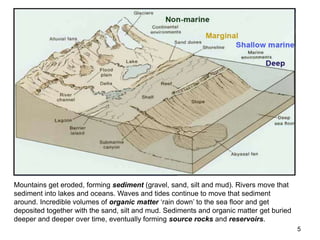
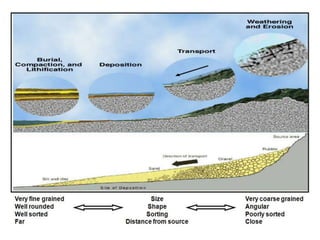
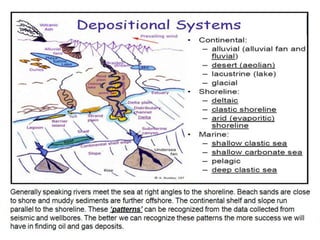
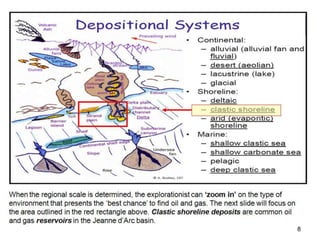
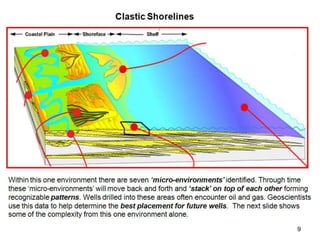
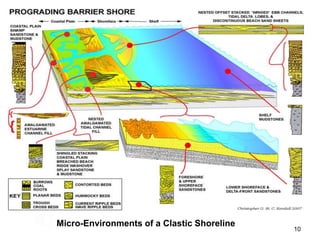
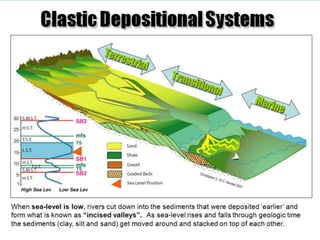
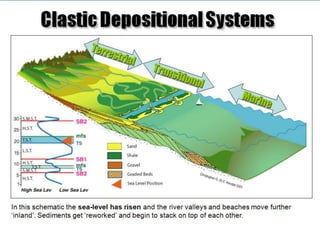
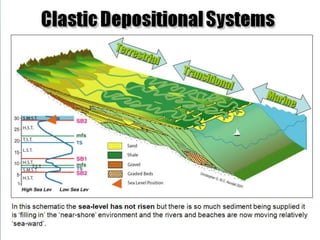
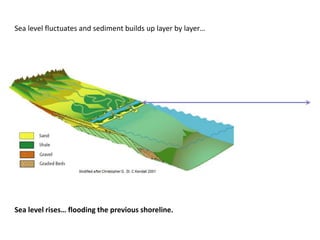
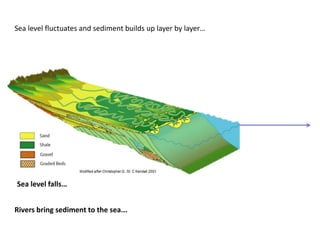
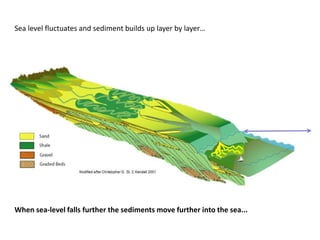
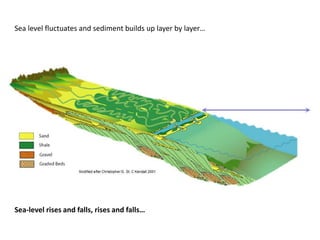
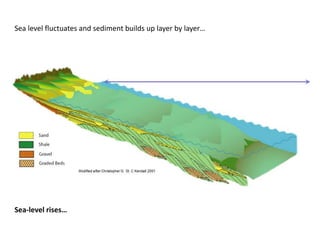
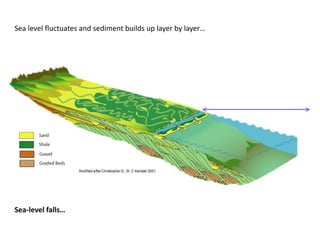
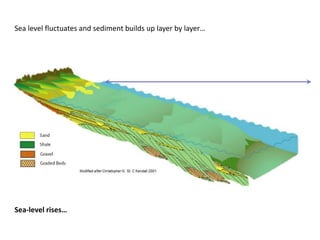
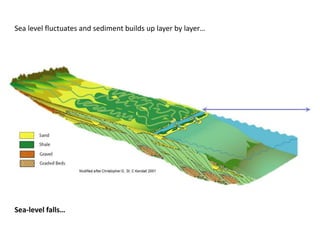
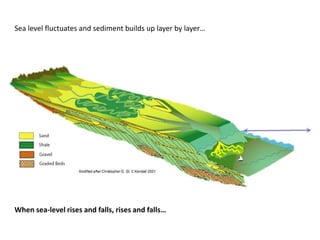
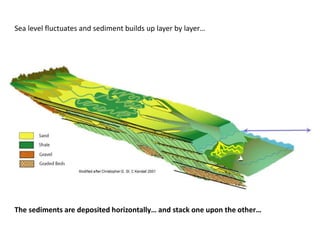
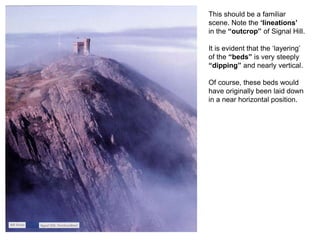
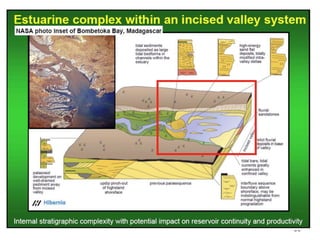
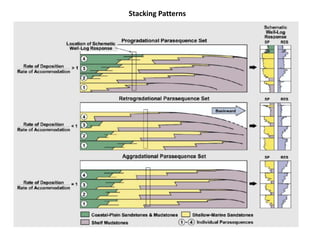
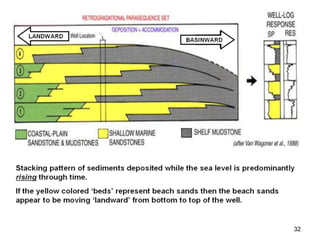
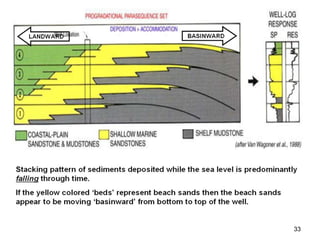
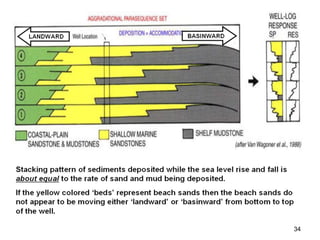
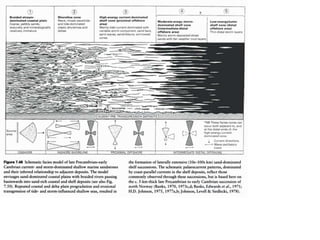
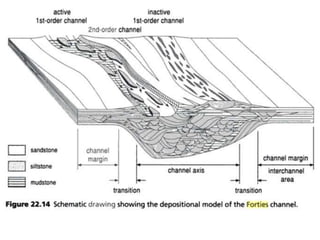
