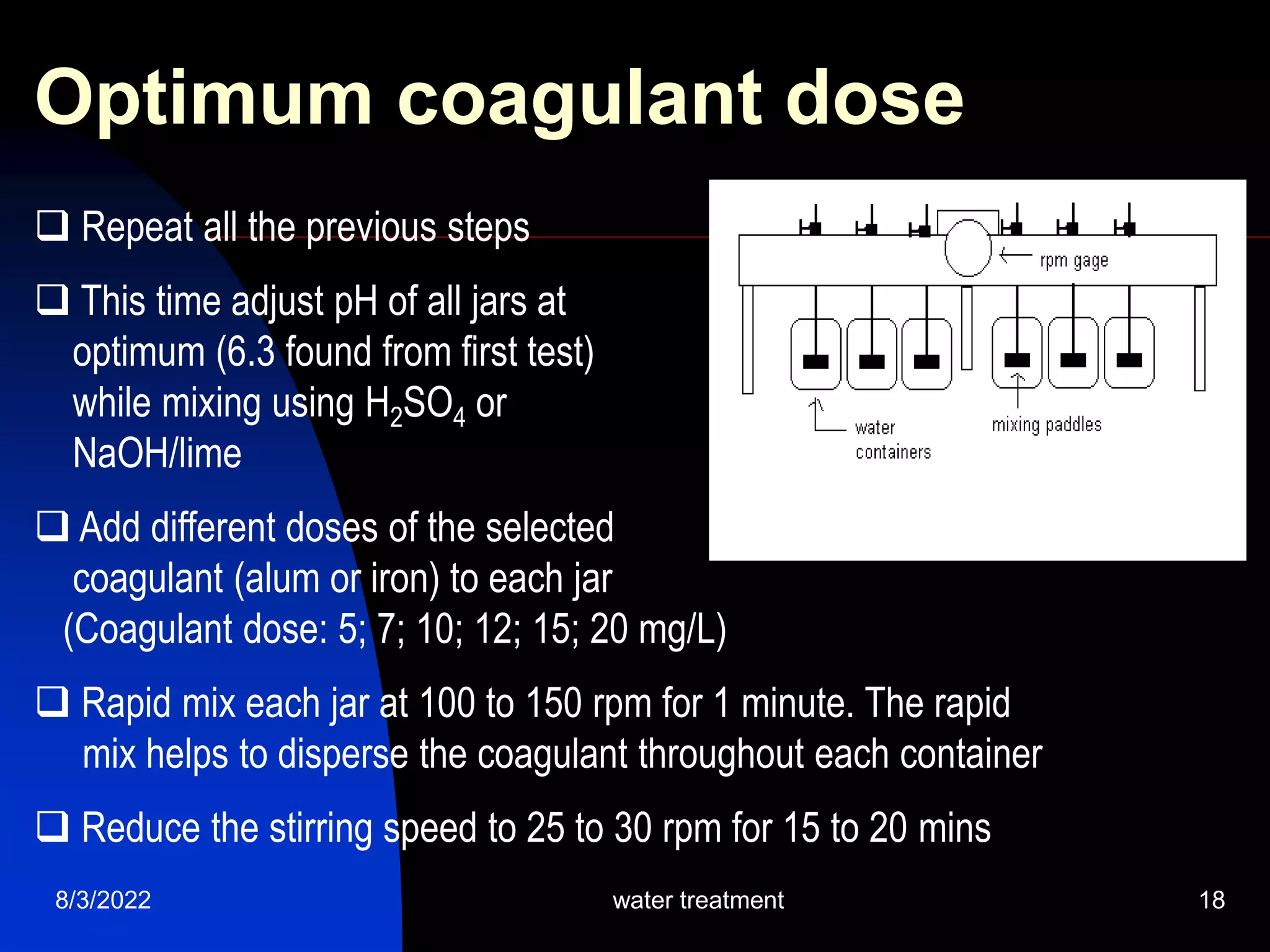
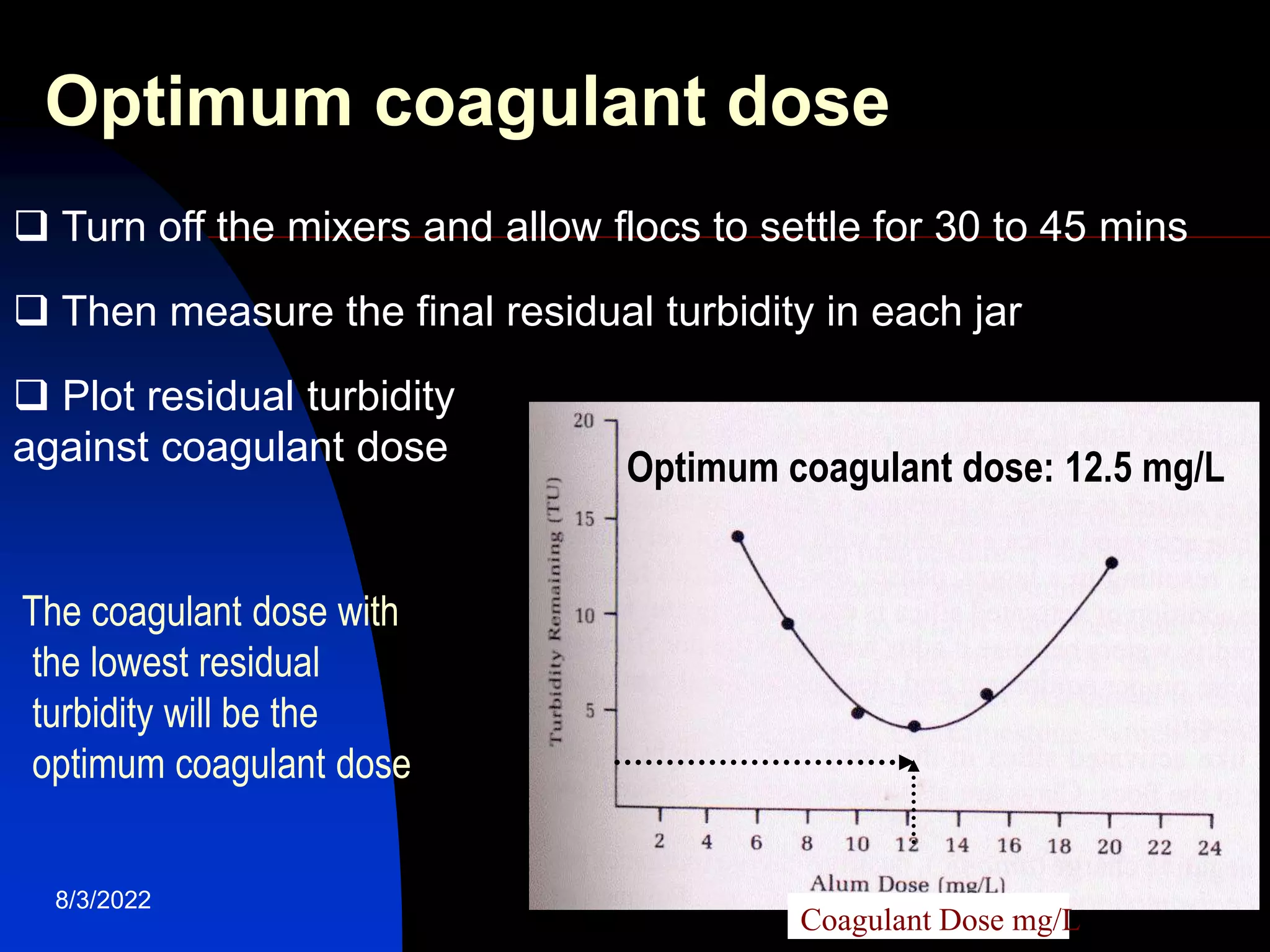
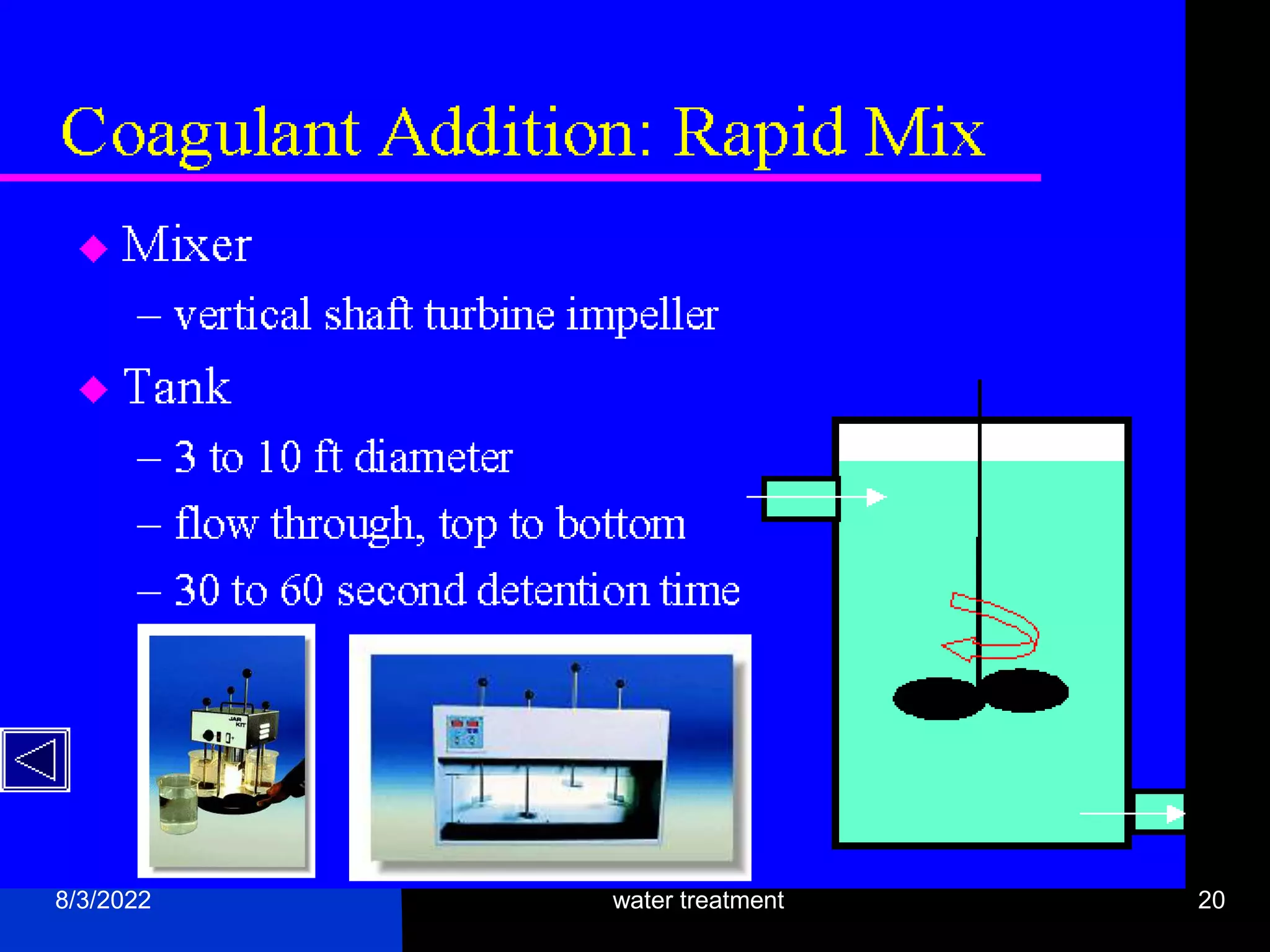
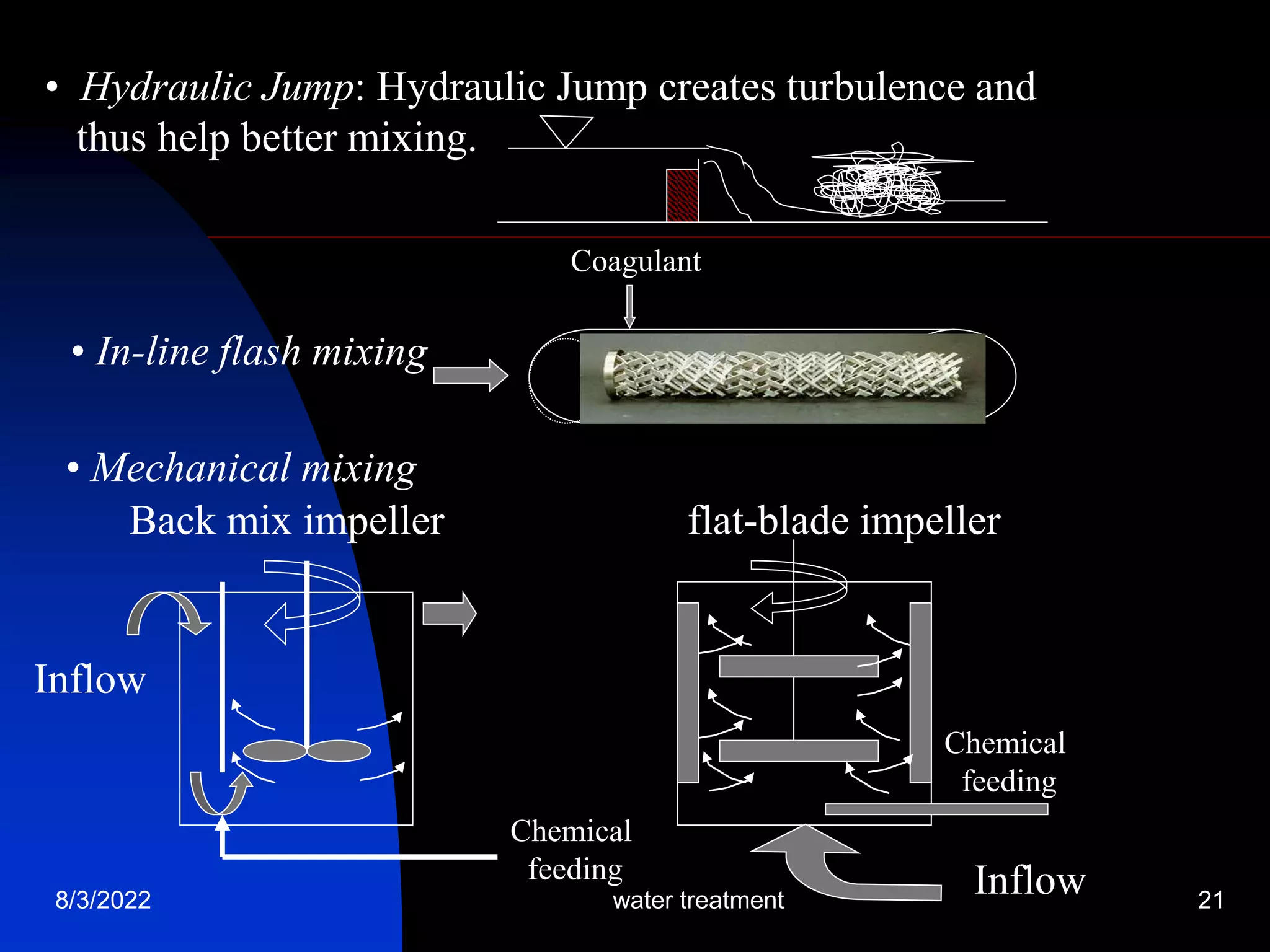
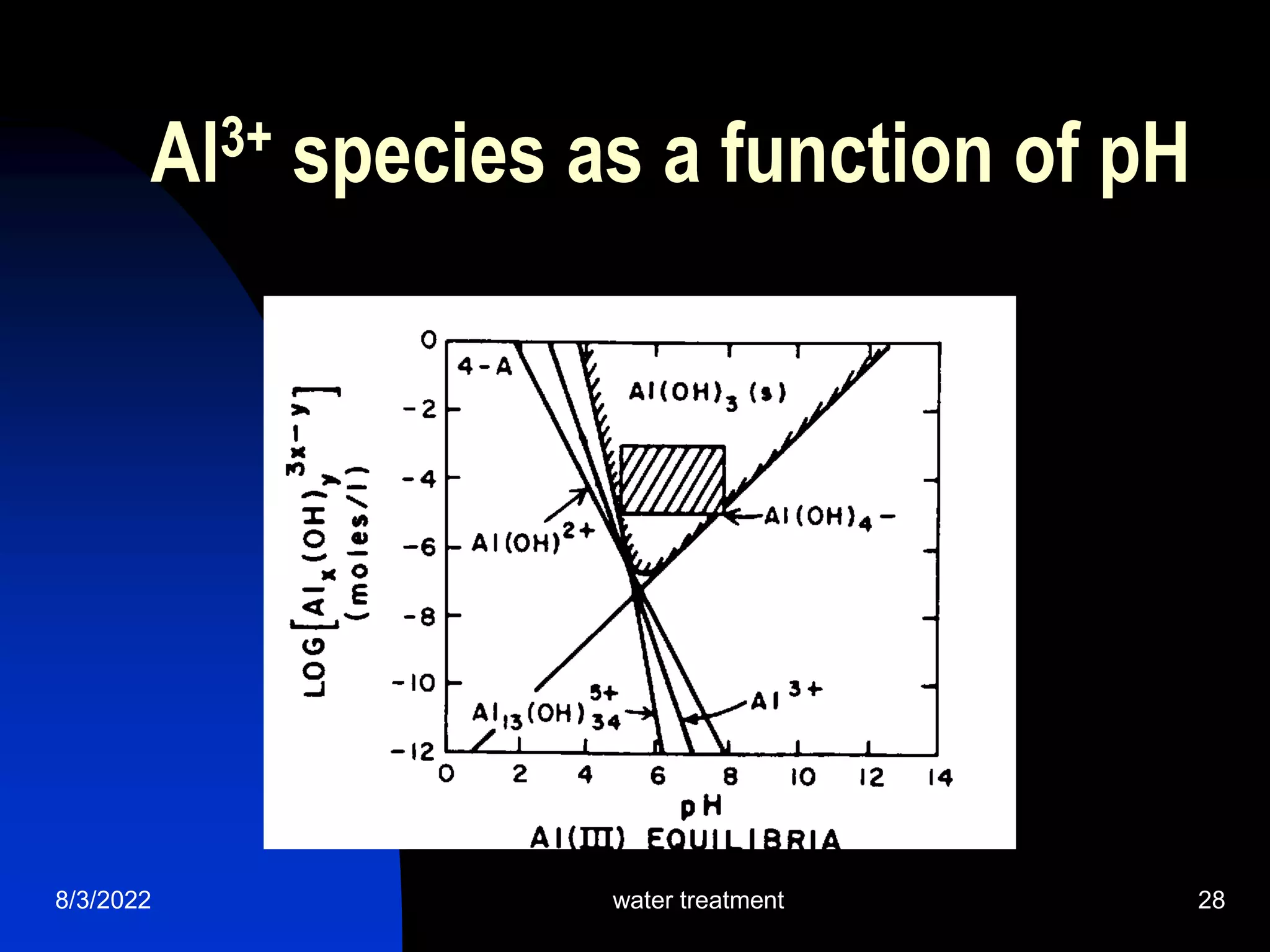
