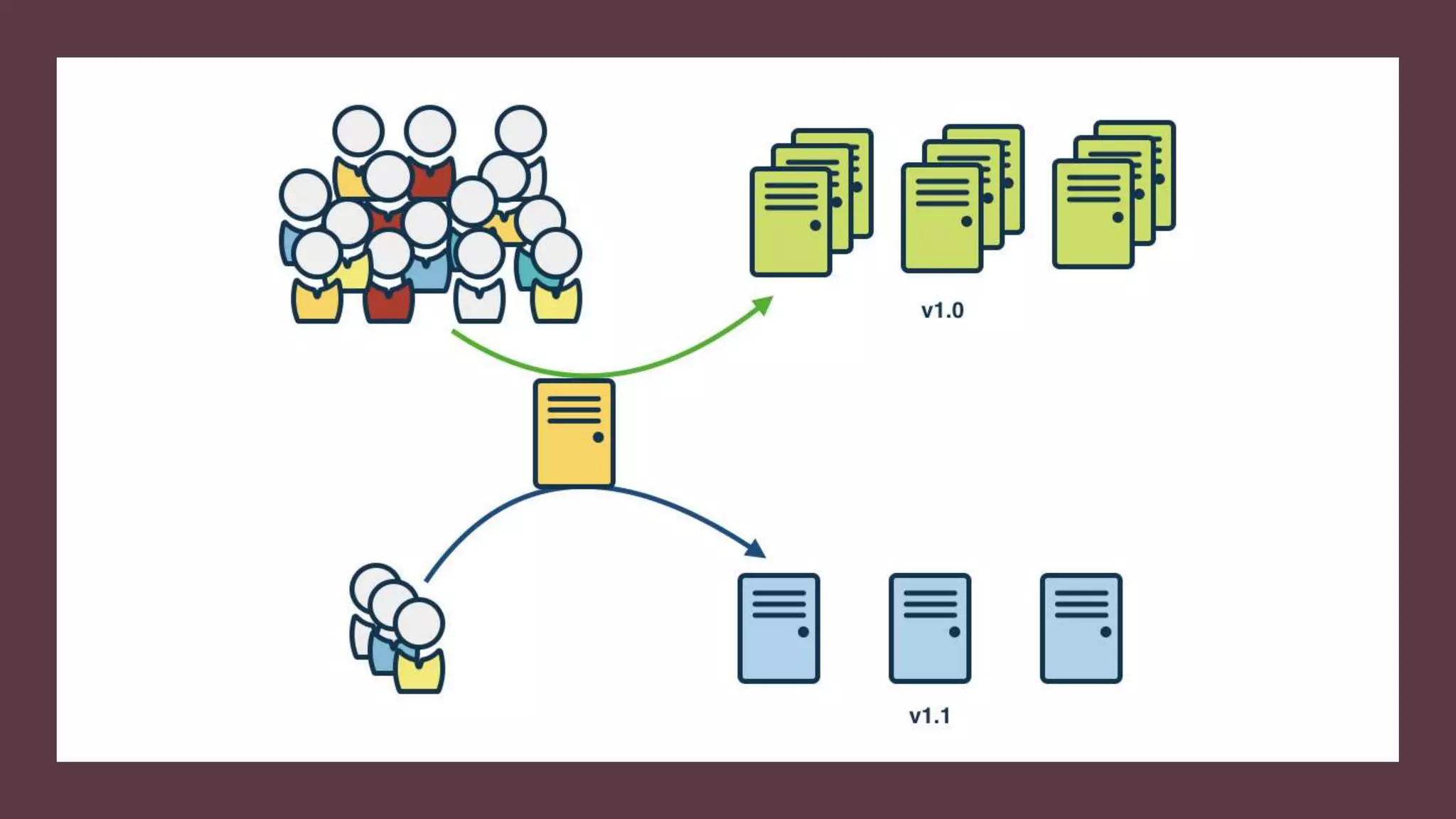
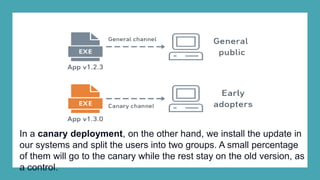
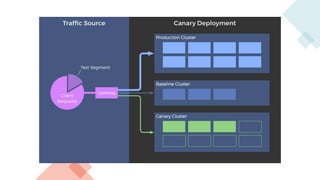
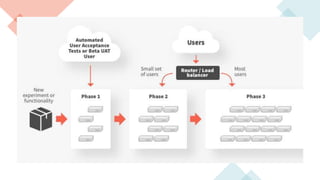
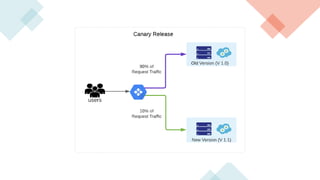
A canary deployment is a staged rollout strategy where a new software version is deployed to a small subset of users first. Their feedback is used to evaluate the new version before a full rollout. Specifically:
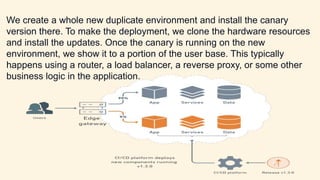
- The new version is deployed to a duplicate environment and a small percentage of users are routed to it to test in a real-world setting.
- Metrics are collected from these "canary" users to analyze performance and errors.
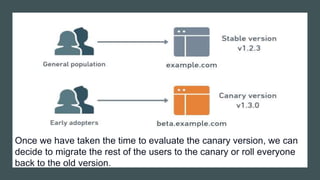
- If testing is successful, more users are gradually routed to the new version. Otherwise, it can be easily rolled back.
- This allows identifying issues before full deployment while avoiding downtime and enabling easy rollbacks compared to "big bang" launches.