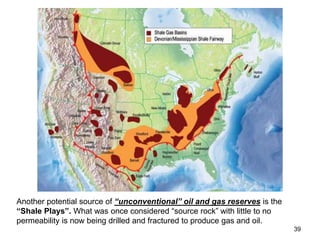
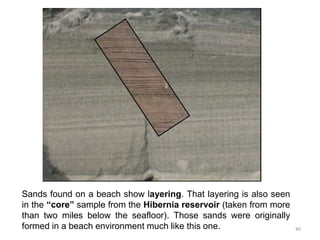
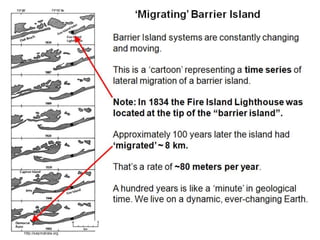
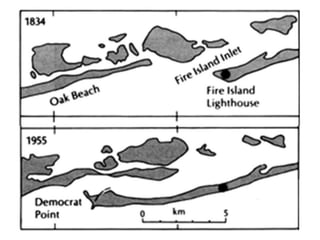
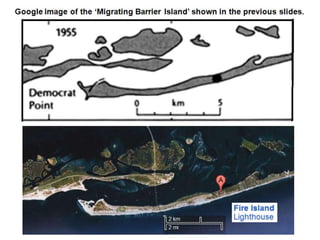
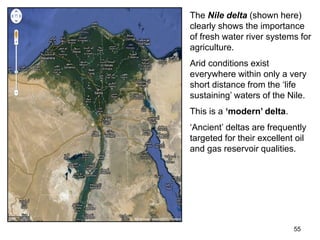
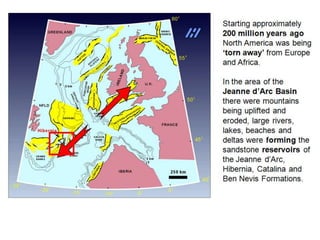
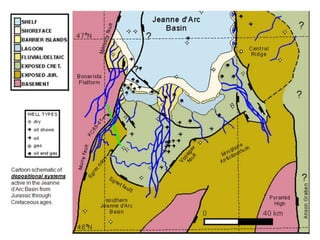
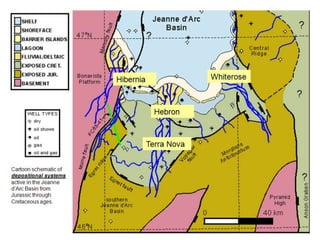
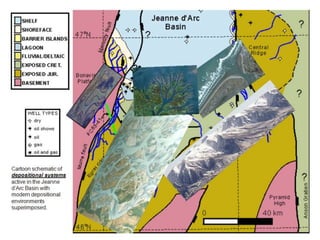
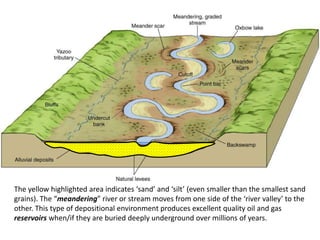
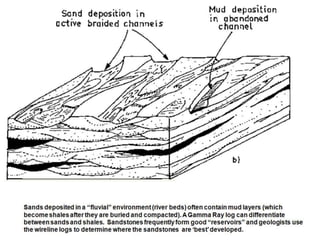
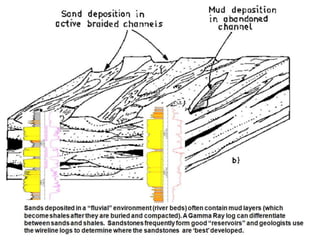
The document discusses the processes involved in the deposition and formation of reservoir rocks, illustrating how erosion, sediment movement, and stratification occur in various environments, including clastic shorelines and river deltas. It emphasizes the importance of understanding ancient depositional environments in locating oil and gas reserves, linking modern geological features to their older counterparts. Additionally, it highlights the role of organic matter and sedimentary layering in the creation of viable sources for fossil fuels.