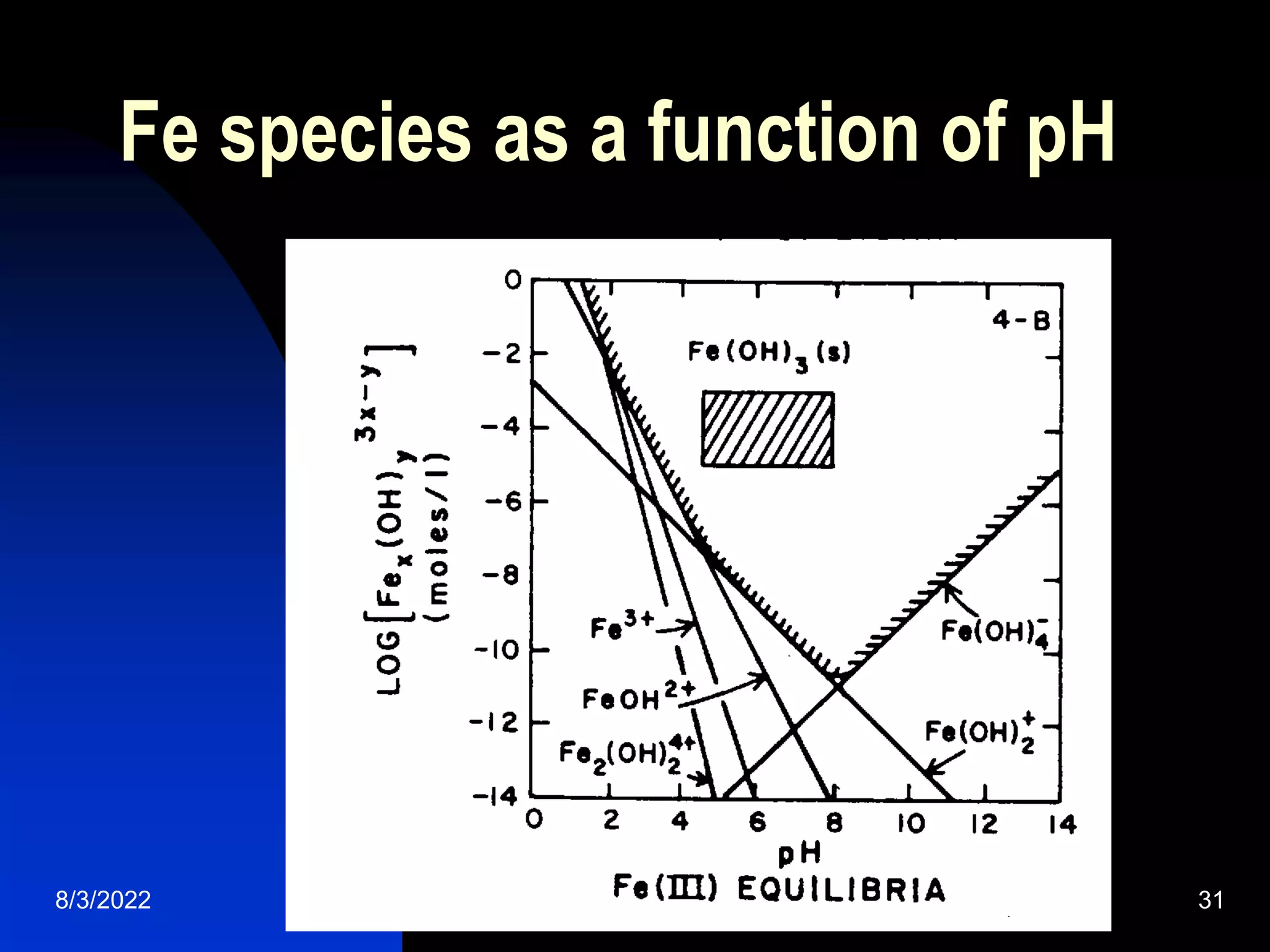
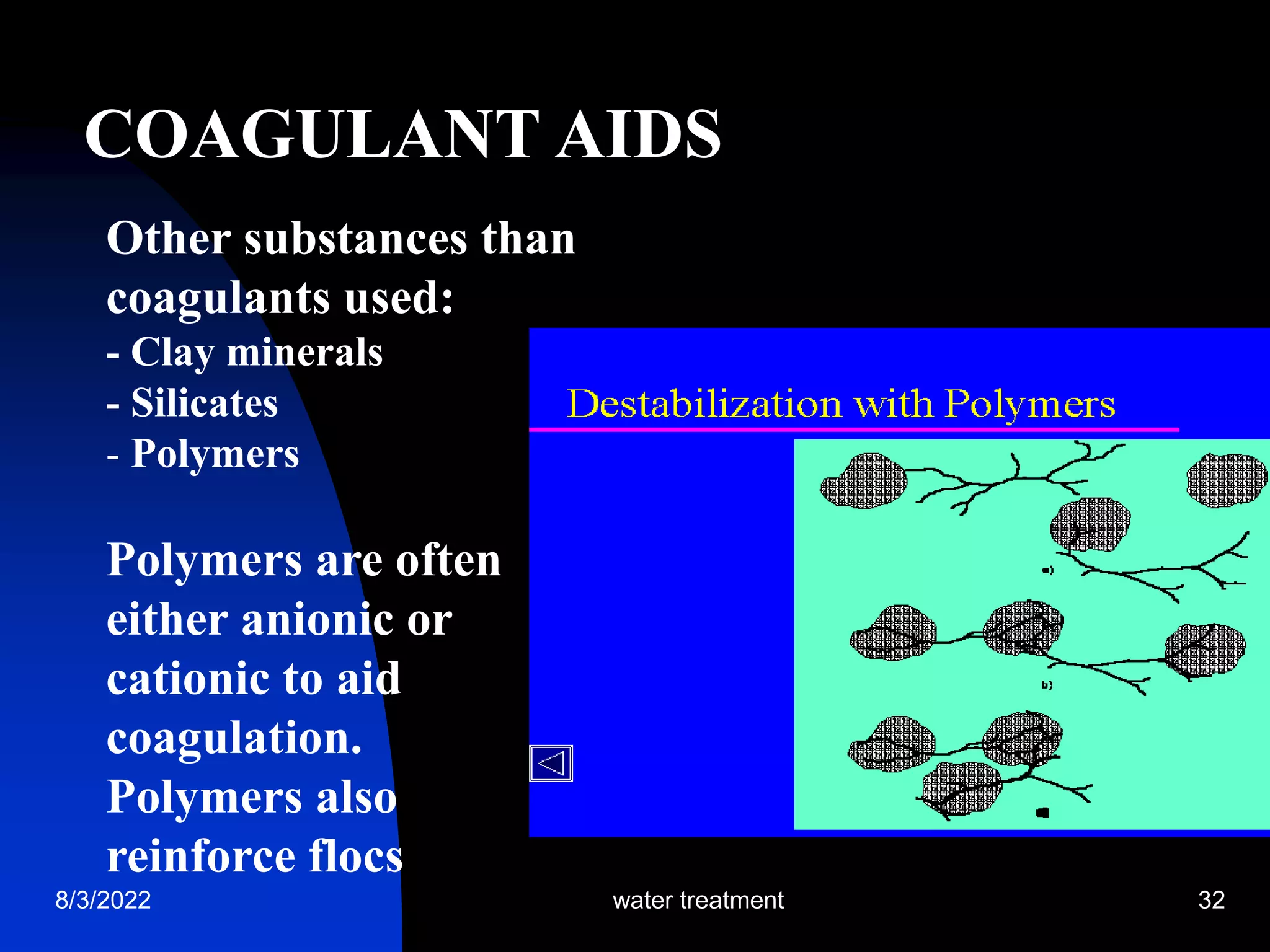
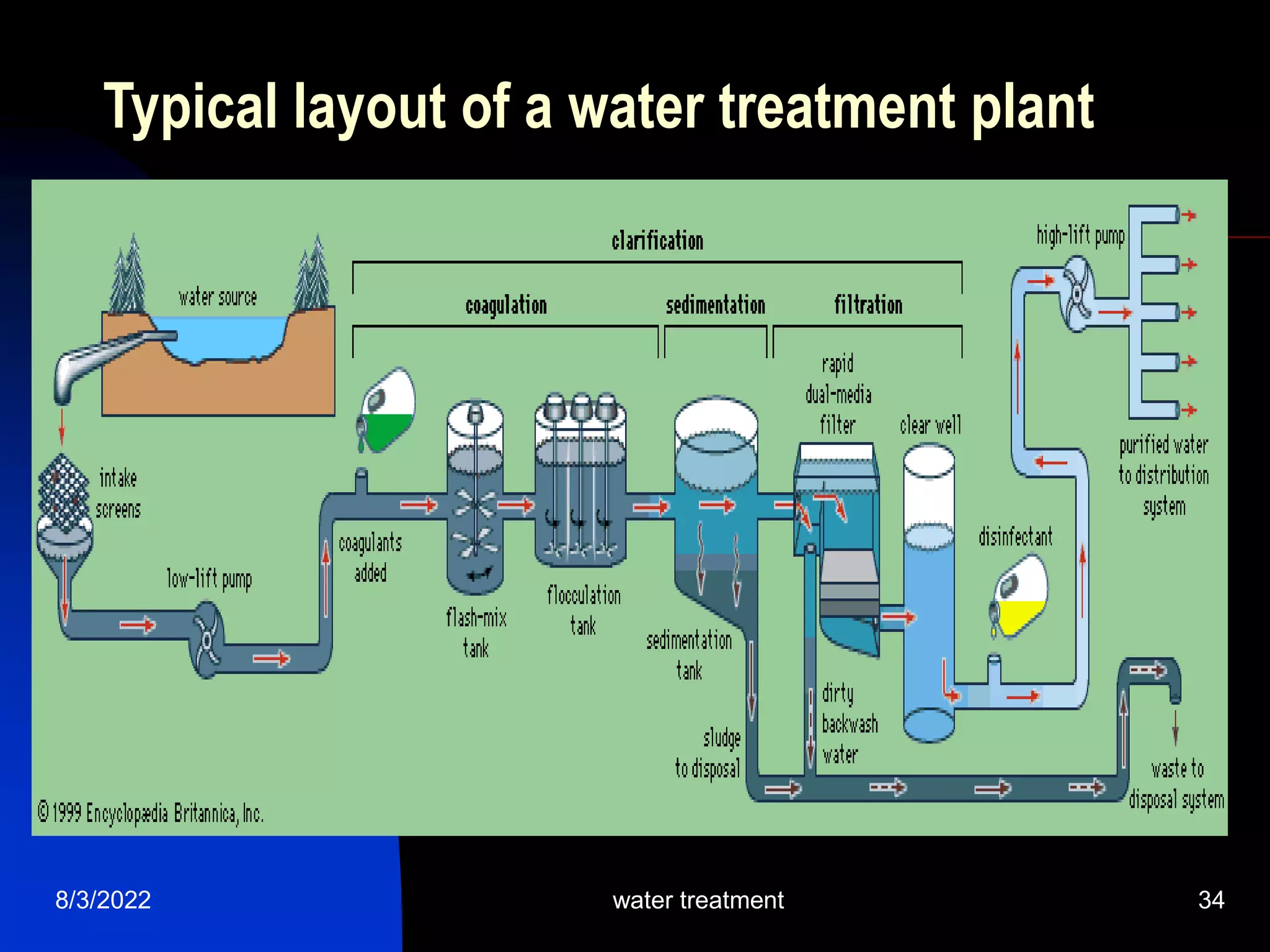
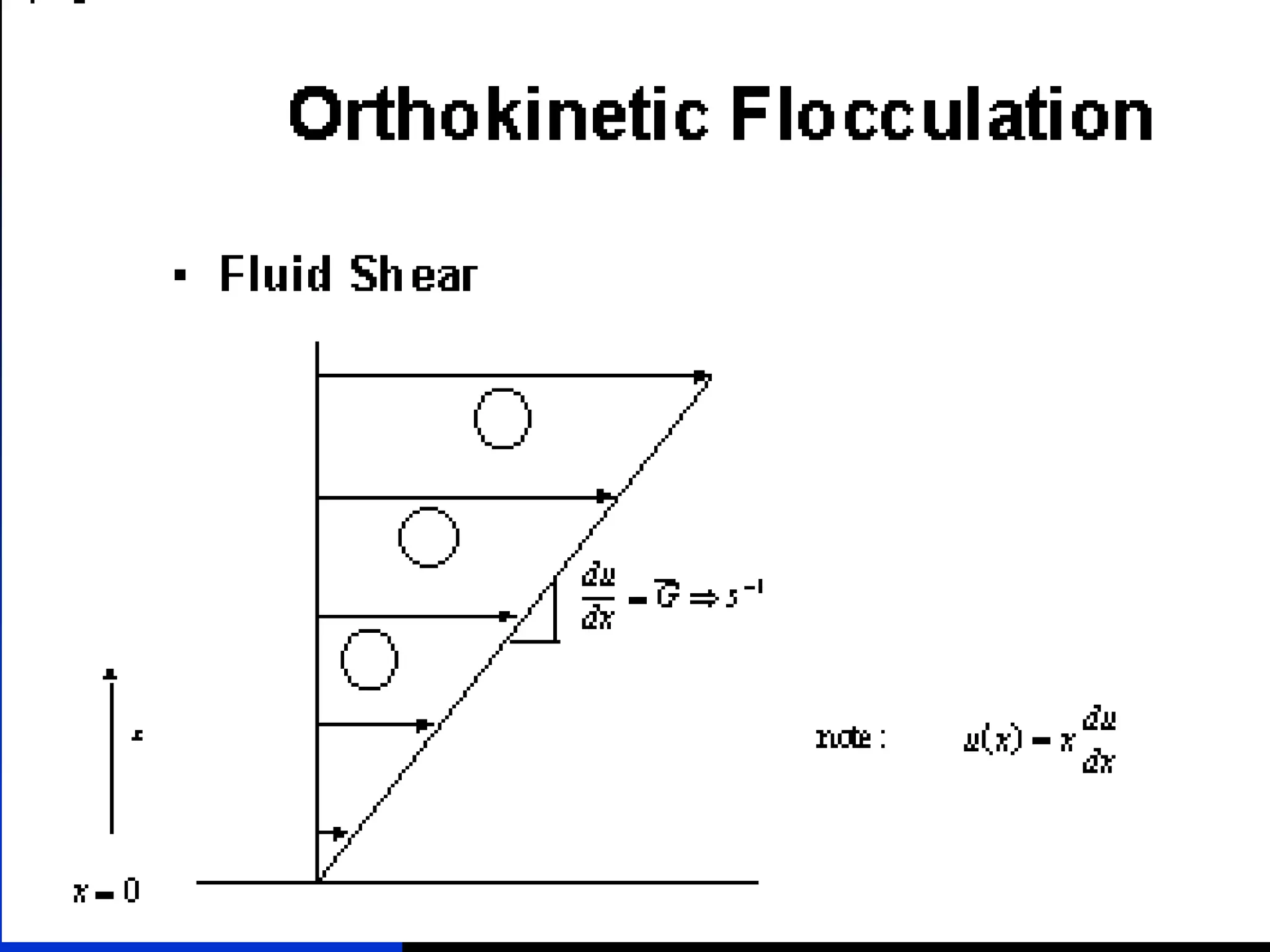
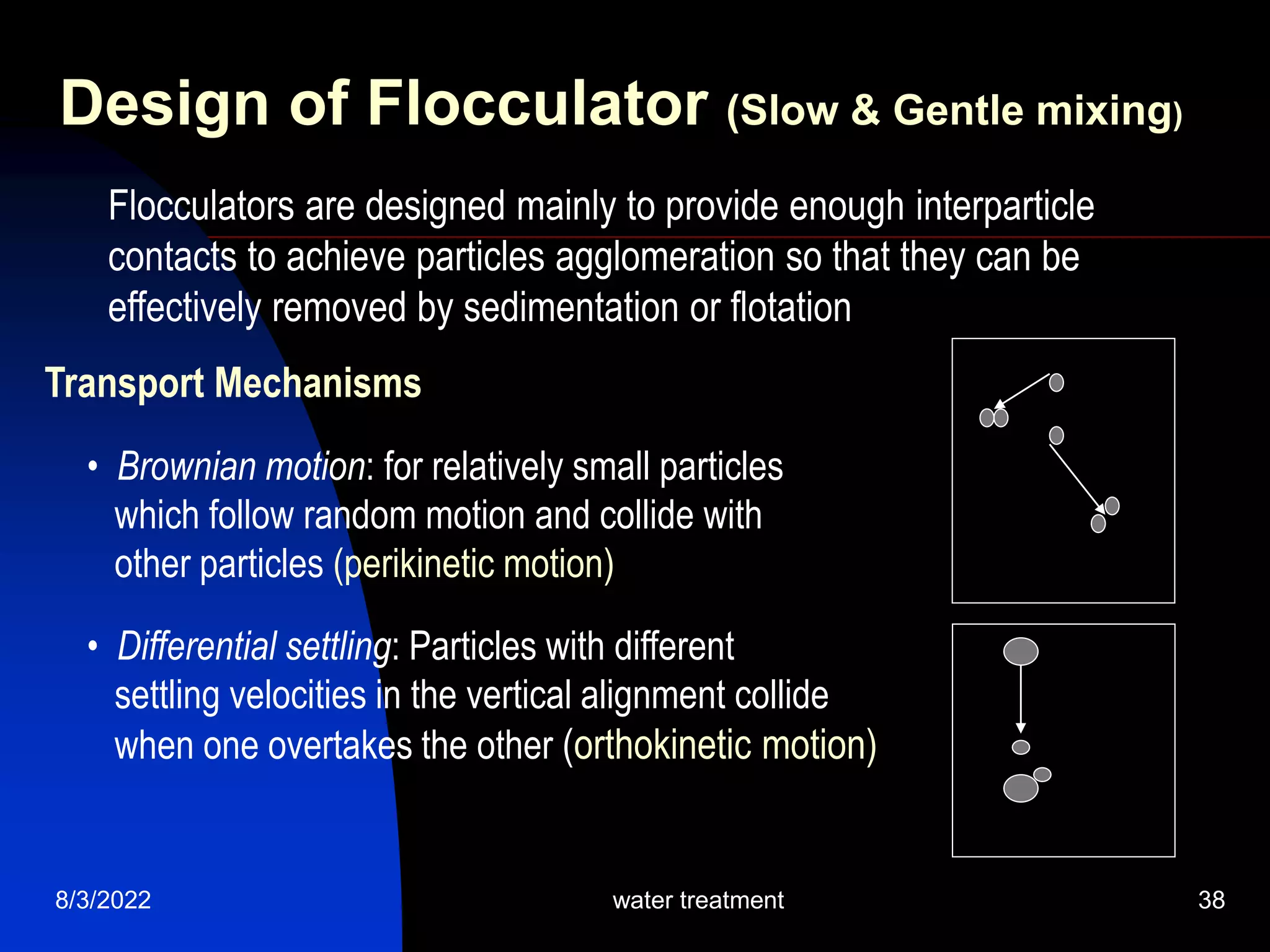
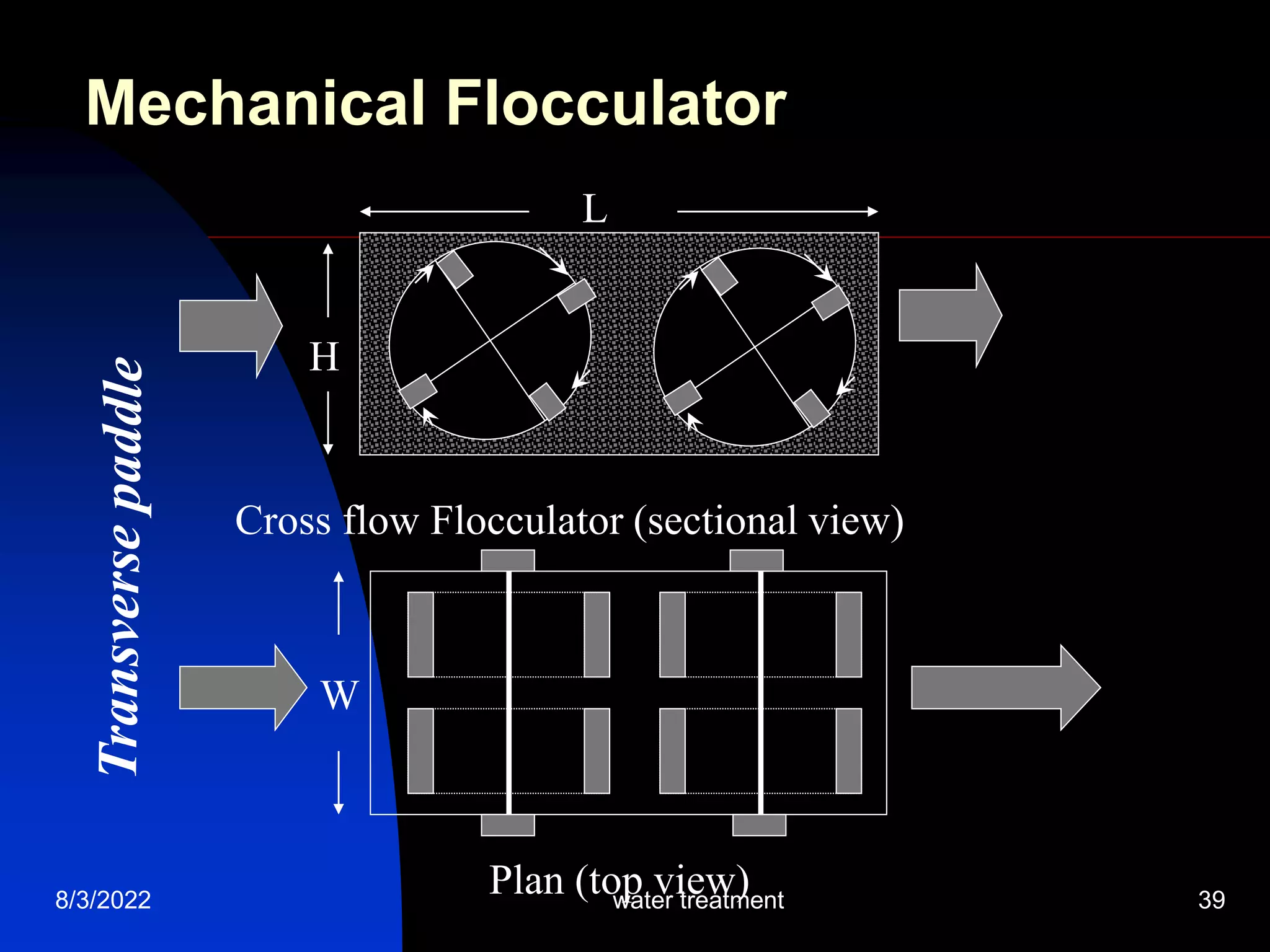
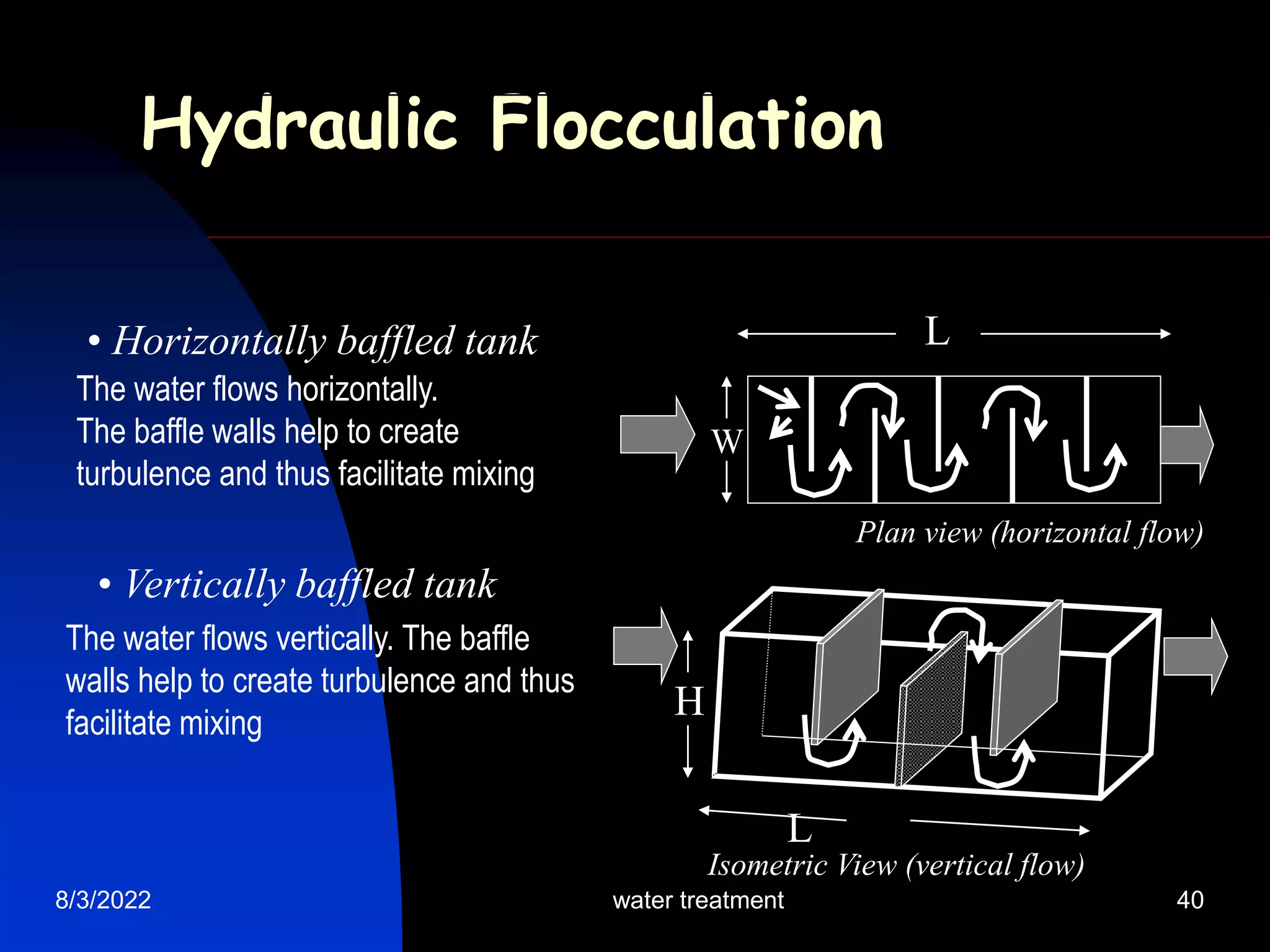
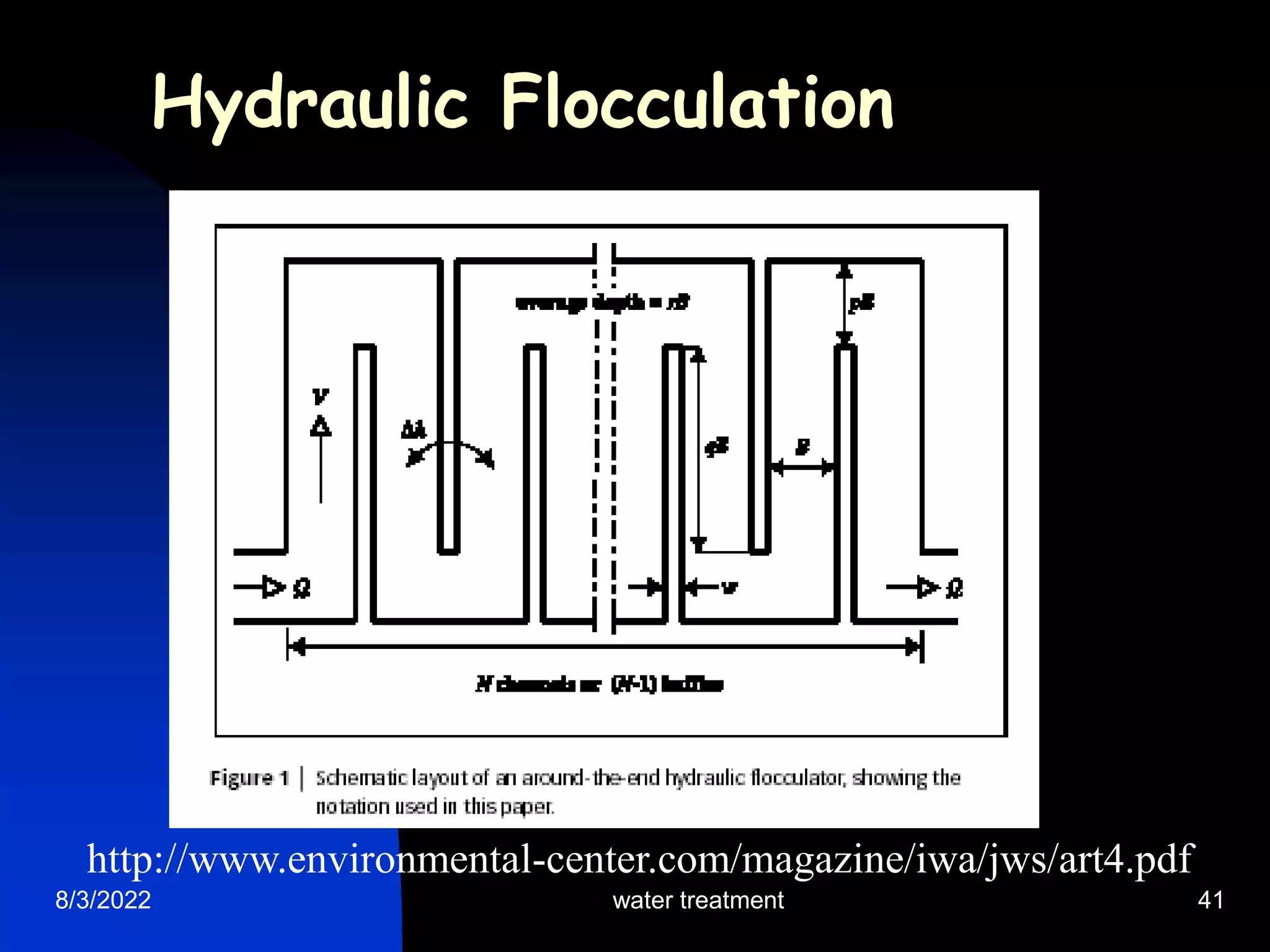
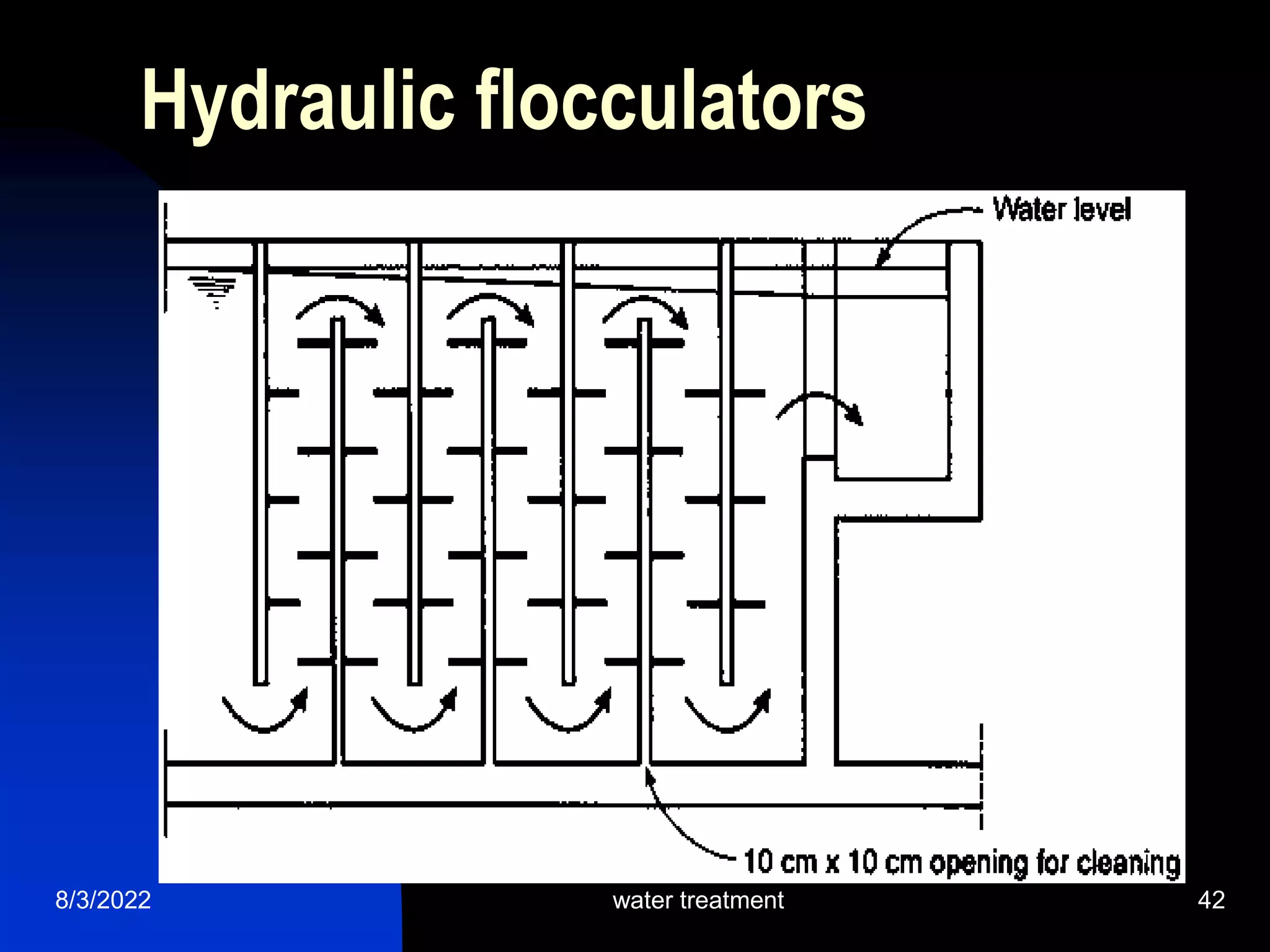
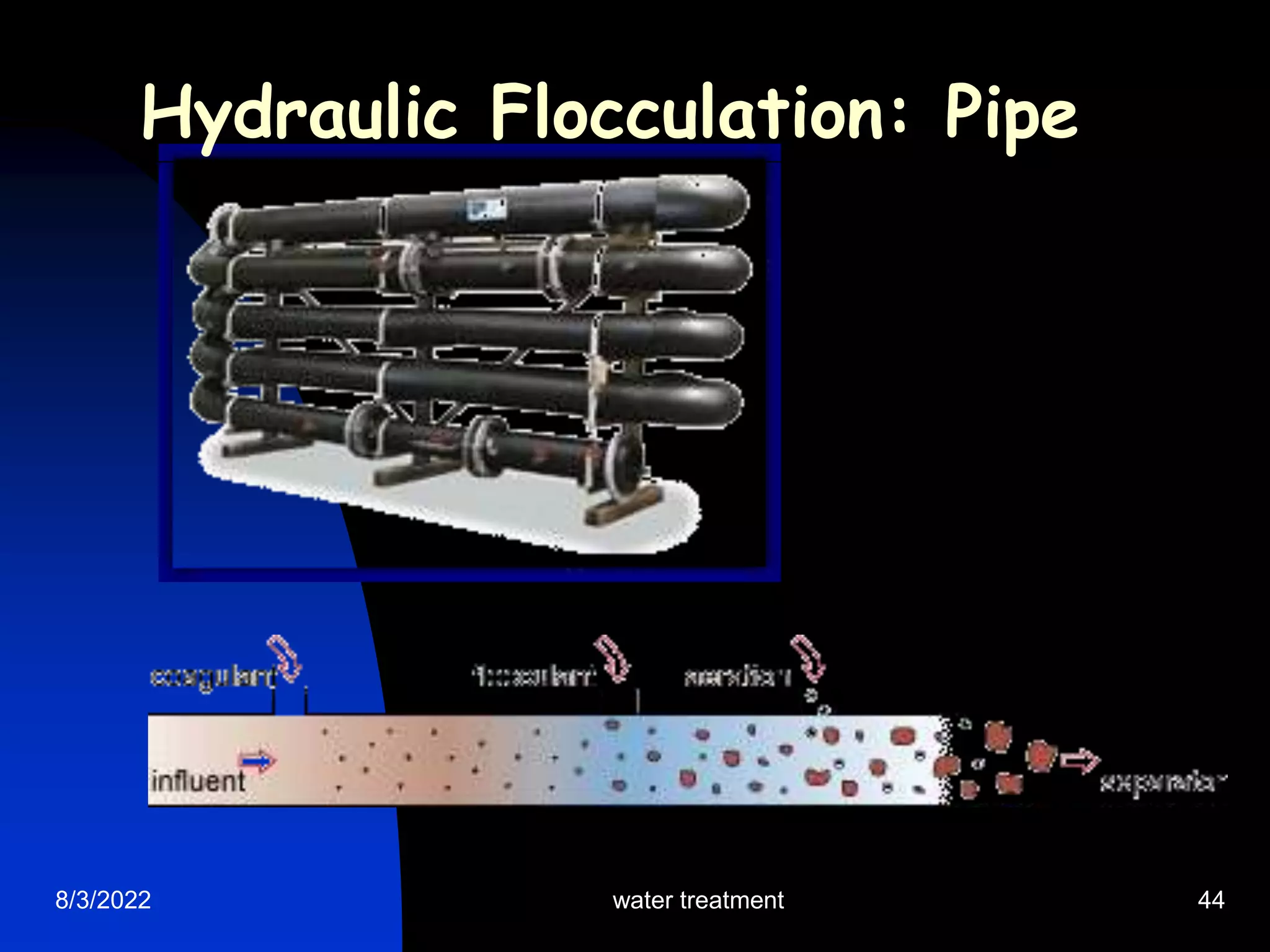
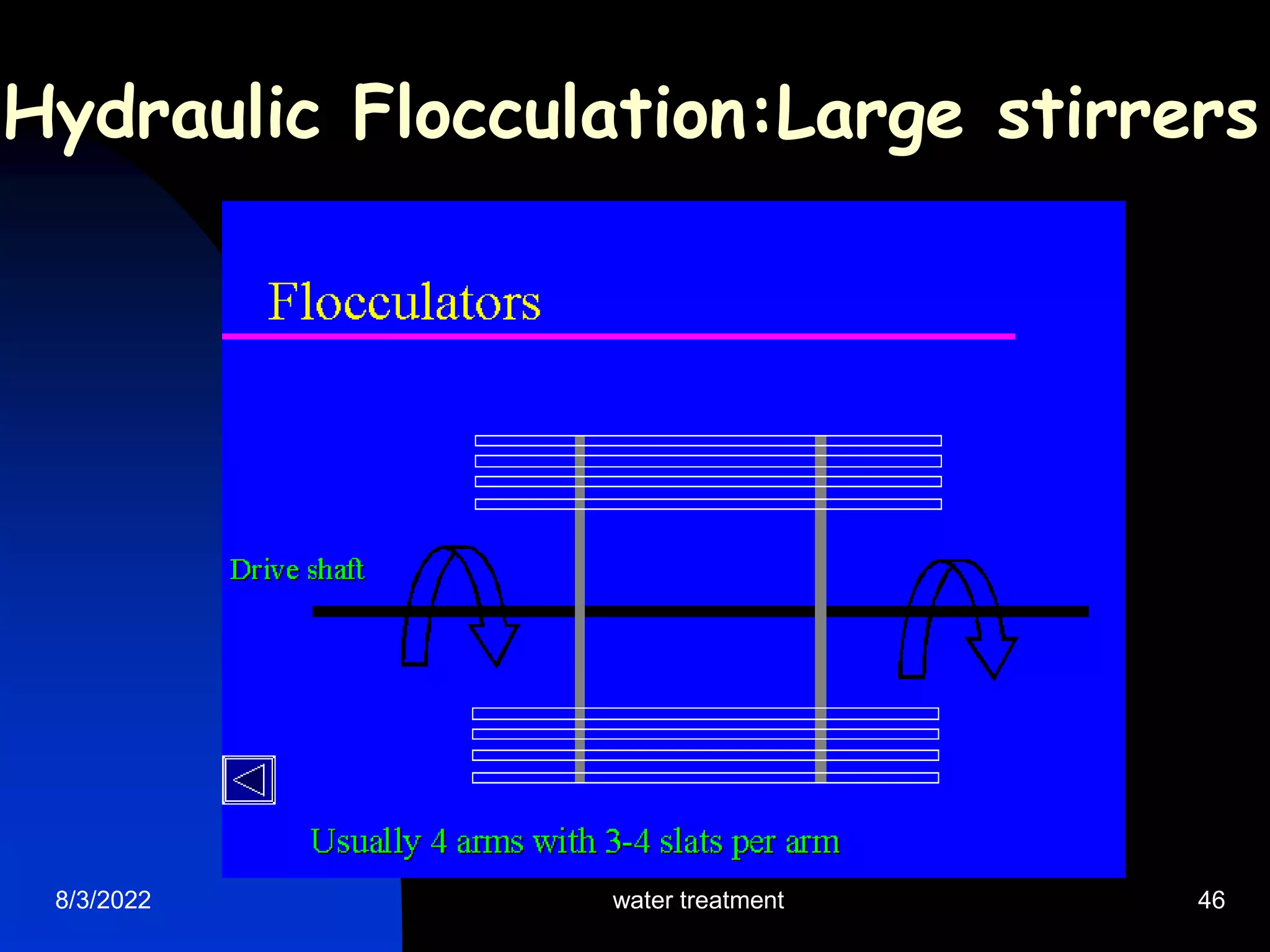
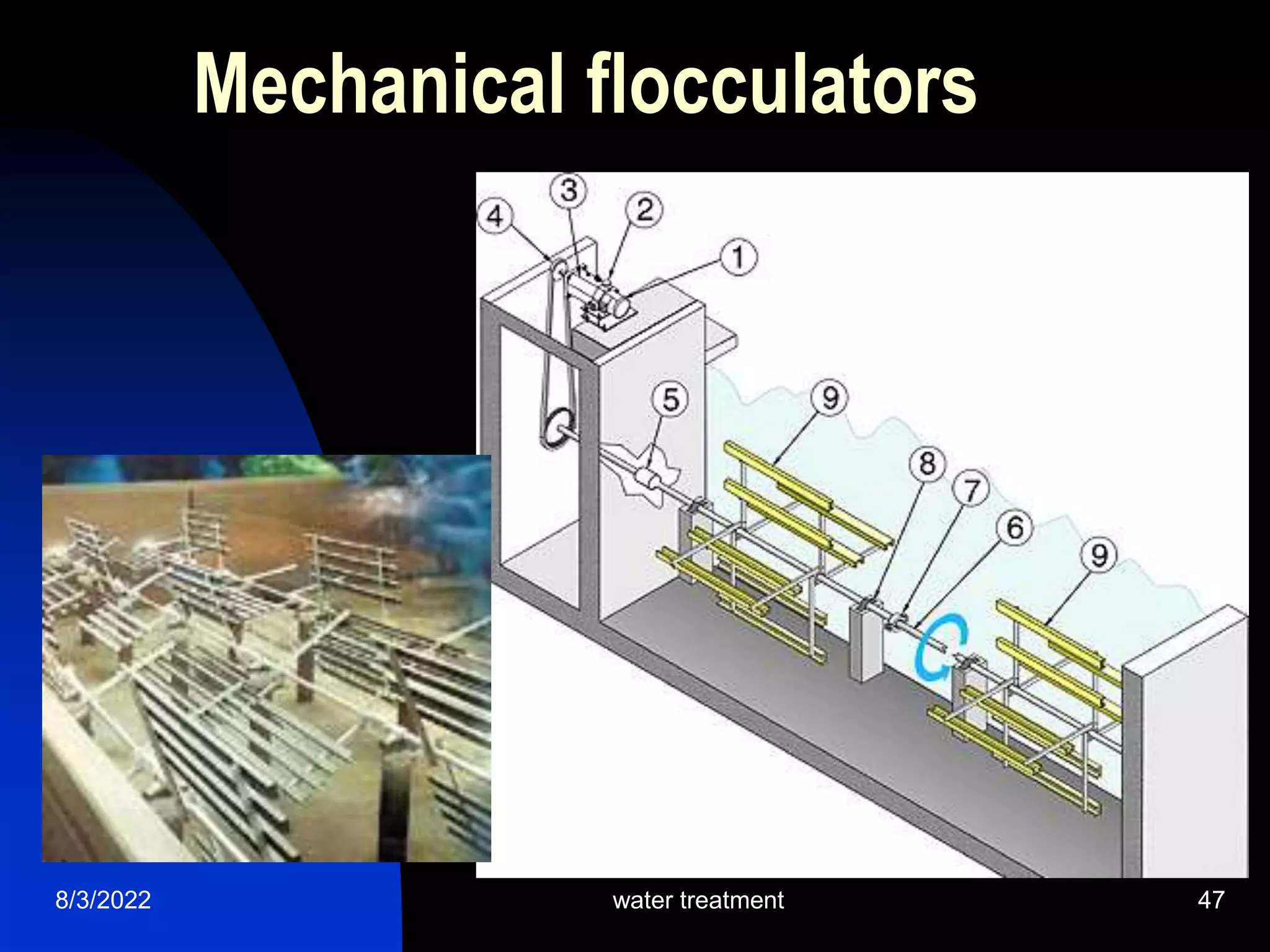
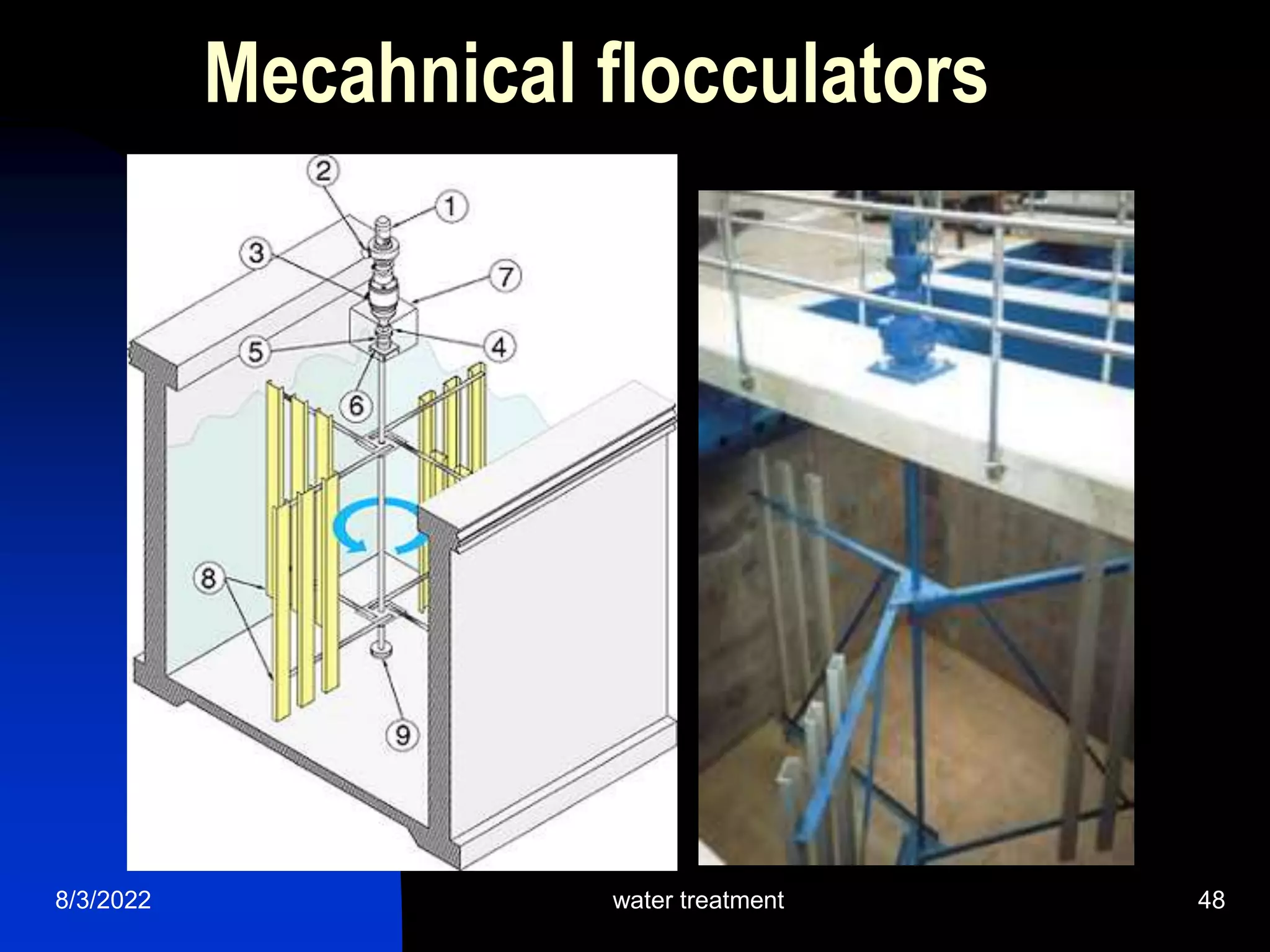
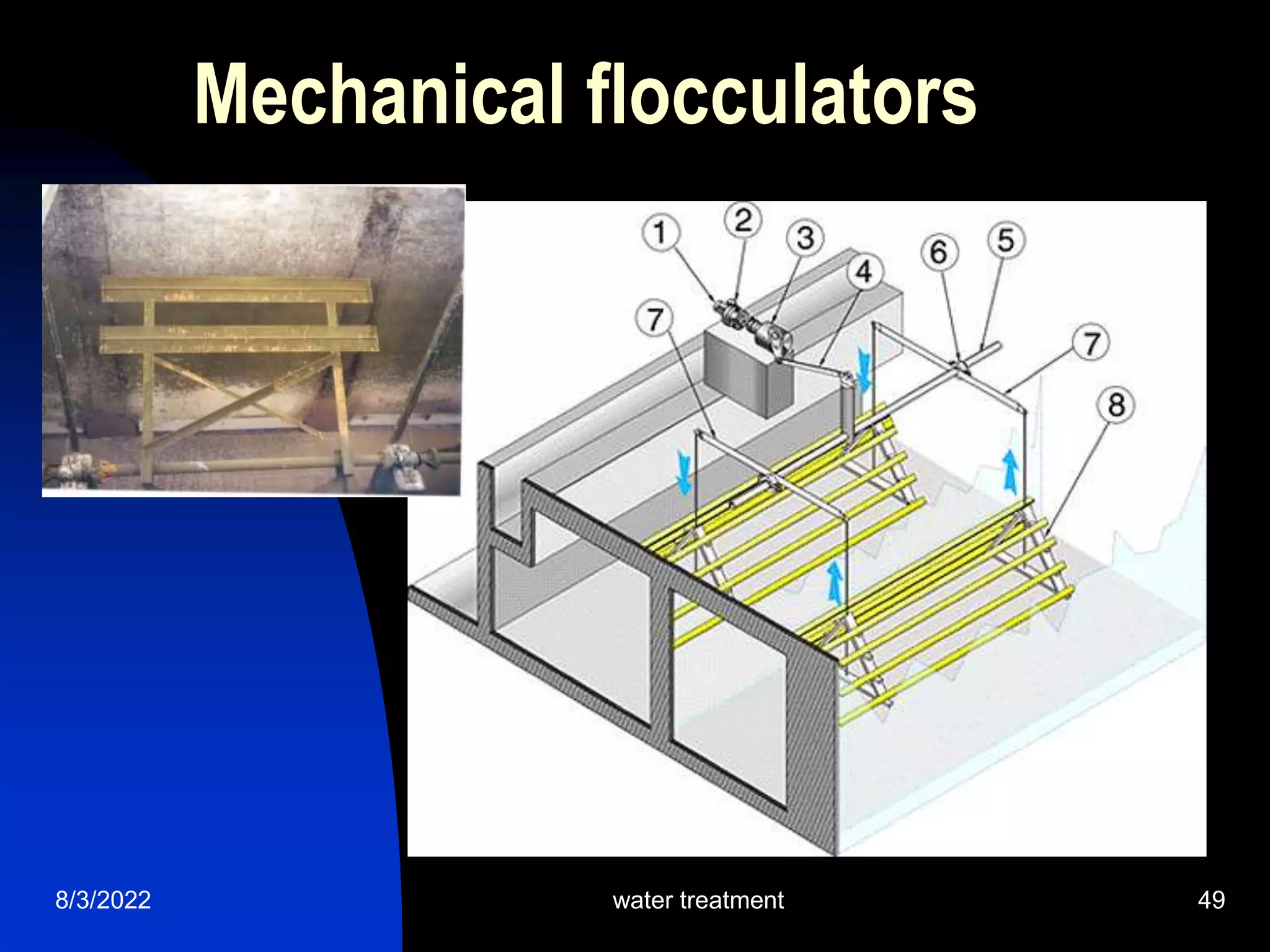
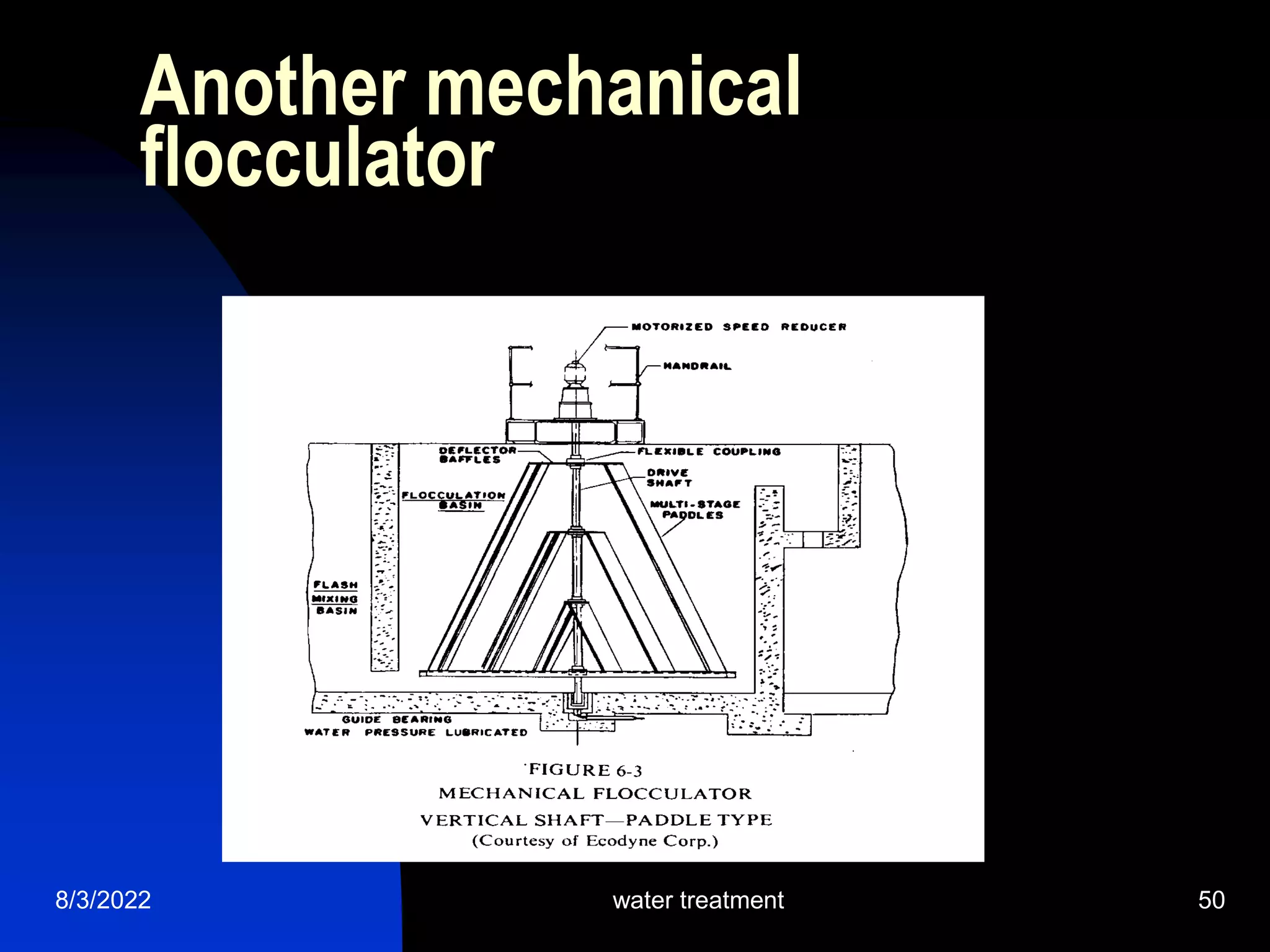
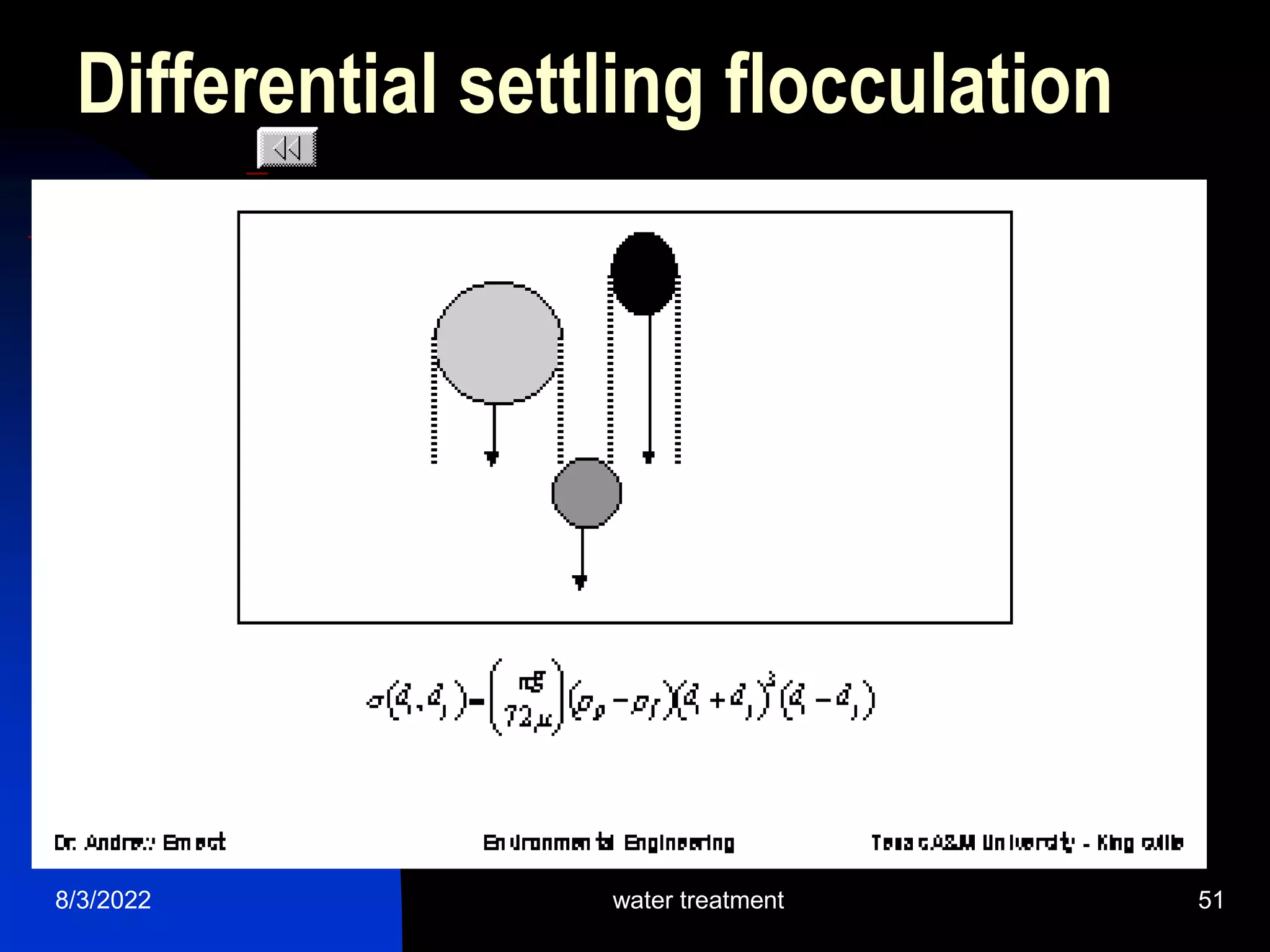
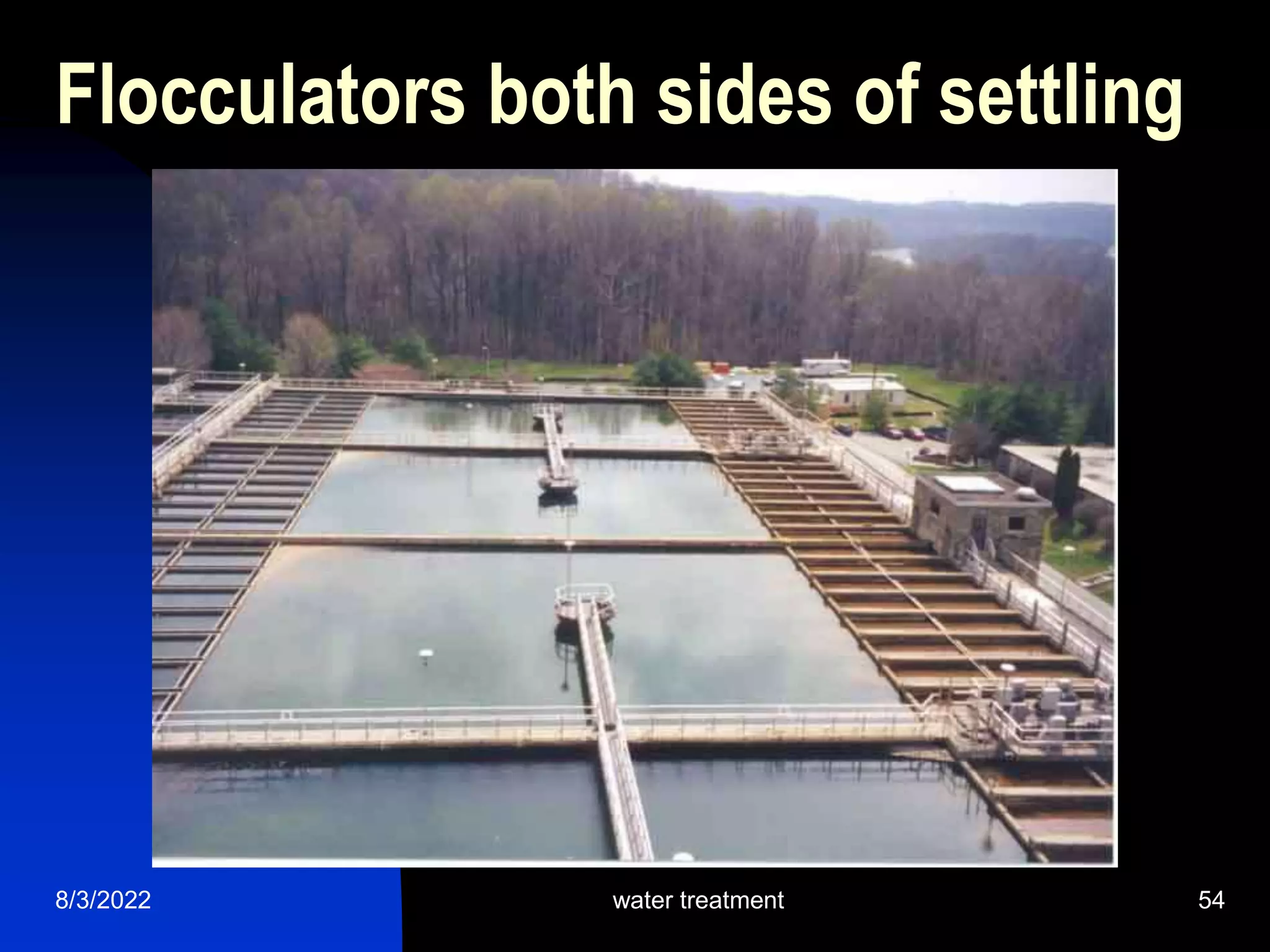
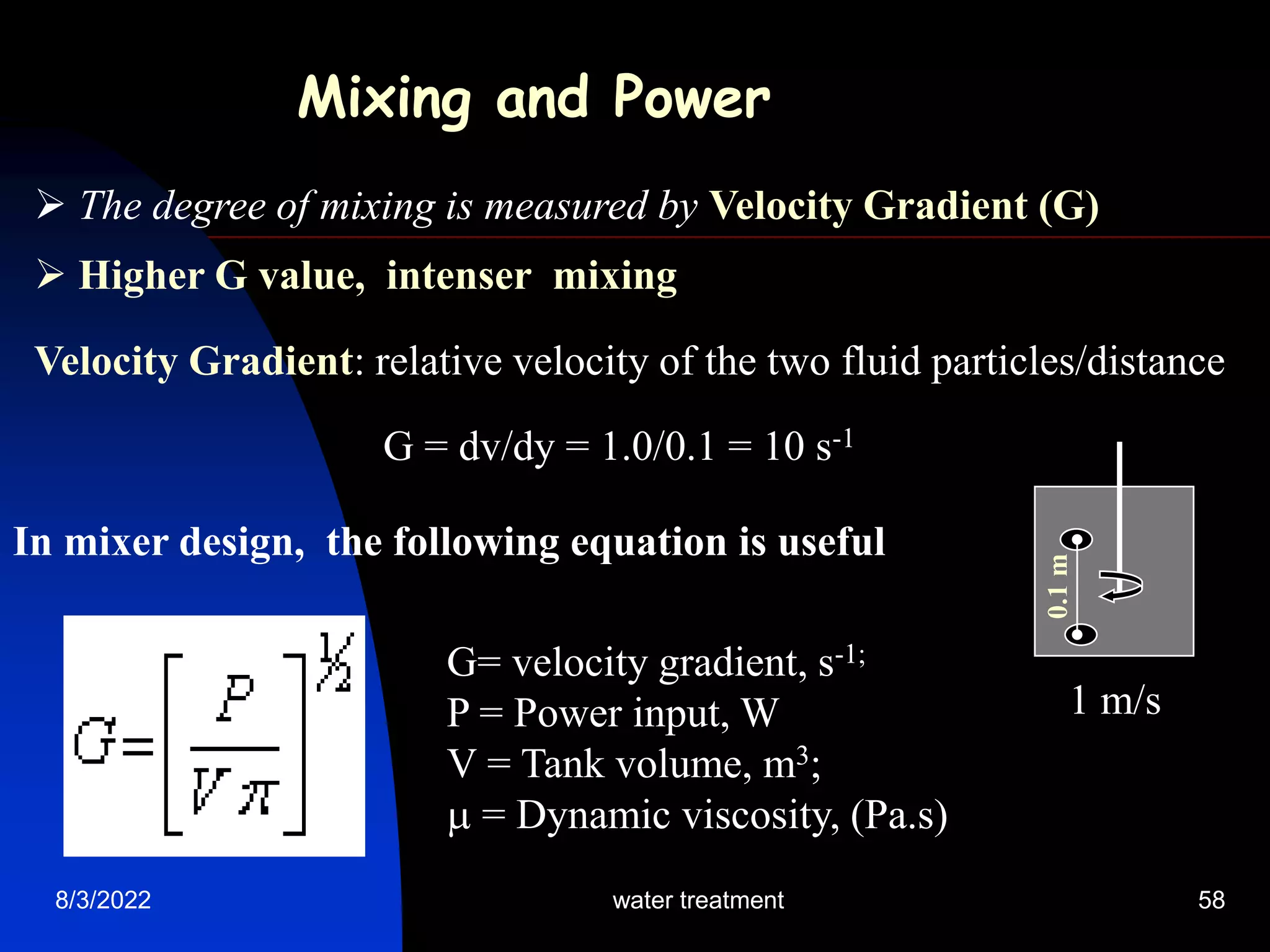
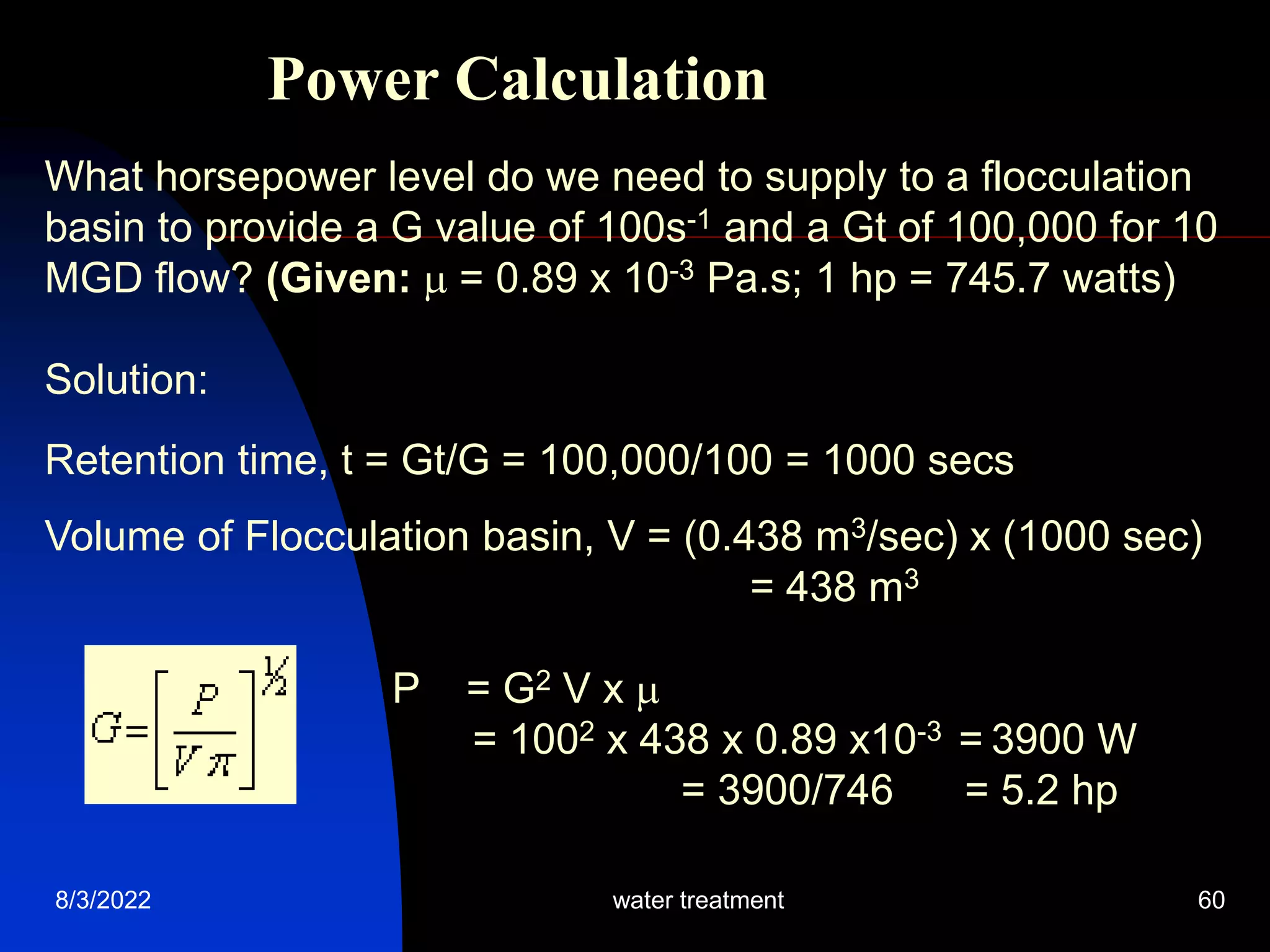
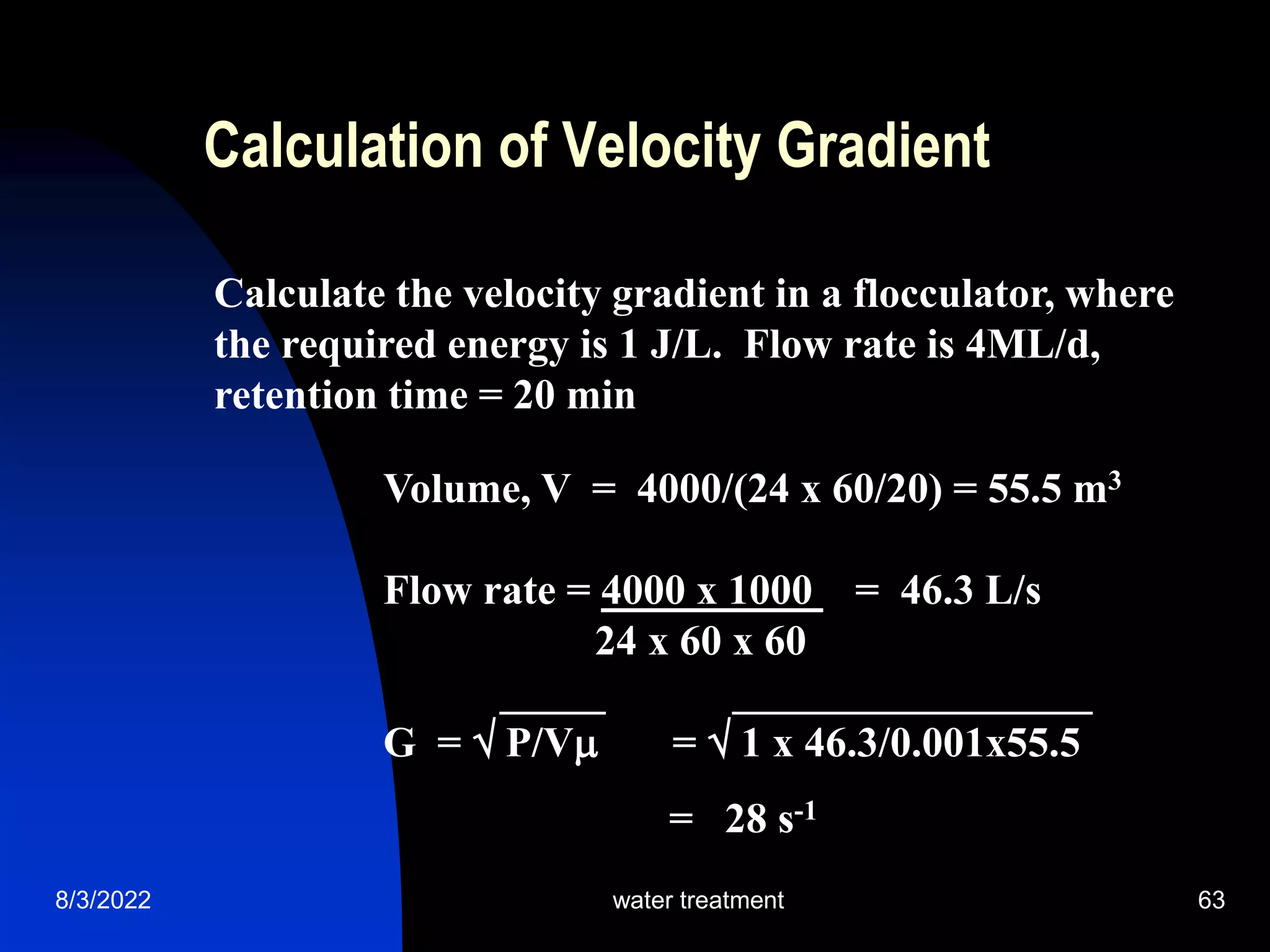
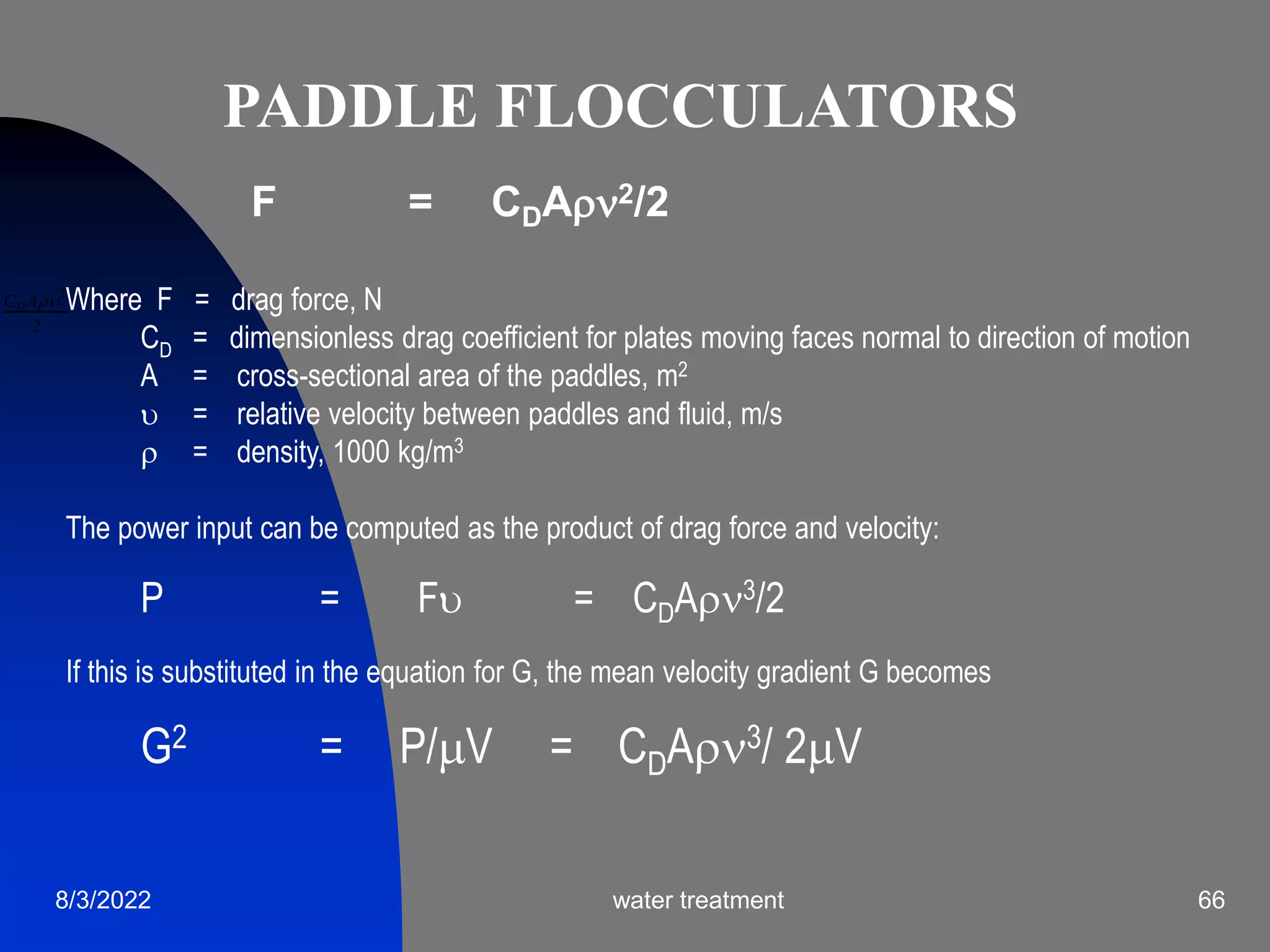
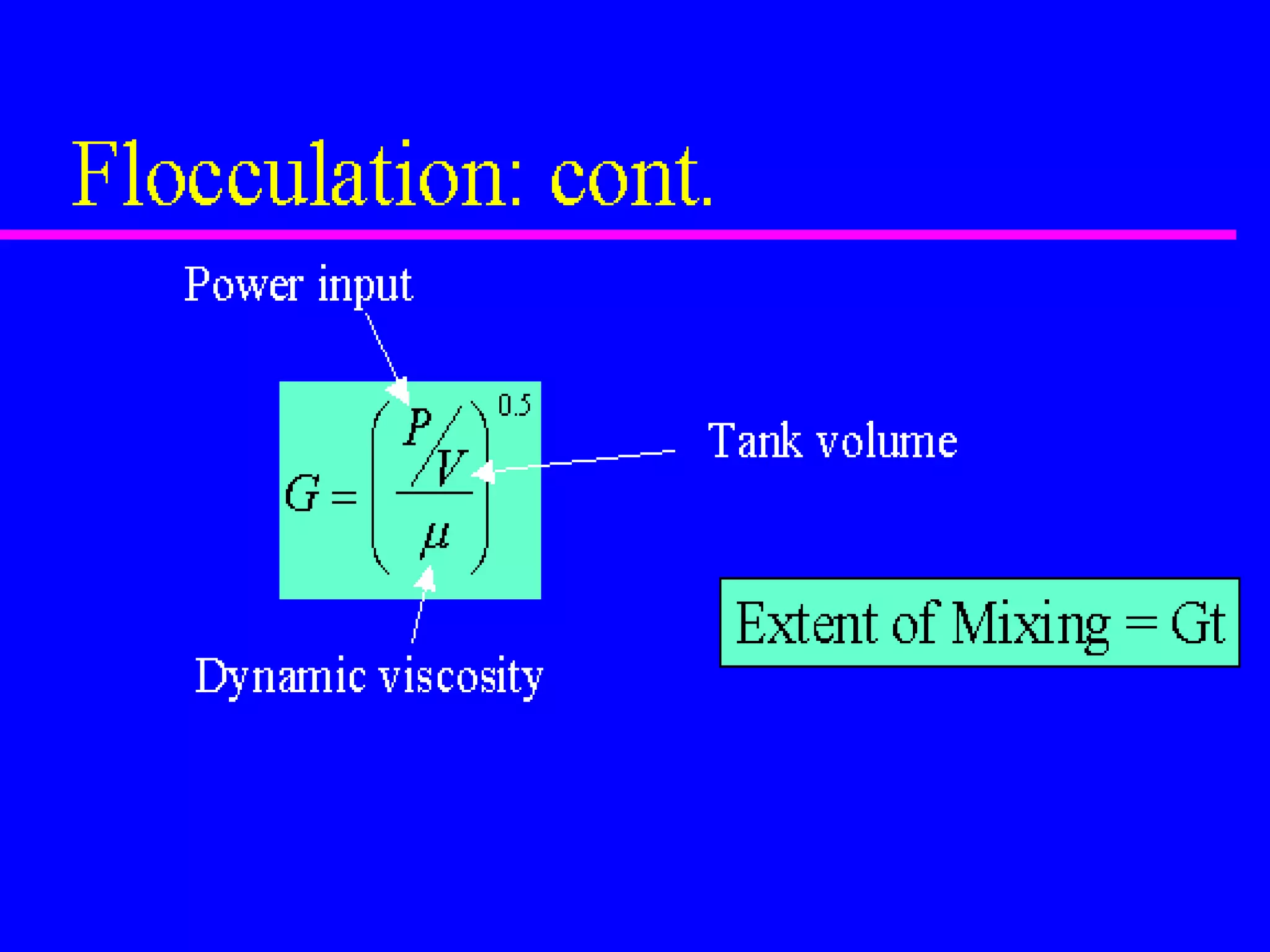
The document discusses coagulation and flocculation processes in water treatment. Coagulation involves adding chemicals like aluminum sulfate or ferric chloride to destabilize colloidal particles in water by neutralizing their negative charges. Flocculation is the process of agglomerating the destabilized particles into larger flocs that are easier to remove through sedimentation or flotation. Jar tests are used to determine the optimum pH and coagulant dose for treatment. Factors such as coagulant type and dosage, flocculator design parameters, and alkalinity consumption are considered to optimize the processes.